Txx F M
Yielding that (DF(x)y) i = rF i(x) y In other words, DF is a linear map from Rm to Rm which we may represent by the socalled Jacobian matrix DF(x) = 0 B @ @F 1 @x 1 (x)@F 1 @xm.

Txx f m. 0 Example 28 In C 1,1 define the metric given by d(f, g) = max 1 x 1 fjf(x) g(x)jg It’ not hard to show that C 1,1 endowed with this metric d is a complete metric space Example 29 Let Rn endowed with any of the metrics d 1,d2 and. Proof Assume that (X,d) is a complete metric space Let (F n) be a sequence of nonempty closed subsets of X such that F n1 ⊆ F n for every n ∈ N and (diam(F n)) converges to 0First, we show that T ∞ n=1 F n is nonempty For each. # P(x) or M X(t) = X x P(x) t 1!.
F 2/ C 1,1 since f is not continuous at x = 0, even though d(fm, f) = Z 1 1 jfm(x) f(x)jdx = 1 2 1 m!. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history. Welcome to H&M, your shopping destination for fashion online We offer fashion and quality at the best price in a more sustainable way.
As before the problem doesn’t have negative eigenvalues If λ = 0, the general solution is X(x) = αx β so that 0 = X′(0) = β, implies that λ0 = 0 is an eigenvalue with the unique (up to multiplication by a constant) eigenfunction X0(x) ≡ 1If λ>0, then the general solution of the problem. Math 6 HWK 22b Solns contd 84 p399 which is exactly right Problem 5, §84 p399 Let T R2 −→ R3 be the linear transformation defined by T(• x 1 x 2 ‚) = 2 4 x 1 2x 2 −x 1 0 3 5 (a) Find the matrix for T relative to the basis B = {u. X x x2P(x) We see that M X.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. F (s)· b(f(s),g(s),h(s))−g (s)· a(f(s),g(s),h(s))=0 Burger’s Equation Solve the Cauchy problem u t uu x =0, u(x,0)= h(x) (51) The characteristic equations are dx dt = z, dy dt =1, dz dt =0, and Γ may be parametrized by (s,0,h(s)) x = h(s)ts, y = t, z = h(s) u(x,y)=h(x−uy) (52) The characteristic projection in the xtplane1. F(x) ∈ Y Following is some commonly used terminologies 1 X is called the domain of f 2 Y is called the codomain of f 3 If f(x) = y, then we say y is the image of x The preimage of y is preimage(y) = {x ∈ X f(x) = y} 4 The range of f is the set of images of elements in X In this section we deal with functions from a vector sapce.
May 04, 21 · Version printed on 05/04/21 SCHOOL HOLIDAYS SCHOOL HOLIDAYS ORIENTATION WEEK wk1 of 26/52 WEEK 1 of S/H WEEK 2 of S/H WEEK 3 of S/H WEEK 4 of S/H WEEK 5 of S/H WEEK 6 of S/H DEC New Years JAN 21/12/ 22/12/ 23/12/ 24/12/ 25/12/ 28/12/ 29/12/ 30/12/ 31/12/ 1/1/21 4/1/21 5/1/21 6/1/21 7/1/21 8/1/21 11/1/21 12/1/21. ˚ M m;n(F) !. For ∀t ∈ a,b,∀m,n ∈ N,fm(t)−fn(t) ≤ kfn − fmk, which means (fn(t))∞n=1 is a Cauchy sequence in R and must converge to an element in R So we can define a function f a,b → R that f(t) = lim n→∞ fn(t), ∀t ∈ a,b First, we will show that fn → f when n → ∞ ∀ε > 0, there is an N st ∀n,m.
X x xP(x) t2 2!. Be the function which sends a matrix A= (a ij) to its transpose At = (a ji) Since the tranpose of a sum of two matrices is the sum of the tranposes, ˚respects addition Formally if A= (a ij) and B= (b ij) 2 M m;n(F) then At is the matrix with entries (a ji) and Bt is the matrix with entries (b ji) A B is the matrix. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more.
Zdgh^Yad fadgh^ X bd_ \^c^ Hd edZc å edcåa, mhd =dY c YdXdf^a `dc`fhcd dWd bc mr naV d hdb, mhd cVghVad Xfbå edZa^hrgå X Wda n^fd`db bVgnhVW edcVc^b dh`fdXc^å d bda^hX cV ^cqk åq`Vk, `dhdfd Ic dh`fqXVa bc X hmc^ bcdY^k ah dgaVc^ Zdgh^Yad fadgh^, mhdWq dh`fqhrgå Mai Pf^ghdXi. Where X;Y 2Rm n Notation Here, Rm nis the space of real m nmatrices Tr(Z) is the trace of a real square matrix Z, ie, Tr(Z) = P i Z ii Note The matrix inner product is the same as our original inner product between two vectors of length mnobtained by stacking the columns of the two matrices. Pages 600 This preview shows page 57 73 out of 600 pages 56 • Since M X (t) = ∞ X x =0 eθ.
De ne f X!R by f(x) = d(T(x);x) The function f is continuous, since if x n!xand y n = T(x n), then y n!T(x) by the continuity of T, and f(x n) = d(y n;x n) !d(T(x);x) = f(x) by the continuity of d Since f X!R is a continuous function on a compact set, it attains its minimum value at some a2X If T(a) 6=a, then f(T(a)) = d(T(T(a));T(a)). T(x)=x i v i!!. Now define the matrix A = (aáé) ∞ Mnxm(F) with column vectors given by Ai = vá ∞ Fn In other words (remember these are columns), Ai = (aèá, , añá) = (vèá, , vñá) = vá where vá = Íj ˆ= 1 févéá and {fè, , fñ} is the standard basis for Fn Writing out T(x) we have T(x)=x i v i i=1 m.
Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Signal and Linear System Theory 21 Problem Solutions Download Signal and Linear System Theory 21 Problem Solutions. 1 Let (X,A,µ) be a finite measure space, and {fk k > 1} a sequence of squareintegrable functions with the following property For all ε > 0 there exists an M0 ∈ N so that sup M>M0 M X k=M0 fk L2(X,µ) < ε Show that the series.
Where IRm n and b2IRm When n. F(ξ) dξ G(η) Hence, the general solution of wξη = 0 is given by w(ξ,η) = F(ξ) G(η), where F and G are two arbitrary C2function Then, since u(x,y) = w(ξ(x,t),η(x,t)), we find that u(x,y) = F(xct) G(x−ct) (62) Conversely, if F and Gare of class C2, then udefined by u(x,t) = F(x ct) G(x−ct) is a classical solution of (61). Rng( T) = f( v) 2W Vg Example Consider the linear transformation T M n(R) !M n(R) de ned by T(A) = AAT The range of T is the subspace of symmetric n n matrices Remarks I The range of a linear transformation is a subspace of its codomain I The range of a matrix transformation is the column space of the matrix.
Remark 11 Observe that in the case m = 2, that is, two vectors, say x;y2Rm, then Theorem 11 says that det(A) = (xx)(yy) (xy)2 0 which is the same as the Cauchy Schwarz inequality Recall from Examples 12 and 13 that this proves the triangle inequality for the ordinary Euclidean metric In the exercises you will see that the case m= 3 proves. X x x3P(x) To nd the k th moment simply evaluate the k th derivative of the M X(t) at t= 0 EXk= M X(t) k th derivative t=0 For example First moment M X(t)0 = X x xP(x) 2t 2!. Making a Taylor expansion of Fin ", and denoting F= (F 1;;F m) where F i denotes the ith component of the map we obtain F i(x "y) = F i(x) "rF i(x) y o(");.
Case for 0 measure), then we know there exists an F ˙ set F Esuch that m(E˘F) = 0 We use the set F to partition Einto an F ˙ set and a set of measure 0, E= F(E˘F) Therefore f(E) = f(F) f(E˘F) However, we know f(F) is an F ˙ set and f(E˘F) is a set of measure zero, therefore f(E) is measurable Problem 45. A quadratic form is a function f Rn!R of the form f(x) = xTAx= i;j=1 A ijx ix j I in a quadratic form we may as well assume A= T since xTAx= xT((A AT)=2)x ((A AT)=2 is called the symmetric part of A) I uniqueness if xTAx =xTBxfor all x2Rn and AT, B= T, then A= B 8. For example if f X → X is a map on a T 1 topological space with a unique fixed point a, such that for each x in X we have f n (x) → a, then there already exists a metric on X with respect to which f satisfies the conditions of the Banach contraction principle with contraction constant 1/2 In this case the metric is in fact an ultrametric.
YingweiWang MethodsOfAppliedMathematics On the other hand, kx0 − y0k ≤ ky0 −y n k kky n k −x0k → d, as k → ∞ So y0 is just what we want to find 2 Lineartransformation Question Find the norm of the operator A ∈ B(X) given by (Af)(t) = tf(t), 0 ≤ t ≤ 1,. M{x>v{t > x x > t x > {x>{z{>xyyxv x x > y> {x>b y x >b xz t xw>ft tzxG x >i z t >y >^ x F>ltyx >t w>axt {>Cbfik^lDH>h >bfik^l> x > > xG x xw> w wx>t w>x u tvx >t > vx x F> t xzx >t w> u}xv x > > {x x>yx w H>. 168 62 Matrix Transformations and Multiplication 621 Matrix Linear Transformations Every m nmatrix Aover Fde nes linear transformationT A Fn!Fmvia matrix multiplication We de ne T Aby the rule T A(x)=AxIf we express Ain terms of its columns as A=(a 1 a 2 a n), then T A(x)=Ax = i=1 x ia i Hence the value of T A at x is the linear combination of the columns of A which is the ith.
For arbitrary functions f and g, thus proving our claim ⁄ Geometric Interpretation The general solution of the wave equation is the sum of two arbitrary functions f and g where f = f(xct) and g = g(x¡ct)In particular, f(xct) is a wave moving to the left with speed c, while g(x¡ct) is a wave moving to the right with speed c 53 Initial Value Problem. Where f ' is the history of f up to time t defined by f'(r) f(t x), 0 < r < oo , and the inequality (19) reduces to the dissipation inequality. Course Title FINC 11;.
Sep 03, 13 · Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Exponential Families Exponential Families MIT Dr Kempthorne Spring 16 í MIT Exponential Families. Start with some sequence (f n) n≥1 ⊂ C b K(Ω), which convergens in norm to some f ∈ ‘∞ K (Ω), and let us prove that f Ω → K is continuous (the fact that f is bounded is automatic) Fix some point p 0 V of p 0, such that f(p)−f(p 0) < ε, ∀p ∈ V Start by choosing n such that kf n −fk < ε 3 Use the fact that f n is.
27r f ire'' dw 2 t~(j) (eie sin oot t Therefore, sin (wot) 1 y(t) = cos (wet) s I I t I Fourier Transform Properties / Solutions S99 From the multiplicative property, we have Y(w) = X(W) * r(o W) 7r(WO (0, Y(o) is sketched in Figure S99 I T2C Iw cj W() Wc Wc ± W()ic 0 C Cj C 0u cj(. 6DAVIDZYWINA §23 Composition of linear transformations and matrix multiplication Problem 1 (a)False ThisisanincorrectstatementofTheorem211 Ifdim W =dimZ. If one sets f(x) = e ax and g(x) = e bx, and then cancels the common factor of e (a b)x from both sides of the result, the ordinary binomial theorem is recovered Applications Multipleangle identities For the complex numbers the binomial theorem can be combined with de Moivre's formula to yield multipleangle formulas for the sine and cosine.
M X(t) = X x etXP(x) = X x " 1 tx 1!. 2 Verify that for all pairs of differential functions f and g of one variable, u(x,y) = f(x)g(y) is a solution of the PDE uuxy = uxuy Solution First, compute ux, uy and uxy ux = g(y)f′(x) uy = f(x)g′(y) uxy = f′(x)g′(y) Substituting into the PDE, we have uuxy = f(x)g(y)f′(x)g′(y) = uxuy Hence, u(x,y) = f(x)g(y) is a solution of. U(x;t) = X(x)T(t) If we substitute X (x)T t) for u in the heat equation u t = ku xx we get X dT dt = k d2X dx2 T Divide both sides by kXT and get 1 kT dT dt = 1 X d2X dx2 D DeTurck Math 241 002 12C Solving the heat equation 9/21.
;F T) by dQ dP = E Z b(X)dX T Finally, let W t= X t X 0 Z t 0 b(X s)ds By Girsanov’s theorem, W is a QBrownian motion Hence (;F T;Q;F;W;X) is a weak solution of the SDE Problem 4 By inspecting the proof of Novikov’s condition, show that if there exists an increasing sequence t n!1such that E(e12(hMitnh Mitn 1)). Let A be an m×n matrix Define TRn 6 Rm by, for any x in Rn, T(x) = Ax Then T is a linear transformation Furthermore, the kernel of T is the null space of A and the range of T is the column space of A Thus matrix multiplication provides a wealth of examples of linear transformations between real vector spaces. 219 (Canonical Forms) Consider the follwing function f(A,B,C,D) = Σm(0,1,2,7,8,9,10,15) (a) Write this as a Boolean expression in canonical minterm form A B C D.
56 since m x t x x 0e θ θ x x e tx x x0e θ θe txx School Trinity Lutheran;. Problem 3 Let X be a Banach space, and let T X → X be a bounded linear operator on X such that kTk < 1 Let x0 be an element of X Show that there exists a unique x ∈ X such that x = x0 Tx (Hint use the contraction principle). X x x2P(x) t3 3!.
Let A be a rectangular m × n matrix with full column rank and m > n Consider the QR decomposition of A 1 Show that P 0 = I−QQT is the projection matrix onto the nullspace of AT 2 Show that for every x we have kAx−bk2 2 = kA(x−x 0)k2 2 kAx 0 −bk2 2 where x 0 is the least squares solution of Ax = b 3. Example 5 The differentiation map T P(F) → P(F) is surjective since rangeT = P(F) However, if we restrict ourselves to polynomials of degree at most m, then the differentiation map T Pm(F) → Pm(F) is not surjective since polynomials of degree m are not in the range of T 4 Homomorphisms.
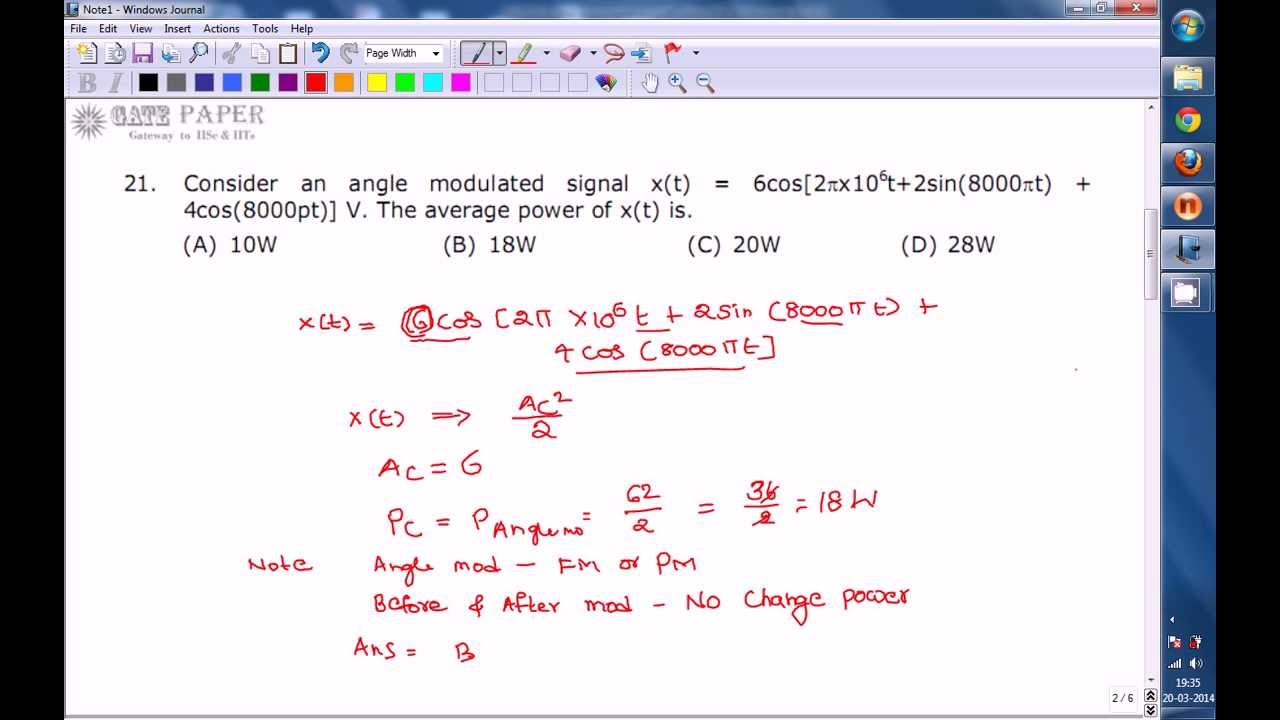
Gate 10 Ece Average Power Of Angle Modulated Fm Signal Youtube

What Are The Kinematic Formulas Article Khan Academy
Find The Indicated Values Where G T T 2 T And F X 1 X F 2g 1 Brainly Com
Txx F M のギャラリー

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2

Prove That Lim X To Infty Frac 1 X Int 0 Xf T Dt A If F Is Continuous And Lim X To Infty F X A Mathematics Stack Exchange

Four Forms Of Fourier Transform

Oneplus Founder Talks Nfc Meeting Demand And What Never Settle Really Means Venturebeat
Prove A Formula For The Integral From 0 To X Of Tm 1 T N Stumbling Robot

Consider The Equation X 2 X 1 2 M 3 X 2 X 1 M 1
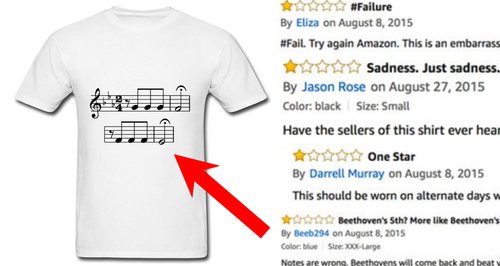
Musicians Are Leaving Savage Reviews Of This Incorrect Beethoven Fifth T Shirt Classic Fm
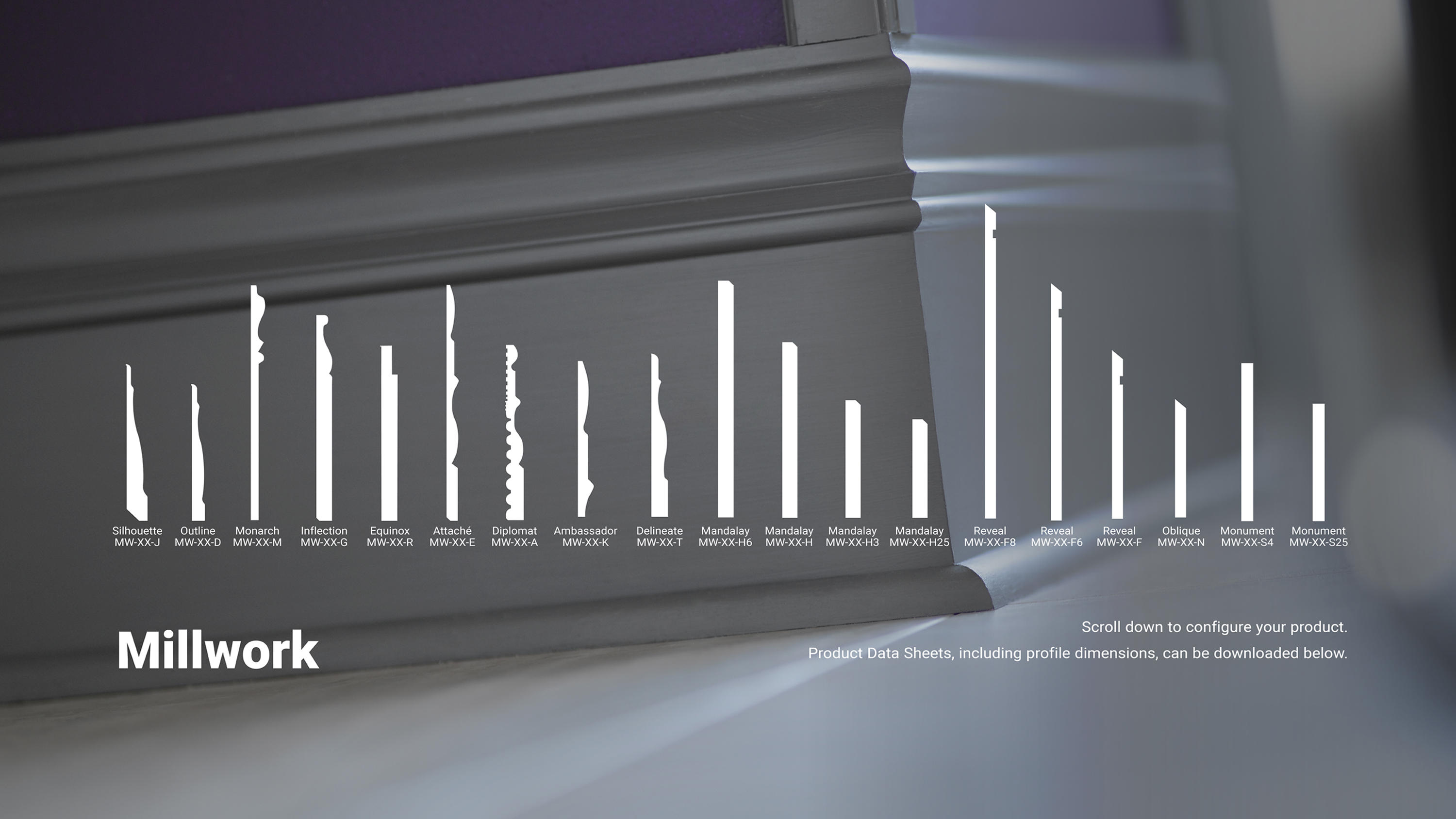
Millwork Chair Rail Commercial Flooring Tarkett

New Viltrox Roadmap Shows Nine New Lenses On The Way Including Micro Four Thirds Cine Lenses Diy Photography

A Given That Quadrilateral Fa See How To Solve It At Qanda

Forms Of Gender X What Do The Letters F M And X Have In Common
Solved Let M X Y Be X Has Sent Y An E Mail Mes

Proof Of Birkhoff Ergodic Theorem Mathematics Stack Exchange

La X 96 3 Wxny 96 3 Fm New York Ny Free Internet Radio Tunein

Amazon Com Derivatives For You You Re Welcome F X Blackpenredpen T Shirt Clothing

Fm Chord 4 Easy Shapes For Beginner Guitarists

How Would I Set Up The Taylor S Inequality To Prove That The Function Is Equal To Its Taylor Series Expansion Mathematics Stack Exchange
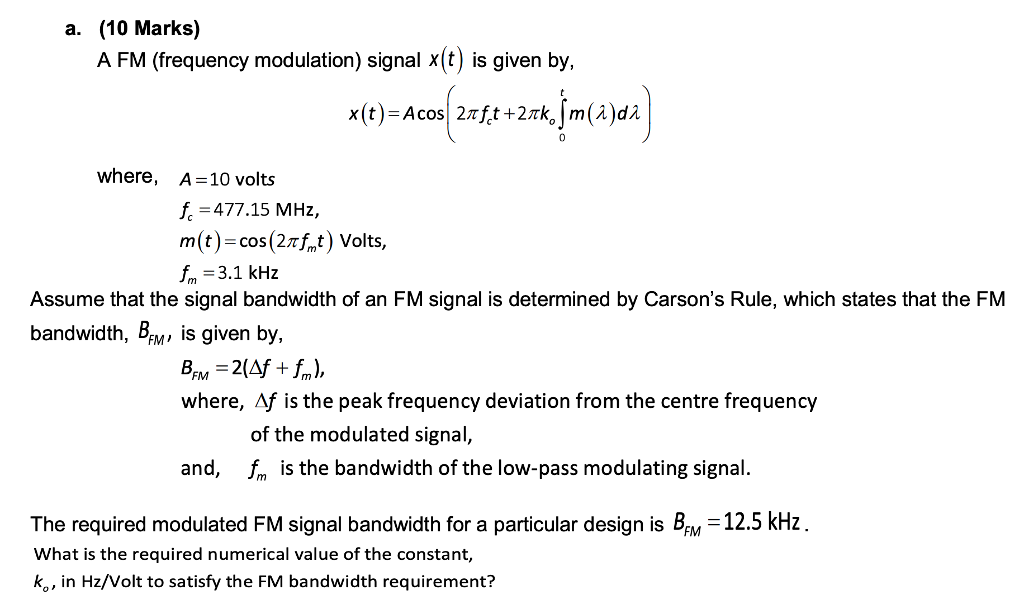
Solved A 10 Marks A Fm Frequency Modulation Signal X Chegg Com

Amazon Com Avoid Negativity F X X Absolute Value T Shirt Clothing

Demodulation Of Fm Data In Free Space Optical Communication Systems Using Discrete Wavelet Transformation Intechopen

Solved Solve The Initial Value Problem X 2x 2x 2delta Chegg Com
Higginbotham Brothers Big Spring Herald

Instantaneous Rates Of Change Ck 12 Foundation

Pdf Taylor Series Method For Solving Linear Fredholm Integral Equation Of Second Kind Using Matlab

Four Forms Of Fourier Transform

Radio X Get Into The Music

Derivative Wikipedia

Solved Find The Inverse Of The Following Functions F X Chegg Com

5t8y08 Vt Iukm

Storage Units In Buda Tx At 2550 Fm 967 Extra Space Storage

Solved For The Following Exercises Compute The Values Gi Chegg Com

Lesson 26 The Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Section 10 Version

Uniform Convergence And Continuity Proof Mathematics Stack Exchange

Ferromagnetism Of Mnxsi1 X X 0 5 Films Grown In The Shadow Geometry By Pulsed Laser Deposition Method Aip Advances Vol 6 No 1

Four Forms Of Fourier Transform

Prove That If F D Rightarrow R Is Continuous Then Chegg Com

Chapter 1 Use The Following To Answer Questions 1 5 In The Questions Below Determine Whether The Proposition Is True Or False Pdf Free Download

Pdf Estimation Of Scale Parameter Of Weibull Distribution That Has Exponential Family Using T O M

Computing The Moment Generating Function Of F X E X Mathematics Stack Exchange
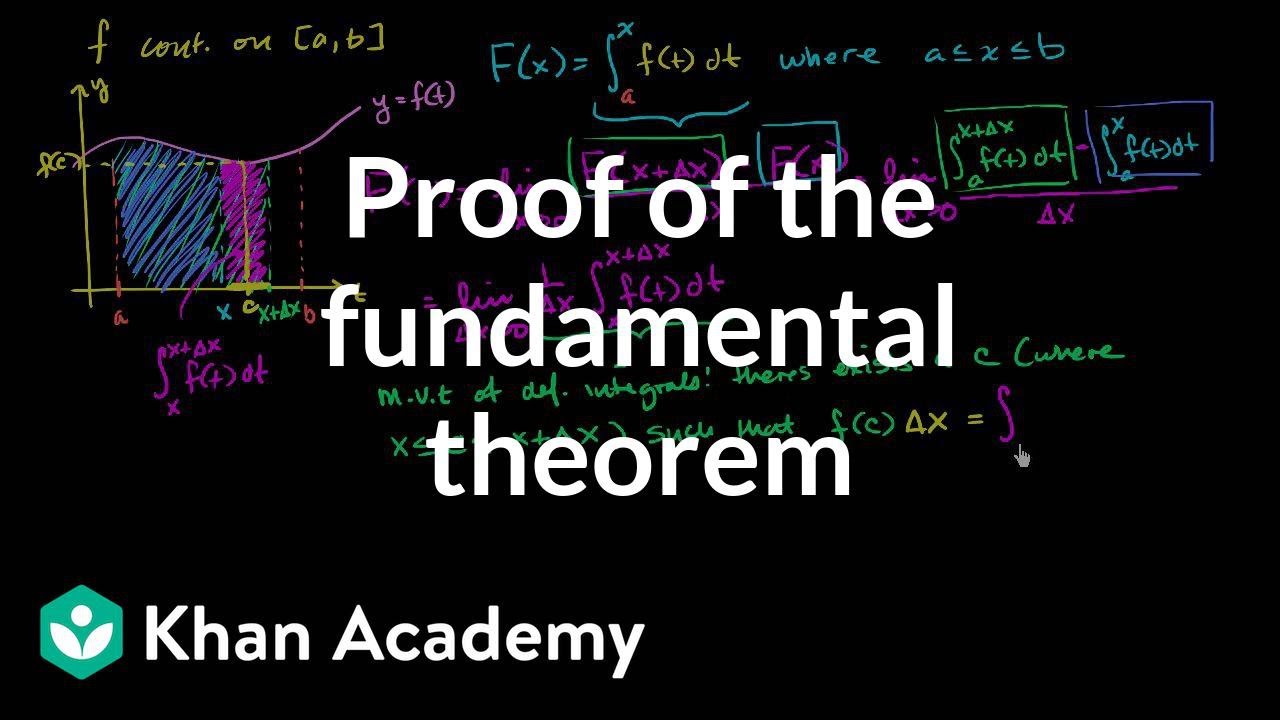
Proof Of Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus Video Khan Academy

Onkyo Tx Sr505 Home Theater Receiver Black Tx Sr505b B H Photo

Function Mathematics Wikipedia
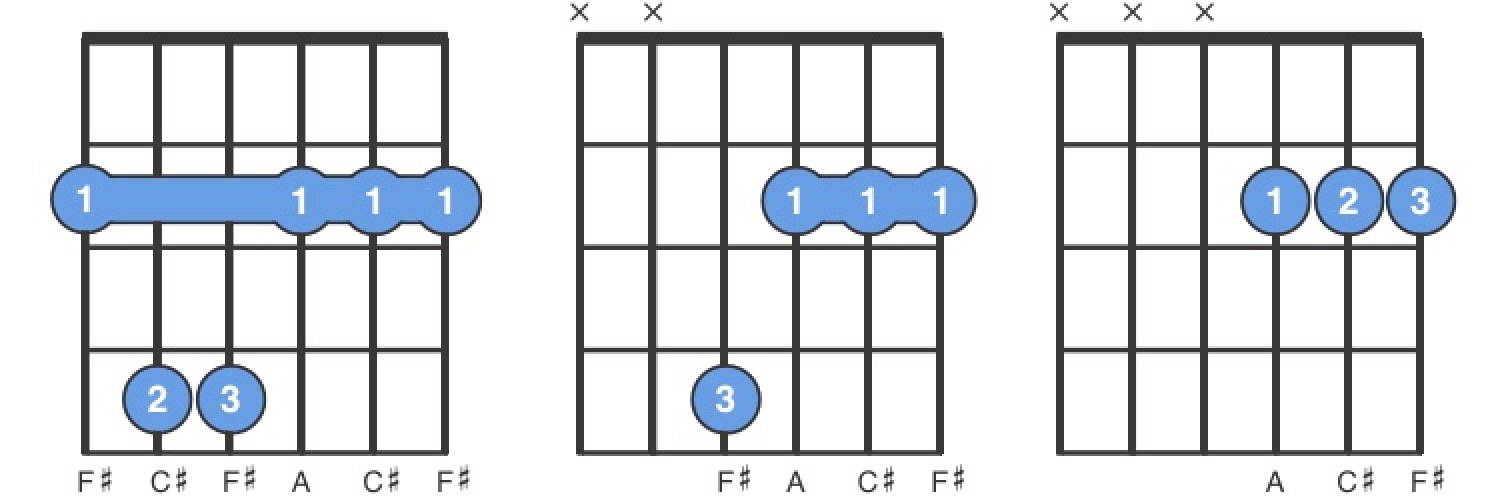
F M Guitar Chord For Beginners Easy To Play F M Chord Chordbank

Why Is Y F A F A X A Linear Mathematics Stack Exchange
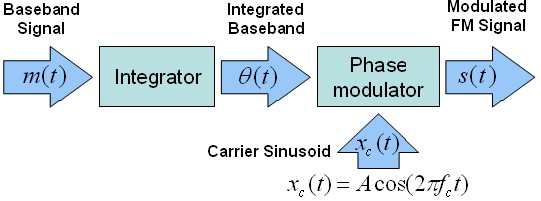
Frequency Modulation Fm Ni
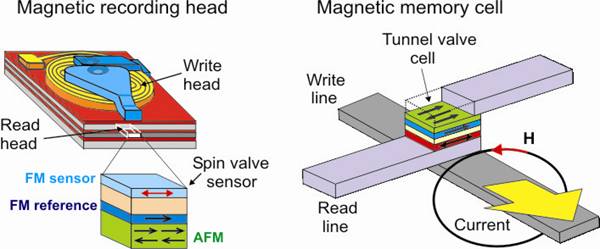
Exchange Bias

Yw6usjhb0segim

Section 2 5 Important Definition In The Text The Definition Of The Moment Generating Function M G F Definition If S Is The Space For A Random Ppt Download
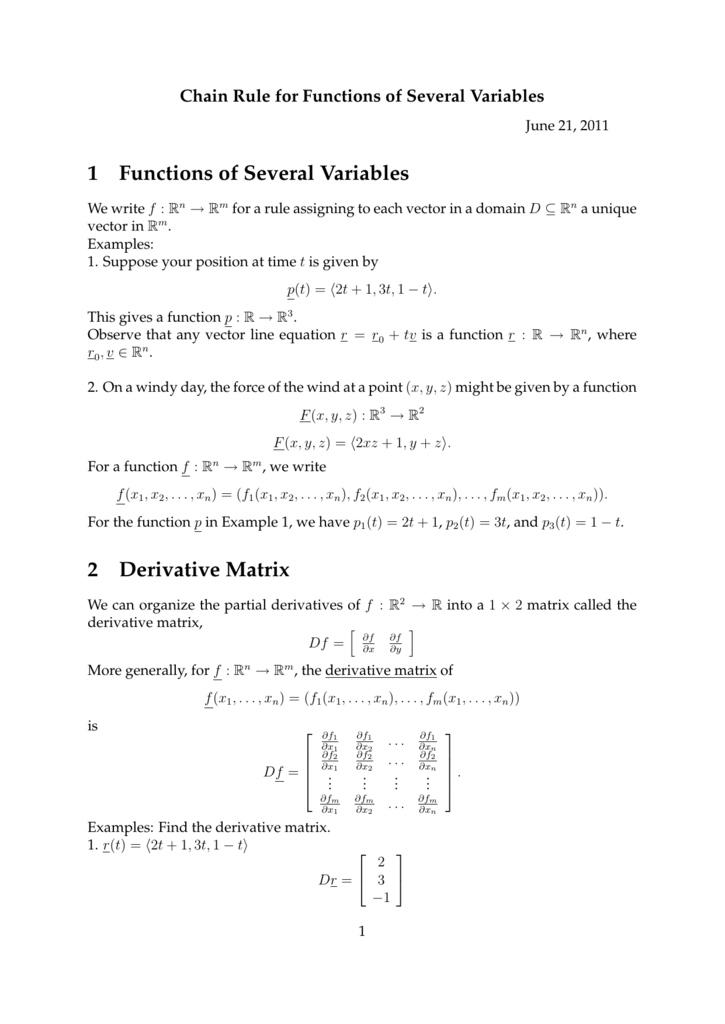
Chain Rule

Section 2 5 Important Definition In The Text The Definition Of The Moment Generating Function M G F Definition If S Is The Space For A Random Ppt Download
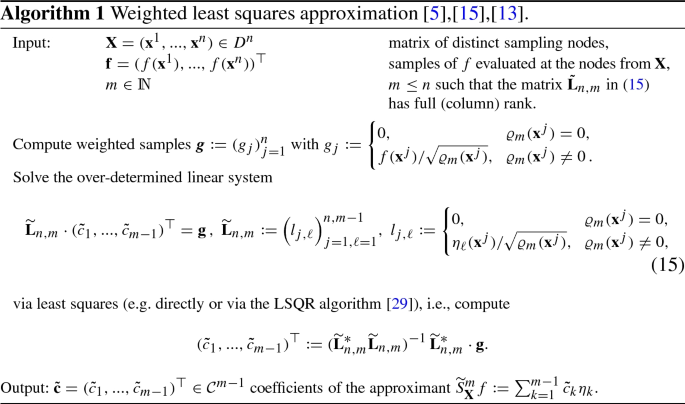
A New Upper Bound For Sampling Numbers Springerlink
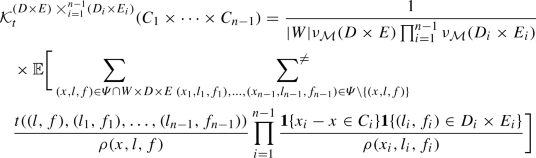
Functional Marked Point Processes A Natural Structure To Unify Spatio Temporal Frameworks And To Analyse Dependent Functional Data Springerlink

Radio X Best Of British Playlist Doesn T Feature Many Women News Clash Magazine

Derivative Wikipedia

If F X X 1 X 1 Then F 2x Is Equal To

Systems Of Differential Equations

x To Change Format After 30 Years Of Modern Rock Radio

Xfm 94 8 Verified Page Facebook
Lee S Rental Big Spring Herald

Section 2 5 Important Definition In The Text The Definition Of The Moment Generating Function M G F Definition If S Is The Space For A Random Ppt Download

Madonna Reinvents The Pop Concert With Madame X Tour Kickoff Setlist Fm

Indie X Fm
Higginbotham Brothers Big Spring Herald
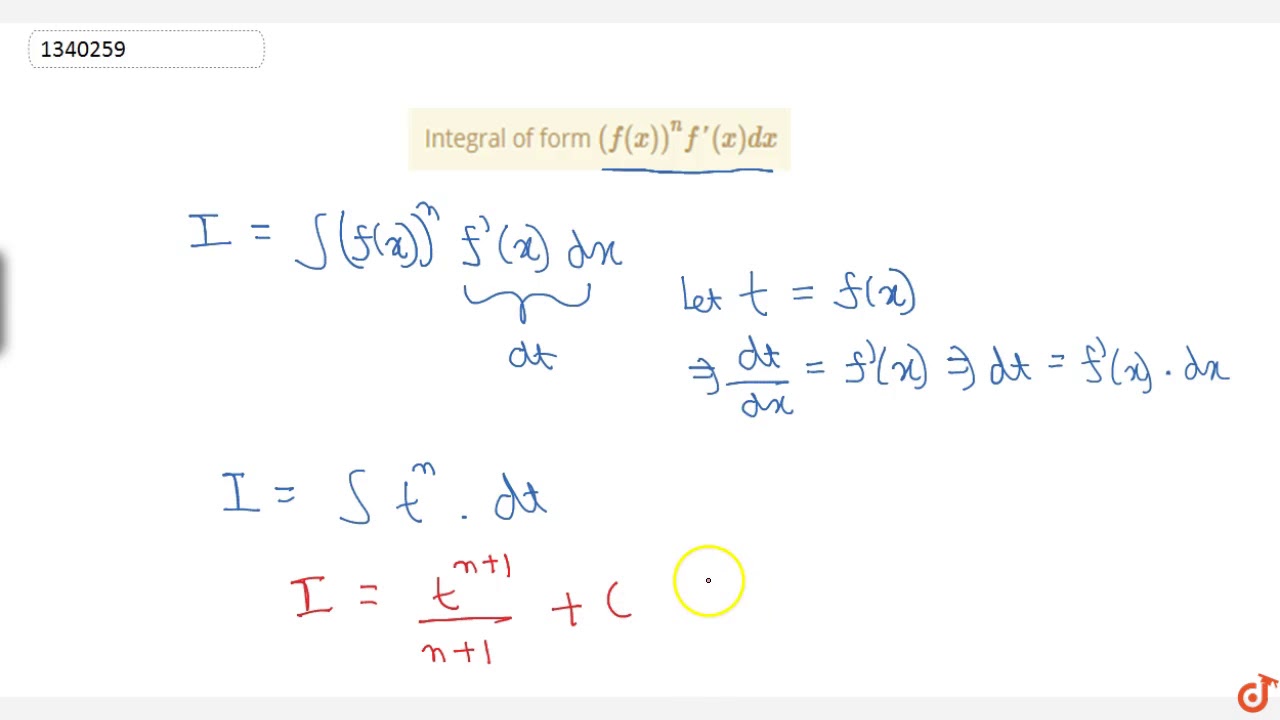
Integral Of Form F X N F X Dx Youtube

Wwfm X Jazzy Sport Everpress

Using Matlab Ode45 To Solve Differential Equations

3m Temflex Multi Purpose Vinyl Electrical Tape 165 Red 3 4 In X 60 Ft 19 Mm X 18 M 10 Roll Pack Amazon Com Industrial Scientific

Panasonic Sc Pmx3db Operating Instructions Manual Pdf Download Manualslib

21 A Let F X Be A Polynomial Of Degree M For Chegg Com

Solved Consider The Initial Value Problem Mx Cx Kx Chegg Com
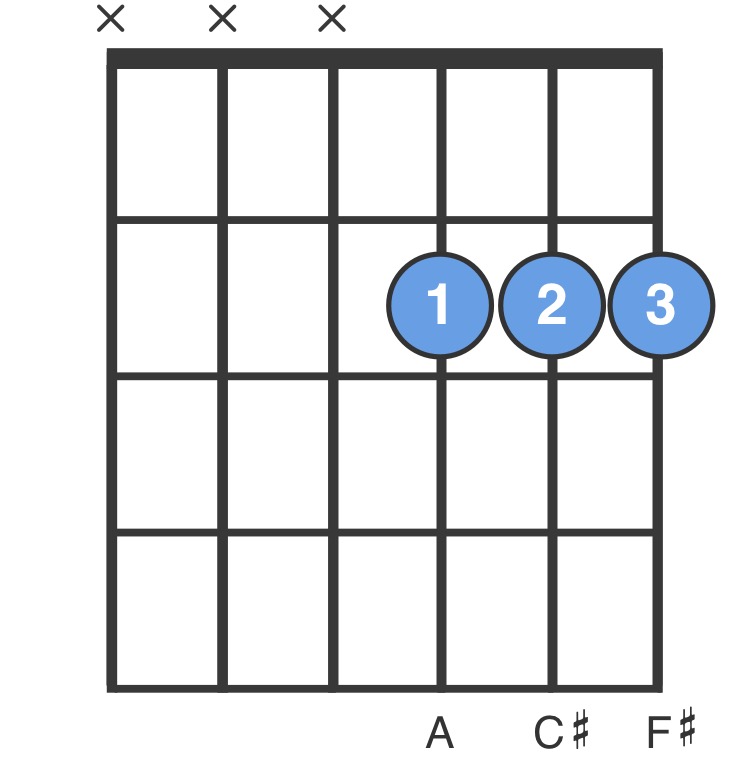
F M Guitar Chord For Beginners Easy To Play F M Chord Chordbank

Taylor Inequality Formula Confusion A Few Questions Mathematics Stack Exchange
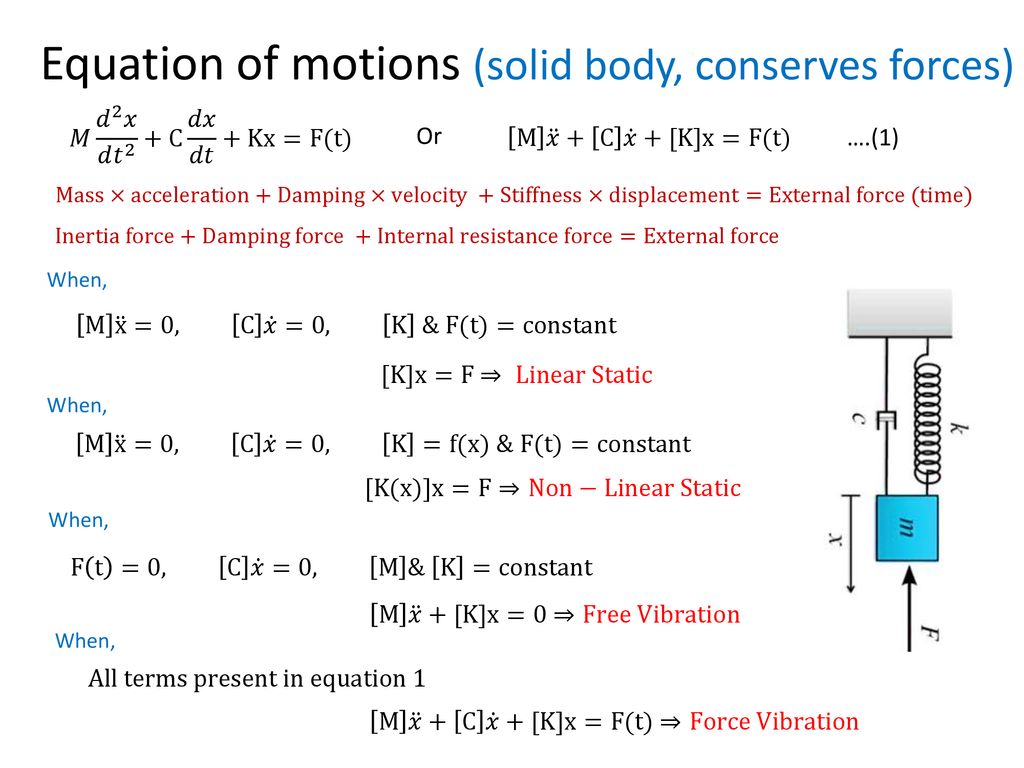
Introduction Of Applied Finite Element Method Ppt Download

Storage Units In Corinth Tx At 31 Fm 2181 Extra Space Storage
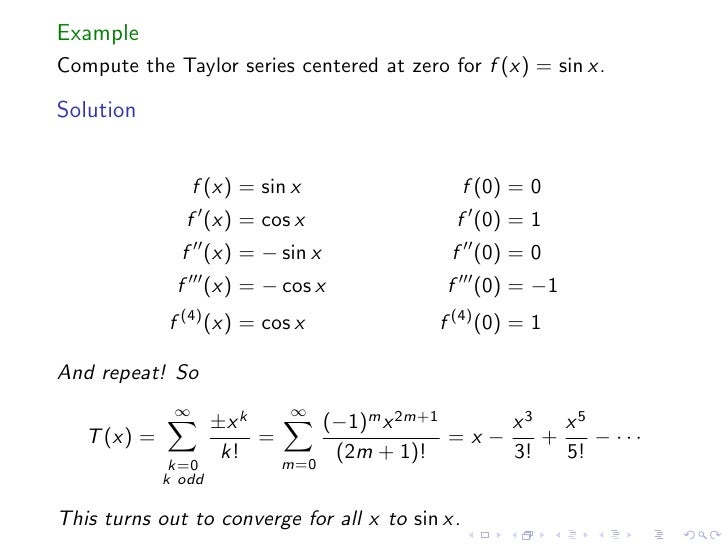
Taylor Polynomials And Series

If M And N Are Positive Integers And F X Int 1 X T A 2n T




