Px I Xy
The pmf of X given Y = 1 Solution pXY=1(1) = p(1,1)/pY (1) = 05/06 = 5/6 pXY=1(2) = p(2,1)/pY (1) = 01/06 = 1/6 2 If X and Y are independent Poisson RVs with respective means λ1 and λ2, find the conditional pmf of X given X Y = n and the conditional expected value of X given X Y = n Solution Let Z = X Y We want to find pX.

Px i xy. We have P ( Y X, Z) P ( X Z) = P ( X, Y, Z) P ( X, Z) P ( X, Z) P ( Z) = P ( X, Y, Z) P ( Z) = P ( X, Y Z) This is also intuitive The probability that X and Y happen if we know that Z happens is the same as the probability that X happens when we know that Z happens and that then Y happens when we know that X and Z happen Share. Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. Discrete case If Xand Y have joint pmf p(x i;y j) then n m n m Cov(X;Y) = XX p(x i;y j)(x i X)(y j Y) = p(x i;y j)x iy j X Y i=1 j=1 0 1 X i=1 X j=1 Continuous case If Xand Y have joint pdf f(x;y) @ over range a;b A c;d then Cov(X;Y) = Z d Z b d b (x x)(y y)f(x;y)dxdy= Z Z xyf(x;y)dxdy c y a c a x 23 Examples Example 1 Flip a fair.
Consider the following open statements p(x) x is irrational q(x, y) xy is rationalNegate and simplify the following statement, and determine if the original statement is. P(X=x Y=y) = P(X=x, Y=y) / P(Y=y) Chain rule (follows directly from the above) P(X=x, Y=y) = P(X=x) P(Y=y X=x ) = P(Y=y) P(X=x Y=y) (really just a reordering of terms in the above) P(X=x Y=y) = P(Y=y X=x) P(X=x) / P(Y=y) Marginalization P(X=x) = ∑ y P(X=x, Y=y). X Y g h i q z ҕ cҕTC h 5 CJ OJ QJ \ ^J aJ h 5 CJ OJQJ\ aJ 1 j h/I 5 6 CJ OJQJU \ aJ 1 jt h/I 5 6 CJ OJQJU \ aJ " h 5 6 CJ OJQJ\ aJ 1 j h/I 5 6 CJ OJQJU \ aJ " h/I 5 6 CJ OJQJ\ aJ j h/I 5 6 CJ OJQJU \ aJ " h 5 6 CJ OJQJ\ aJ h y z W E F $ If ?kd\ $ $ If x 5( # 8 4 4 xa yt $ If gd $ $ If a$ $ If gd d ( , { 6 ܺ u fTB" h M h.
Expected Value and Standard Dev Expected Value of a random variable is the mean of its probability distribution If P(X=x1)=p1, P(X=x2)=p2, n P(X=xn)=pn E(X) =. = (d(x,z)d(y,z))2 Hence, d(x,y) ≤ d(x,z)d(y,z) and the assertion is proved More examples (1) Let n be a prime number On Z we define dd n(x,y) = n−max{m∈Nn m divides xy} The nadic metric satisfies a stronger triangle inequality dd n(x,y) ≤ max{dd n(x,z),dd n(z,y)} (2) Let 1 ≤ p < ∞ Then d p(x,y) = i=1 x i −y i p. Uses an interactive simulation to explain how to read a Pxy diagram for a binary mixture that obeys Raoult's law Explains what happens as the pressure is.
Job ID PROJE CareerBuilder TIP For your privacy and protection, when applying to a job online, never give your social security number to a prospective employer, provide credit card or bank account information, or perform any sort of monetary transaction Learn more By applying to a job using CareerBuilder you are agreeing to comply with and be subject to the CareerBuilder. P((X;Y) 2R) = Z Z R fXY(x;y) dxdy For when the rv’s are continuous 16 Example Movement of a particle An article describes a model for the movement of a particle Assume that a particle moves within the region Abounded by the x axis, the line x= 1, and the line y= x Let. Jun 05, 14 · Details The saturation pressure of component is calculated using the Antoine equation where for hexane and for octane, is saturation pressure (bar), , , and are Antoine constants, and is temperature (°C) Raoult's law is used to calculate the bubblepoint and dewpoint pressures using the factors where is the vapor mole fraction and , is the liquid mole.
Y X x Pr(X = x,Y = y) bytotalprobability, P x Pr(X = x,Y = y) = Pr(X = x), likewise P x Pr(X = x,Y = y) = Pr(Y = y) So, EX Y = X x xPr(X = x) X y yPr(Y = y) = EXEY Notice that EX works just like a mean;. 2 Consider the ODE y′′ p(x)y′ q(x)y = 0 a) Show that if p and q are continuous for all x, a solution whose graph is tangent to the xaxis at some point must be identically zero, ie, zero for all x b) Find an equation of the above form having x2 as a solution, by calculating its derivatives and finding a linear equation. 1 Sum of Independent Binomial RVs • Let X and Y be independent random variables X ~ Bin(n 1, p) and Y ~ Bin(n 2, p) X Y ~ Bin(n 1 n 2, p) • Intuition X has n 1 trials and Y has n 2 trials o Each trial has same “success” probability p Define Z to be n 1 n 2 trials, each with success prob p Z ~ Bin(n 1 n 2, p), and also Z = X Y.
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. Find the minimum value of x^2y^2, where x,y are nonnegative integers and xy is a given positive odd integer Find the minimum value of x 2 y 2 , where x , y are nonnegative integers and x y is a given positive odd integer. May , 21 · Hey everybody, smile I have a joint density of the random variables ##X## and ##Y## given and want to find out ##P(XY>1/2)## The joint density is as.
In fact we can think of it as being the population mean (as opposed to the sample mean). We know from problem MU 29 that Emax(X,Y) = EX EY − Emin(X,Y) From below, in part (c), we know that min(X,Y) is a geometric random variable mean pq −pq Therefore, Emin(X,Y) = 1 pq−pq, and we get Emax(X,Y) = 1 p 1 q. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history.
We read the joint probability p(X = x, Y = y) as \the probability of x and y" 6 Conditional Distributions A conditional distribution is a distribution of a rv given some evidence/prior knowledge This is denoted p(X = x jY = y) (read \the probability of x given y") For example. Semantics Quantifiers x variable xvariant of interpretation I is an interpretation J (DJ,αJ) such that DI = DJ αIy = αJy for all symbols y, except possibly x That is, I and J agree on everything except possibly the value of x. P(x,y ) = p(xy )p(y ) As the left hand side of this equation is a joint probability distribution, and conjunctions of RVs act like RVs, we can extend this to arbitrary numbers of RVs to get, for example.
Definition 1 Two random variables X,Y are said to be independent if for any subsets A,B ⊂ R P(X ∈ A,Y ∈ B) = P(X ∈ A)P(Y ∈ B) Definition 2 Two random variables X,Y are said to be independent if 1 when X,Y are discrete P(X = xi,Y = yj) = P(X = xi)P(Y = yj) 2 when X,Y are continuous f(x,y) = fX(x)fY (y). Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and more. (a) Find PX > Y and PX Y ≤ 1 (b) Find Pmin(X,Y ) ≥ 1 (c) Find Pmax(X,Y ) ≤ 1 Problem 443 Solution The joint PDF of X and Y is fX,Y (x,y) = ˆ 6e−(2x3y) x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0, 0 otherwise (1) (a) The probability that X ≥ Y is Y X X Y³ P X ≥ Y = Z∞ 0 Zx 0 6e−(2x3y) dydx (2) = Z∞ 0 2e−2x −e−3y y=x y=0 dx (3.
Worked examples Multiple Random Variables Example 1 Let X and Y be random variables that take on values from the set f¡1;0;1g (a) Find a joint probability mass assignment for which X and Y are independent, and conflrm that X2 and Y 2 are then also independent (b) Find a joint pmf assignment for which X and Y are not independent, but for which X2 and Y 2 are independent. A motion was made by member Kavanaugh, of continuing support for the weekend polygraph Association State of Louisiana POLYGRAPH BOARD , 5 6 P Q ~ M N c m 8 x o o o o go hP CJ aJ hP 5 CJ aJ hP 0J 5 CJ aJ j hP 5 CJ U aJ hP 5 CJ aJ j hP 5 CJ U aJ hP CJ hP CJ aJ hP CJ aJ hP \ hP 5 j 9}P hP U V j hP U hP j hP U mH nH u j hP CJ U mH nH u ( , 5 6. Feb 28, 17 · The notation P (xy) means P (x) given event y has occurred, this notation is used in conditional probability There are two cases if x and y are dependent or if x and y are independent Case 1) P (xy) = P (x&y)/P (y) Case 2) P (xy) = P (x) Share edited Feb 28 '17 at.
P X y P XY y 006 009 005 0 P X 1 y P XY 1 y 012 007 013 032P X 2 y P XY 2 y P x y p xy y 006 009 005 0 p x 1 y p xy 1 y 012 007 School University of Michigan;. Theorem 2 Let (X;Y) be a bivariate random vector with p X;Y(x;y) X and Y are independent i p X;Y(x;y) = p X(x)p Y(y) X 1;;X n are independent if and only if P(X 1 2A 1;;X n2A n) = Yn i=1 P(X i2A i) Thus, p X 1;; (x 1;;x n) = Q n i=1 p X i (x i) If X 1;;X n are independent and identically distributed we say they are iid (or that they. Eq1) where p (X , Y) {\displaystyle p_{(X,Y)}} is the joint probability mass function of X {\displaystyle X} and Y {\displaystyle Y} , and p X {\displaystyle p_{X}} and p Y {\displaystyle p_{Y}} are the marginal probability mass functions of X {\displaystyle X} and Y {\displaystyle Y} respectively In terms of PDFs for continuous distributions In the case of jointly continuous.
The joint probability mass function of two discrete random variables X and Y is defined as P X Y (x, y) = P (X = x, Y = y) Note that as usual, the comma means "and," so we can write P X Y (x, y) = P (X = x, Y = y) = P ((X = x) and (Y = y)). Jul 05, 14 · Is it possible to convert a general linear second order boundary value ode y'' P(x)y' Q(x)y = g(x), y(a) = y_a, y(b) = y_b to a Fredholm integral equation, explicitly determining the Kernel in the process, without removing the y' term?. X y = x y/2 x y/2 (trường hợp y chẵn) x y = x y/2 x y/2 x (trường hợp y lẽ, ví dụ x 5 = x 2 x 2 x) Bài tập mang tính tham khảo, hỗ trợ các bạn làm quen và.
If discrete random variables X and Y are defined on the same sample space S, then their joint probability mass function (joint pmf) is given by p(x, y) = P(X = x and Y = y), where (x, y) is a pair of possible values for the pair of random variables (X, Y), and p(x, y) satisfies the following conditions 0. B = pxxpyy 100 = xy 1 Step 1 Set MRS equal to price ratio MRS = px py y x = 1 1 y = x this relationship must hold at the utility maximizing point Step 2 Substitute step 1 into budget constraint Since y= x, the budget constraint becomes 100 = xy. P((X,Y) ∈ A) = Z Z A f(x,y)dxdy The twodimensional integral is over the subset A of R2 Typically, when we want to actually compute this integral we have to write it as an iterated integral It is a good idea to draw a picture of A to help do this.
In some cases the conditional probabilities may be expressed as functions containing the unspecified value of as a parameter When both and are categorical variables, a. Course Title STATS 425;. STAT 400 Joint Probability Distributions Fall 17 1 Let X and Y have the joint pdf f X, Y (x, y) = C x 2 y 3, 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < x, zero elsewhere a) What must the value of C be so that f X, Y (x, y) is a valid joint pdf?b) Find P (X Y < 1)c) Let 0 < a < 1 Find P (Y < a X) d) Let a > 1 Find P (Y < a X)e) Let 0 < a < 1 Find P (X Y < a).
Uploaded By trancalvin Pages 112 This preview shows page 63 68 out of 112 pages. F(x,y)dxdy =1 In other words, 1= Z 1 0 dx Z x 0 cxydy = Z 1 0 c 2 x3 dx = c 8 Therefore c =8 (b) Since the region on which f(x,y) 6= 0 is not a rectangle, the joint density functionf(x,y) cannot be written as g(x)h(y) Therefore, X and Y are not independent (c) The marginal density of X is fX(x)= Z R f(x,y)dy For x ∈ 0,1, fX(x)= Z x 0. In probability theory and statistics, given two jointly distributed random variables and , the conditional probability distribution of Y given X is the probability distribution of when is known to be a particular value;.
2 Sec 51 Basics •First, develop for 2 RV (X and Y) •Two Main Cases I Both RV are discrete II Both RV are continuous I (p 185) Joint Probability Mass Function (pmf) of X and Y is defined for all pairs (x,y. P(X Y ≤ 1) = Z 1 0 Z 1−x 0 4xydydx = 1 6 (b) Refer to the figure (lower left and lower right) To compute the cdf of Z = X Y, we use the definition of cdf, evaluating each case by double integrating the joint density over the subset of the support set corresponding to {(x,y) x y ≤ z}, for different cases depending on the value of z. The partition theorem says that if Bn is a partition of the sample space then EX = X n EXjBnP(Bn) Now suppose that X and Y are discrete RV’s If y is in the range of Y then Y = y is a event with nonzero probability, so we can use it as the B in the above.
The result P ( Y ≤ 075 X = 05 ) = 5/6, mentioned above, is geometrically evident in the following sense The points (x,y,z) of the sphere x 2 y 2 z 2 = 1, satisfying the condition x = 05, are a circle y 2 z 2 = 075 of radius on the plane x = 05 The inequality y ≤ 075 holds on an arc The length of the arc is 5/6 of the length. Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Uses an interactive Mathematica simulation to describe a pressuremole fraction diagram (Pxy) that is generated with Raoult's law Behavior is discussed wh.
PX = Y = pq pq −pq (b) What is Emax(X,Y)?. Mar 30, · The Louisiana State University School of Medicine is working to launch two different clinical trials using hydroxychloroquine in relation to COVID19. (Here is an example of doing it without the y'.

Stab52h3 Lecture Notes Lecture 6 Joint Probability Distribution Marginal Distribution Absolute Continuity

Lecture 2 Conditional Probability And Expectation Studeersnel
2
Px I Xy のギャラリー
2
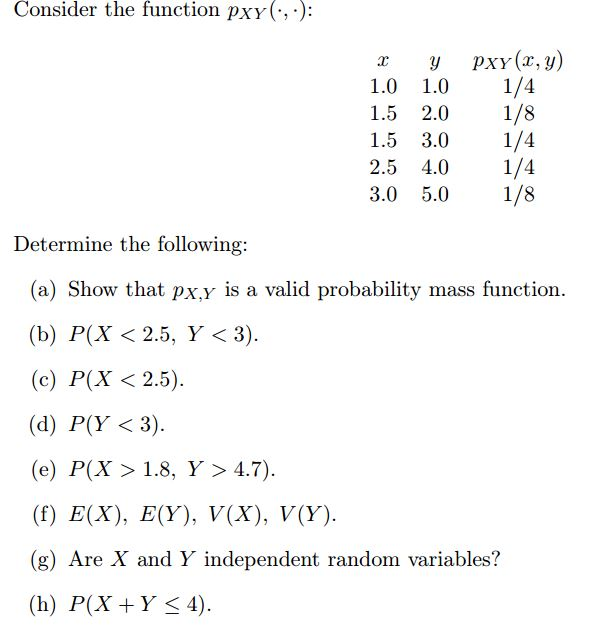
Solved Consider The Function Pxy X Y Pxy X Y 1 0 Chegg Com
2

Xy Is Parallel To Qr And Px Xq Py Yr 1 2 Find Xy Qr Brainly In

Problem Books In Mathematics Exercises In Probability Multivariate Distributions Pdf Document

If X Y Prop X Y Then Prove That Ax By Prop Px Qy Where A B P Q Are Youtube

1 P X Y 1 P Y Probability Of An X Distinction But Not A Download Scientific Diagram

Math Text If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X Text And Y Text Is Given By Math F X Y Frac X Y 30 Text For X 0 1 2 3 Text Y 0 1 2 Math Text Find Math Text A P X
Solve P 2 Px Xy Y 2 0 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community

Jointly Distributed Random Variables Multivariate Distributions Quite Often

Find The Work Done By The Force Field F X Y X 2 I Xy J On A Particle That Moves Once Around The Circle X 2 Y 2 4 Oriented In A
3 4 Joint Probability Distributions Ppt Video Online Download

Discrete Mathematics Lecture 1 5 Nested Quantifiers Studocu

Stab52h3 Lecture Notes Lecture 6 Joint Probability Distribution Marginal Distribution Absolute Continuity

The Use Of Quantifiers In Section 2 1 It Was Mentioned That Sentences Involving A Variable Such As X Are Not Statements Because They Are Neither True Or False Unless The Value For That Variable

Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides

Notes 5 09 Conditional Expectations E X Y As Random Variables Studocu
2

Solved P X Y Means X 2y Xy Where X And Y Are In Chegg Com

Solve The Bernoulli Differential Equation Xy Y 2 X 2y 0 Youtube
2
2

Art Of Problem Solving

Polynomial Equations
2
2

Bivariate And Marginal Probability Distribution Notes Sta 4321 Docsity

Derivation Of Joint Entropy H X Y H X H Y X Mathematics Stack Exchange
2
How To Solve Y Xy X Quora
2

Consider A Curve Y F X In Xy Plane The Curve Passes Through 0

Solved Suppose P X Y Is A Predicate And The Universe Fo Chegg Com
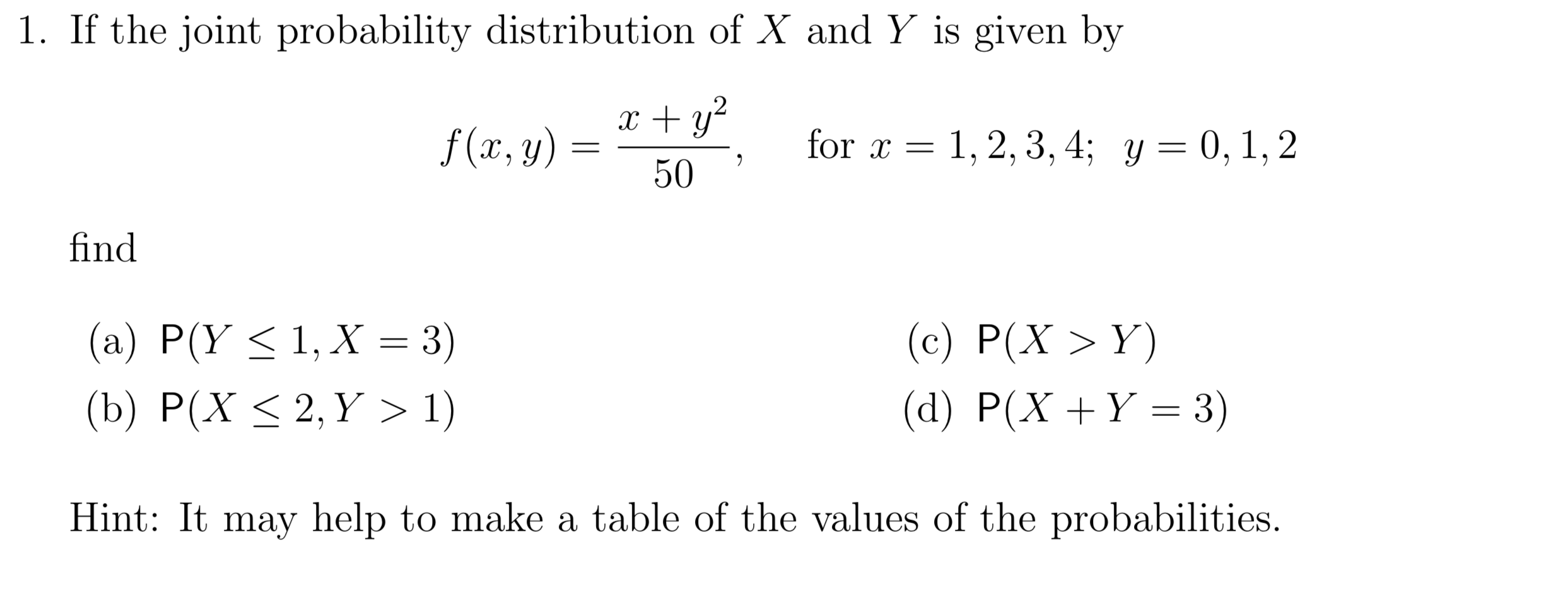
Solved If The Joint Probability Distribution Of X And Y I Chegg Com
2
2
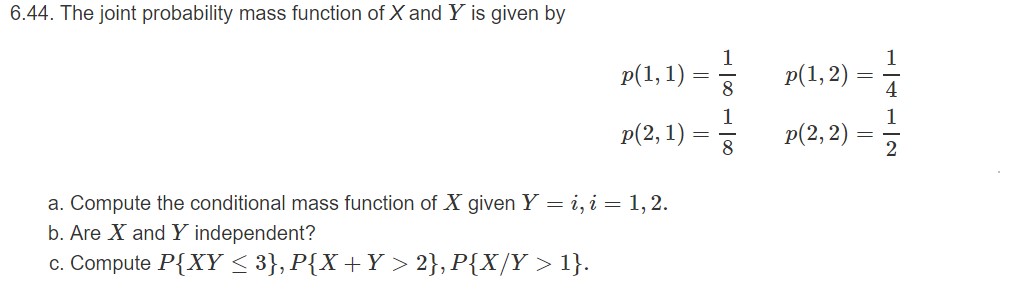
Answered 6 44 The Joint Probability Mass Bartleby
2

What Are The Meanings Of These P X Y P X Y Z P X Y Z Artificial Intelligence Stack Exchange

Important Short Objective Questions And Answers Two Dimensional Random Variables

Important Short Objective Questions And Answers Two Dimensional Random Variables
2
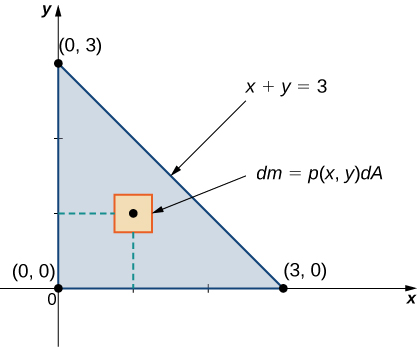
Calculating Centers Of Mass And Moments Of Inertia Calculus Volume 3

Why Is Displaystyle Sum Y P X X Y Y P X X Mathematics Stack Exchange
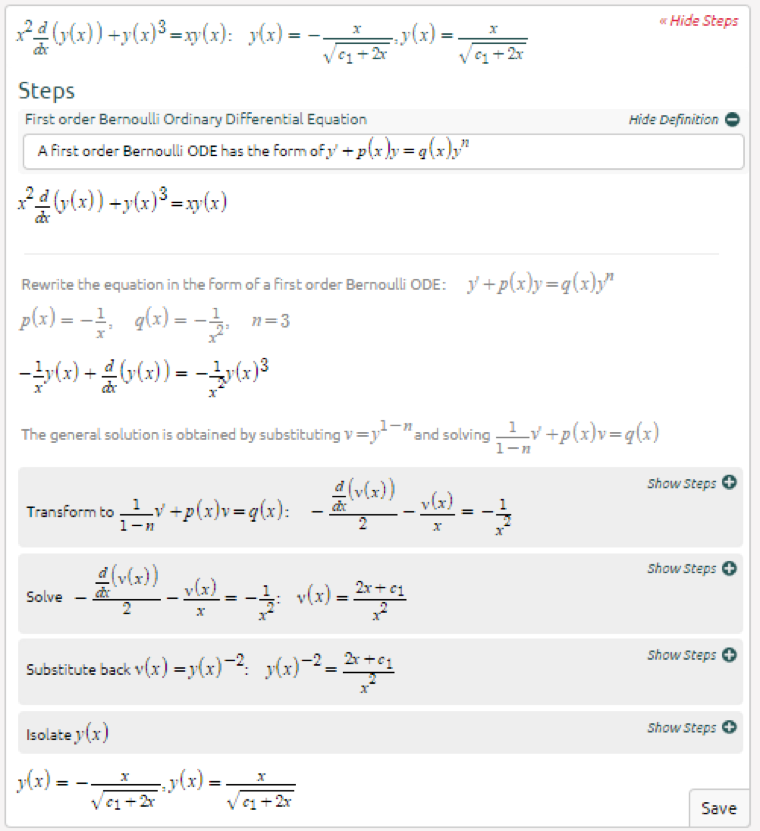
Symbolab Blog Advanced Math Solutions Ordinary Differential Equations Calculator Bernoulli Ode

P Xy And T Xy Diagram Equilibrium Thermodynamics

Expectation
Normal Distribution N µ S Of A Pixel P X Y Download Scientific Diagram
2

Two Dimensional Random Variables Mm Stat International
2
2
2
2
2

Solved X Y Let Px X X Y X 1 2 And Y 1 2 A Ar Chegg Com

Probability Theory Elementary Rules Of Probability Sum Rule Product Rule P Pdf Free Download
The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Is Given By Px Y 1 1 Px Y 1 2 3 Px Y 1 3 00 1 Px Y 2 1 Px Y 2 2 3 Course Hero
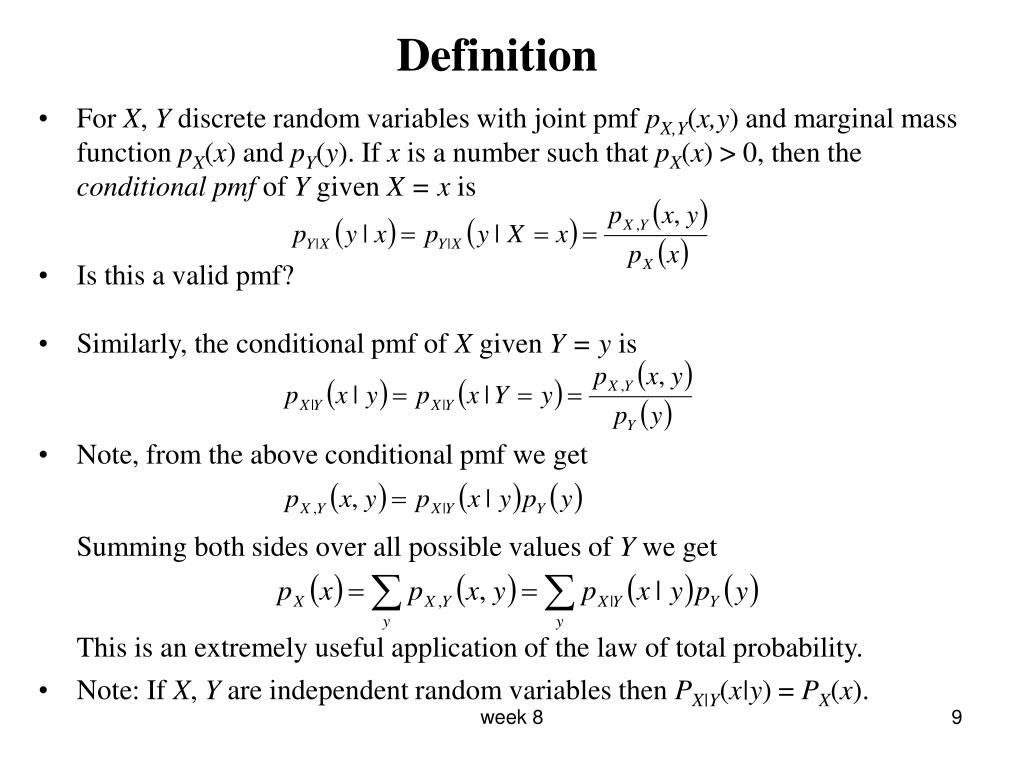
Ppt Joint Distribution Of Two Or More Random Variables Powerpoint Presentation Id 2398
Make Y The Subject Of The Formula P Xy X Y Tutorke
Assume P X Y Means Quot X 2y Xy Quot Where X And Y Are Integers Determine The Truth Value Of The Following Statements Justify Your Answer Course Hero
2

Let X And Y Be Two Events Such That P X 1 3 P X Y 1 2and P Y X

1 1 Px2 Yz Y2 Zx Z2 Xy See How To Solve It At Qanda
2
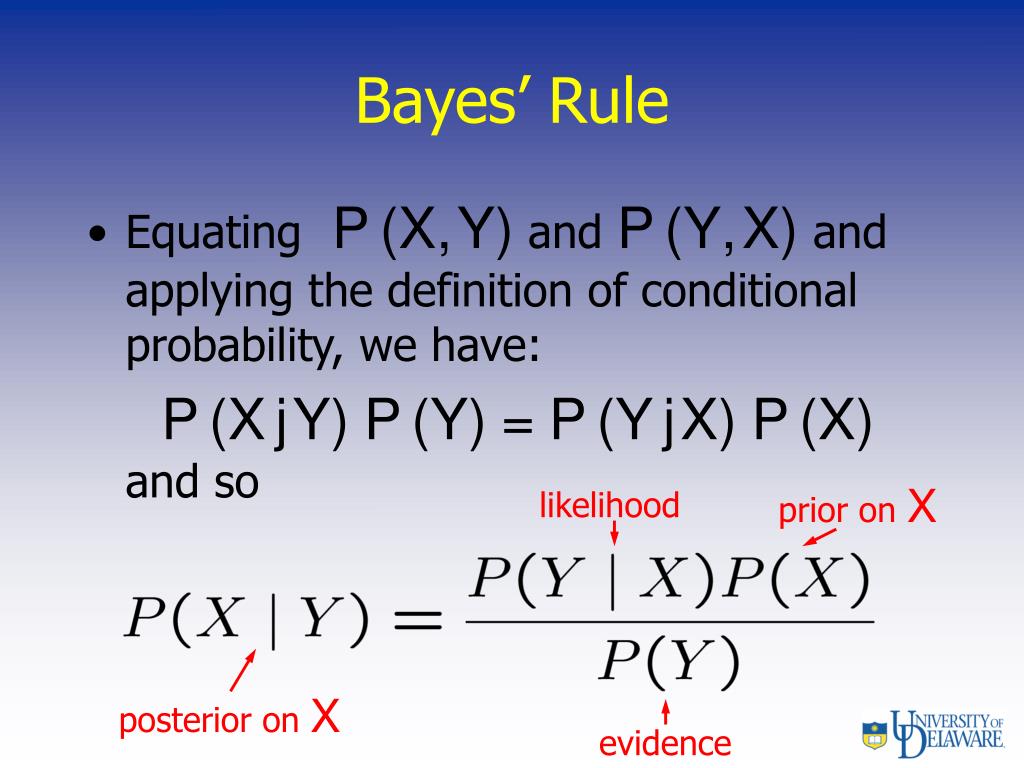
What Is P X Y

Chapter 4 Joint And Conditional Distributions Ppt Download

P Xy And T Xy Diagram Equilibrium Thermodynamics

Conditional Entropy Wikipedia
Consider The Following Joint Probability Mass Function P X X Y Y 0 1 2 0 1 4 1 8 X 1 1 8 1 4 0 2 0 0 1 4 Find A P X Lt 0 5 Y Lt 1 5 B Course Hero
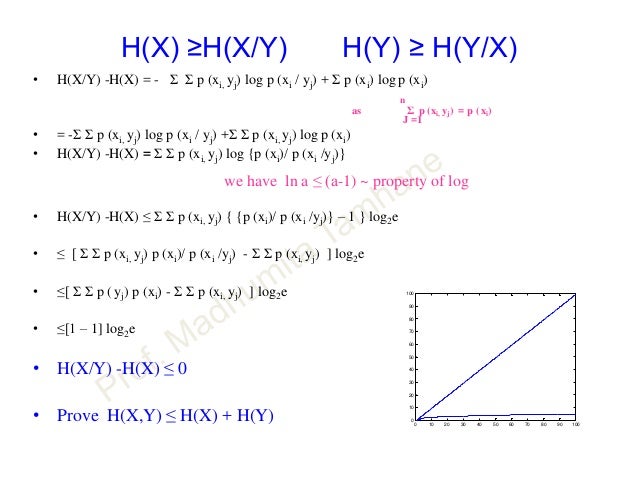
Information Theory

First Order Categorical Logic 4 Diagonal Argument
2
2

Answered 4 1 3 Let The Joint Pmf Of X And Y Be Bartleby

Using Properties Of Determinants Prove That X X 2 1 Px 3 Y Y 2 1 Py 3 Z Z 2 1 Pz 2 1 Pxyz X Y Y Z Z X Where P Is Any Scalar Mathematics Shaalaa Com

Pointwise Mutual Information Wikipedia
2

Probability And Random Variable Powerpoint Slides
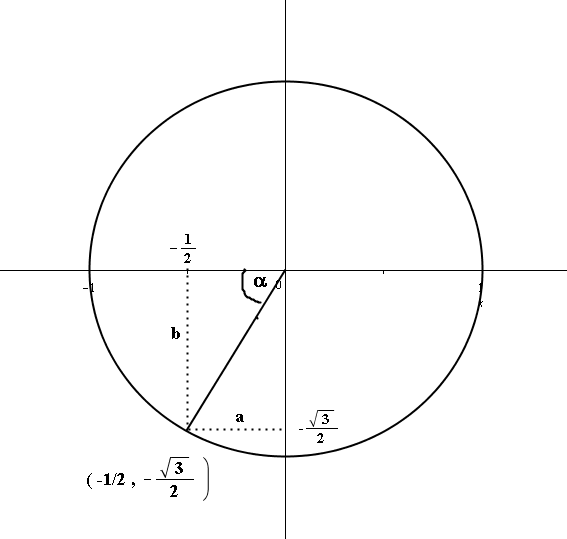
Find X Y On The Unit Circle Given That The X Coordinate Of P Is 1 2 And P Is In Quadrant Iii Socratic

Rk 10 Px Dino Lite Xy Positioning Arm 195x60x54mm Distrelec Export Shop
2
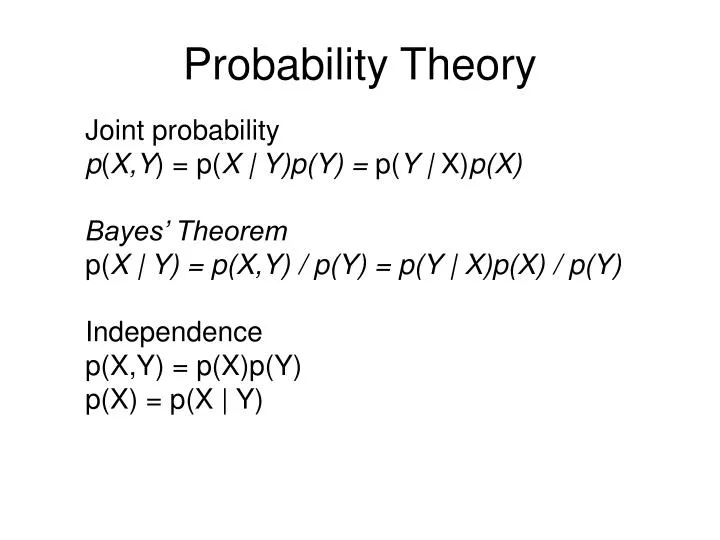
Ppt Probability Theory Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Plos One An Improved And Efficient Mutual Authentication Scheme For Session Initiation Protocol

A Generative Approach To Classification By Rahul Agarwal Towards Data Science

The Joint Probability Mass Function Of X And Y Is Given By Begin Array L L P 1 1 Frac 1 8
2

Factorisation Of Xy Pq Qy Px Brainly In

Shearing In 2d Graphics Geeksforgeeks

Answered 5 Let X And Y Be Random Variables Bartleby

Jointly Distributed Random Variables Ppt Video Online Download

Jointly Distributed Random Variables Multivariate Distributions Quite Often

File Drosophila Xy Sex Determination Svg Wikimedia Commons

Cdf Of Max X Y Youtube
2
2

Use Green S Theorem To Find The Work Done By The Force F X Y X X Y I Xy 2 J In Moving A Particle From The Origin Along The X Axis To 5 0




