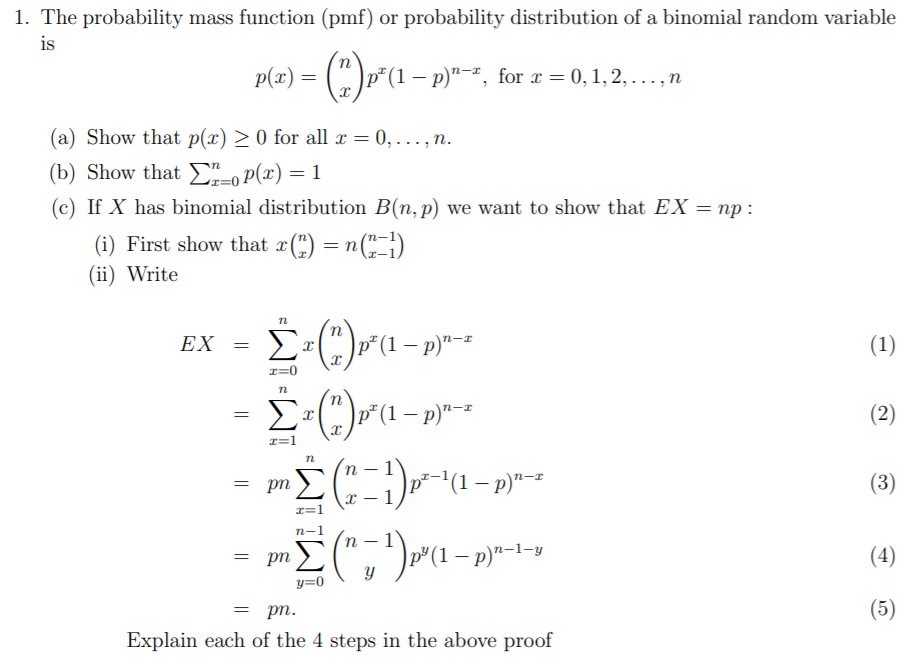
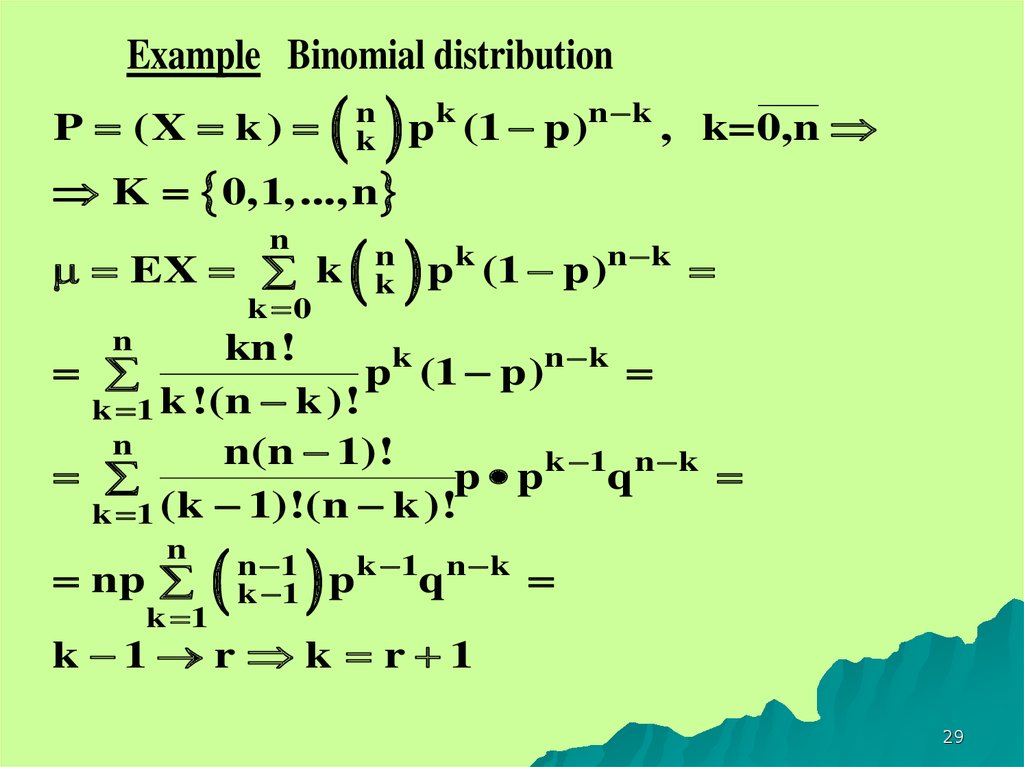
P Bnpx
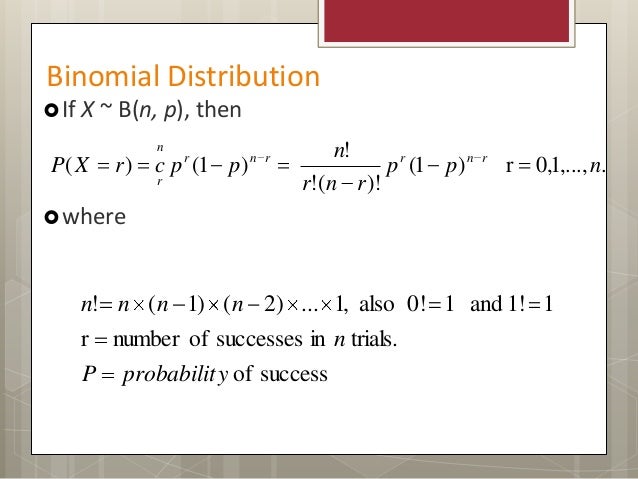
= 1) E(X) = np = 3* 03 = 09 P(X=x)=!( )!!.

P bnpx. Pn x Now we show by induction that x;. X (b) et xand p x eb the orrcesponding quantum mechanialc operators this time Evaluate the omc mutator x;. How to use Binomial Distribution Calculator with step by step?.
B(x;n,p)= n x px(1−p)n−x This is the probability of having x successes in a series of n independent trials when the probability of success in any one of the trials is p If X is a random variable with this probabilitydistribution, E(X)= x=0 x n x px(1−p)n−x = x=0 x n!. Var(X) = np(1−p) M(s) = (pes 1−p)n Keeping in the spirit of (1) we denote a binomial n, p rv by X ∼ bin(n,p) 3 geometric distribution with success probability p The number of independent Bernoulli p trials required until the first success yields the geometric rv with pmf p(k) = ˆ p(1−p)k−1, if k ≥ 1;. N, p) b Show that B(x;.
P(A∩B) = 05 P(A ∪ B) probability of events union probability that of events A or B P(A ∪ B) = 05 P(A B) conditional probability function probability of event A given event B occured P(A B) = 03 f (x) probability density function (pdf) P(a ≤ x ≤ b) = ∫ f (x) dx F(x) cumulative distribution function (cdf) F(x) = P(X. Nov 01, 05 · When A and B are independent events, or in other words when the probability of “A given B” is the same as the probability of A by itself Unfortunately, if you dig a little into the definition of conditional probability (ie, what I mean when I say the probability of “A given B”) you’ll find that mathematically the statement P(A n B)=P(A) x P(B) is the definition of “A and B are. X n x n − px (1p) nx VAR(X) = np(1p) = 3* 03 * 07 = 063 SD(X) = np(1p) Calculations shown for Binomial (n=3, p=03) = 0794 Note this is equivalent to counting success = 1 and.
EX = X n EXjBnP(Bn) Now suppose that X and Y are discrete RV’s If y is in the range of Y then Y = y is a event with nonzero probability, so we can use it as the B in the above So f(xjY = y) is de ned We can change the notation to make it look like the continuous case and write f(xjY = y) as fXjY (xjy) Of course it is given by fXjY. A Show that b(x;. B(X,n,bCP(X)) = α/2, (6) and if X = n then bCP(n) = 1 The Clopper–Pearson confidence interval for p if 0 < X < n is defined in a way very analogous to the way 2sided precise confidence intervals are for the normal µ and σ2 This makes the Clopper–Pearson intervals intuitive, and they have been called “exact,” but they are not.
Suppose that X ∼ Binomial(n, p) and Y ∼ Binomial(m, p) are independent, and denote Z = X Y (a) For each integer ‘ ∈ {0, 1, , n m}, compute the probability mass function of X given (b) Find the conditional expectation E X Z that Z = ‘ Hint Notice that Z ∼ Binomial(n m, p) Hint Write Z = X Y as a sum of n m i. 0 In probability P(jX n ¡Xj >†)!. A bn(P) nfEP(Tn) T(P)g B n˙n 2(P) nVarP(Tn) C 3;n(P) EPTn EP(Tn)3=˙n 3(P) D Hn(x;P) PrP(p n(Tn T(P)) x) E Kn(x;P) PrP(p nkPn PkKol x) F Ln(x;P) PrP(p nkPn PkF x) where Fis a class of functions for which the central limit theorem holds uniformly over F(ie a Donsker class) Research Day Talk September 27, 1013.
Formula (b) of Theorem 22 gives a useful inequality for the probability of an intersection Since P(A∪B) ≤ 1, we have P(A∩B) = P(A)P(B)−1 This inequality is a special case of what is known as Bonferroni’s inequality Theorem 23 If P is a probability function, then a. Exp ip xa ~ = X1 n=0 1 n!. X= b 2 p b 4ac 2a (mod p) Voila!.
0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 1,then E(y/x) = a)4 b)2 c) 8 7 d) 6 7 18 E(Y /X = x) is called a)regression curve of x on y b)regression. On a Win32 system, the following result will be printed 0018FF 18FF As you may see, the output results for "%p" and "%X" are rather similar This similarity leads to inaccuracy in the code and this, in turn, results in errors occurring when you port a program to a 64bit. N, 1 – p) = 1 – B ( n – x – 1;.
Then P(X=1) is equal to a)2 b) 2 0 c) 2 2 d) 2 4 15 If X ~ B (n, p),n = 4 and also P (X = 2) = 3P (X = 3),the value of p is a)1 b) 5 7 c) = 5 5 d)none of the above 16 If f (x, y) = 4xy;. For X ~ B(n, p), if V(X) = 24 and p = 04, then n = Maharashtra State Board HSC Science (Electronics) 12th Board Exam Question Papers 164 Textbook Solutions Online Tests 60 Important Solutions 39 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos & Videos 445 Time Tables 24. Exp ip xa ~ First we expand the exponential in a power series, and use the fact that the commutator is linear in its arguments x;.
Disjoint P(A and B) = 0 If two events are mutually exclusive, then the probability of either occurring is the sum of the probabilities of each occurring Specific Addition Rule Only valid when the events are mutually exclusive P(A or B) = P(A) P(B) Example 1 Given P(A) = 0, P(B) = 070, A and B. Apr 22, 21 · The problem with above solutions is, overflow may occur for large value of n or x Therefore, power is generally evaluated under modulo of a large number Below is the fundamental modular property that is used for efficiently computing power under modular arithmetic. N, p) ( ;.
BJ Thomas 1942–21 Singer of ‘Raindrops Keep Fallin’ on My Head’ dies at 78 By Harrison Smith NC mom, teens went into high school and assaulted a girl in her classroom, authorities. If X is a binomial random variable, then X ~ B (n, p) where n is the number of trials and p is the probability of a success To form a proportion, take X, the random variable for the number of successes and divide it by n, the number of trials (or the sample size) The random variable P′ (read "P prime") is that proportion, P ′ = X n. Ia ~ n x;.
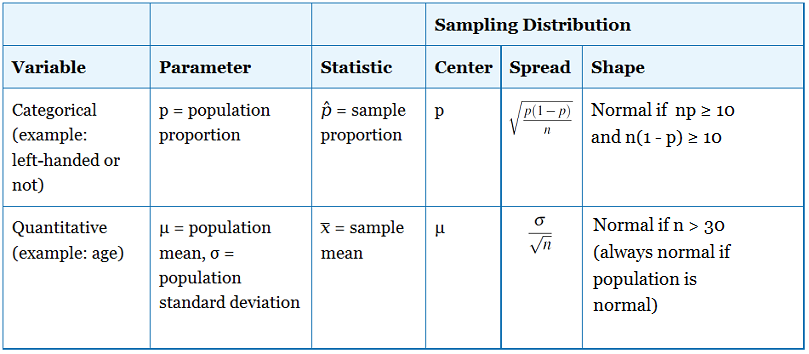
If P(AB) = P(A) Ex) Probability that card drawn in event A is a Jack given event B was the drawing of a red card Pr(AB) = Pr(𝐴∩𝐵) Pr (𝐵) = 2 52 26/52 = 1/13 It was stated that if A and B are mutually exclusive > (A∩B) = 0 then A and B are never independent Various examples were then given to demonstrate independent events. 2/10/12 Lecture 10 3 Sampling Distribution of Sample Proportion • If X ~ B(n, p), the sample proportion is defined as • Mean & variance of a sample proportion µ pˆ = p, σ pˆ = p(1 − p) / n size of sample count of successes in sample ˆ = = n X p. Apr 22, 12 · I guess I'm not really seeing what to do with the general case In a specific case like X^2,P^2 you can use your commutation relation to exchange X's and P's and you can get something like i*hbar*(2XP2PX) (or as an expression in terms of PX or XP alone, but I'm not really seeing how to generalize that or what combination of operators the answer should be expressed in.
Step 1 Enter the number of trials (n) Step 2 Enter the number of success (x) Step 3 Enter the Probability of success (p). Given that X ~ B(n,p), if n = 10, E(X) = 8, find Var(X) Maharashtra State Board HSC Commerce 12th Board Exam Question Papers 195 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 2470 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes & Videos 253 Time Tables 23 Syllabus. Pn x = i~npn 1 x for n 1.
0 as n !1 Let F n denote the cdf of X n and let F denote the cdf of X X n converges to X in distribution, written X n!d X, if, lim n F n(t)=F(t) at all t for which F is continuous Here is a summary Quadratic Mean E(X n ¡X)2!. As n !1 X n converges to X in probability, written X n!p X, if, for every †>0, P(jX n ¡Xj >†)!. Stepbystep solution Chapter Problem FS show all show all steps Step 1 of 5 The discrete distribution which can take only one value at a time representing as success or failure for a number of trials is known as Binomial Distribution.
0 for all †>0 In. The Binomial Distribution If a discrete random variable X has the following probability density function (pdf), it is said to have a binomial distribution P (X = x) = n C x q (nx) p x, where q = 1 p p can be considered as the probability of a success, and q the probability of a failure. Int *b = &a;.
= x(x1)(x2)1, and 0!. The answer is interesting and di cult It turns out that half of the numbers from 1 to p 1 have square roots, and the other half do not. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Given X B(n, p) If n = 10 and p = 04 , find E(X) and Var(X).
This yields (n 1) p1 ≤ x * ≤ (n 1) p 3 Suppose a particular state allows individuals filing tax returns to itemize deductions only if the total of all itemized deductions is at least $5000 Let X (in 1000s of dollars) be the total of itemized deductions on a randomly chosen form. Let x= P n i=1 a ib i, y= P m j=1 c jd j Then we have x y= i=1 a ib i m j=1 c jd j = i=1 a ib i m j=1 ( c j)d j 2IJ since it is a finite sum (n msummands) with summands obtained as products of elements from Iwith elements from J Now, let r2R Then we have rx= i=1 (ra i)b 1 2IJ since ra i 2I It follows that IJ/R Moreover. Then X is the first time we get the rth success, so that P{X > n} is the probability that the total number of successes in the first n trials is strictly less than r.
N, 1 p) = b(n x;. Given that mathX\sim \text{Binom}(n=4, p)/math, math\Pr(X = 2) = {4 \choose 2} p^2 (1p)^2 = 6p^2(1p)^2/math math\Pr(X = 3) = {4 \choose 3} p^3 (1p) = 4p. , ) (1 ) ,xx1 0,1, , n b x n p p p x xn 8 Example 31 Each of six randomly selected cola drinkers is given a glass containing cola S and one containing cola F The glasses are identical in appearance except for a code on the bottom to identify the cola.
X ∼ B (n, p) If values of mean and variance of X are 1 8 and 1 2 respectively then total number of possible values of X are A 5 4 B 5 5 C 1 2 D 1 8 Video Explanation Answer M e a n = n p = 1 8 V a r i a n c e = n p q = 1 2. If these conditions are met, then X has a binomial distribution with parameters n and p, abbreviated B(n,p) Example Suppose individuals with a certain gene have a 070 probability of eventually contracting a certain disease. The quadratic formula Every step works just as usual except we have the following Question How do we take square roots mod p?.
N, p) Hint At most x S’s is equivalent to at least ( n – x) F’sc What do parts (a) and (b) imply about the necessity of including values of p greater than 5 in Appendix Table A1?. Let X 1;;X n˘P The sample mean is X n= b n= 1 n X i X i and the sample variance is S2 n = ˙b 2 n = 1 n 1 X i (X i b n) 2 Some authors instead de ne the sample variance as ˙b 2 n = 1 n X i (X i b n) 7. How do you read the statement “ X ~ b(n, p)”?.
11 COMPUTING PROBABILITIES AND EXPECTATIONS BY CONDITIONING 127 Therefore, conditioned on X Y = n, X is Binomial(n, λ1 λ1λ2 Example 112 Let T1,T2 be two independent, Exponential(λ) random variables, and let S1 = T1, S2 = T1 T2Compute fS1(s1S2 = s2) First,. B L H B X K P X R I W A G B N PHOENIX, ARIZONA PHOENIX, ARIZONA N O T E C h a rt n o t to s c a le W 1 1 3. Apr 05, 13 · int a = 10;.
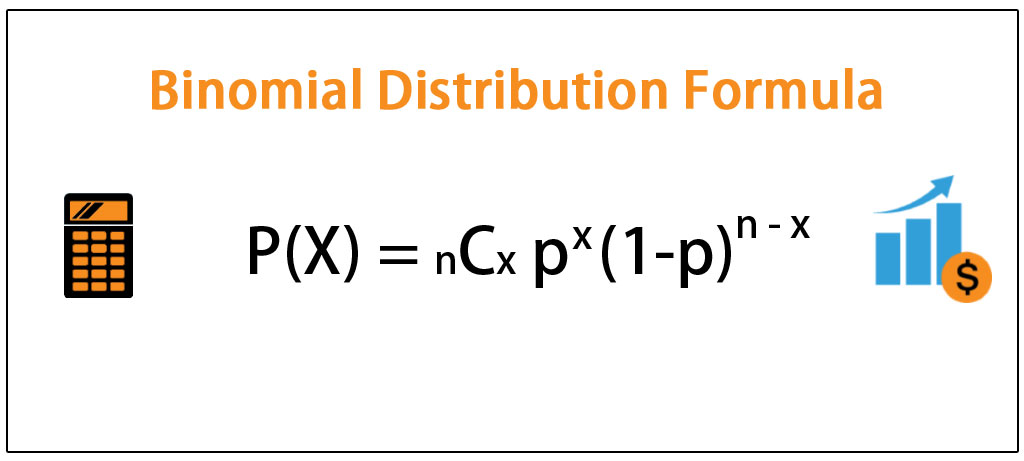
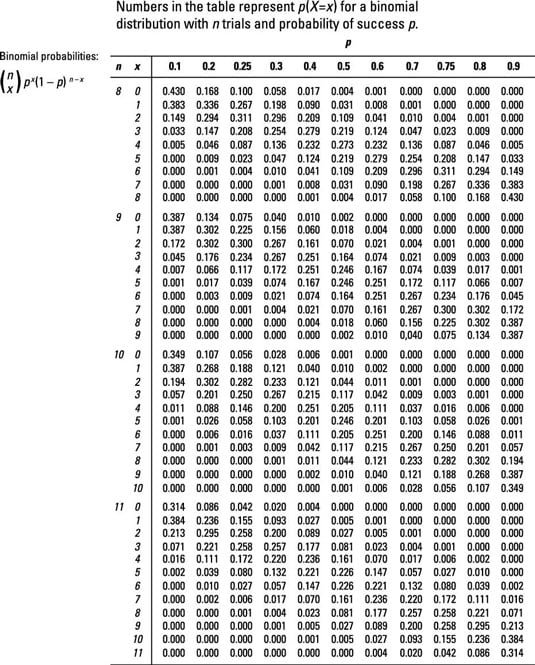
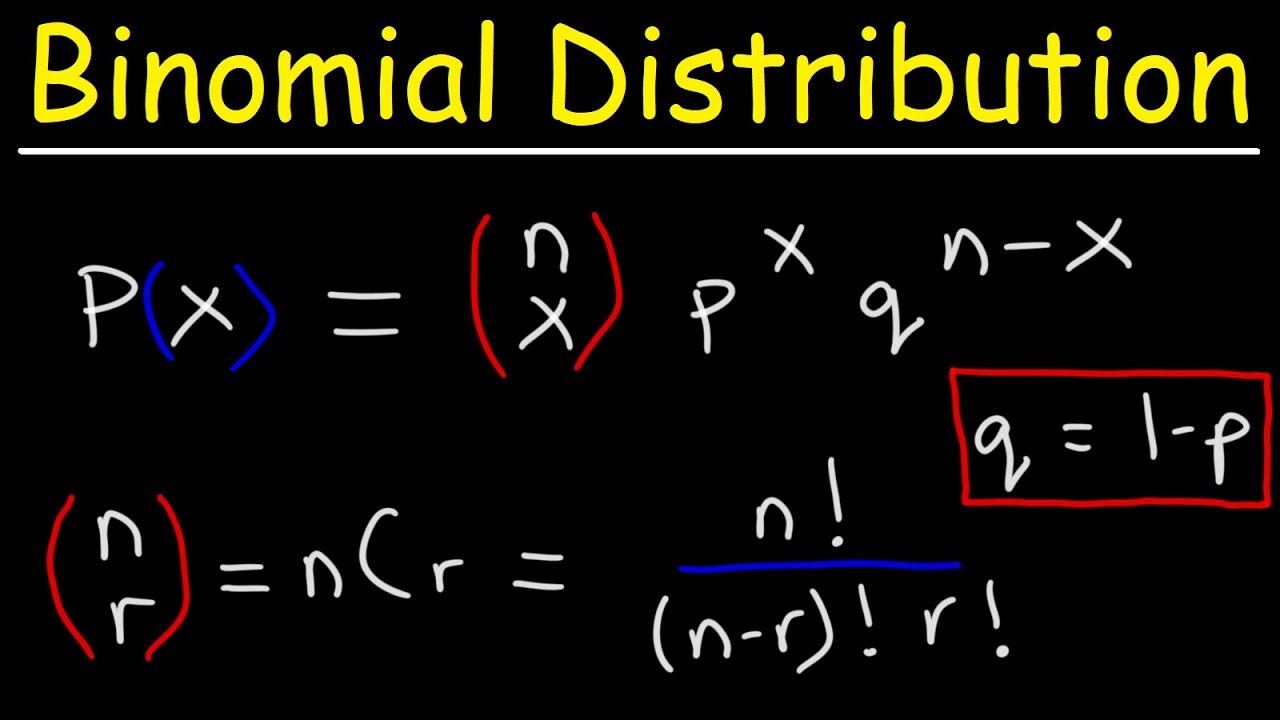
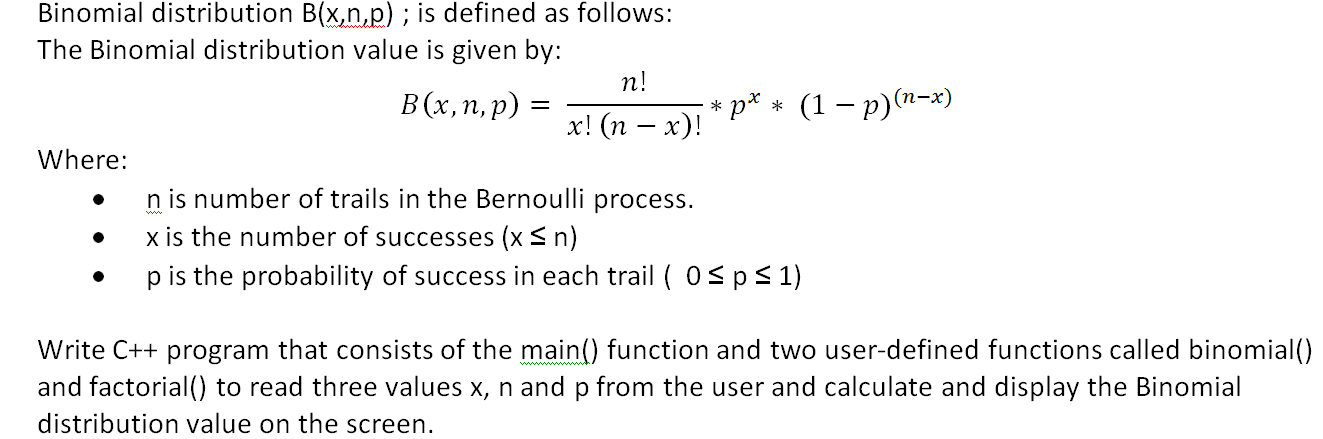
X d J N J K e P N f ` LK f b LK f J K b I c N I b _ g ^ e W018MS0006O Submission Type Official Approval Date11/29/18 Superseded SPA ID WA. Let X be Binomial(n, p) The probability of having x successes in n trials is (where x!. So 0≤X ≤n Formula for Binomial Probabilities For a binomial random variable X that represents the number of successes in n trials with success probability p, the probability of obtaining x successes is 𝐏(𝐗=𝐱)= 𝐂𝐱𝐩𝐱( −𝐩)𝐧−𝐱 𝐧 where x = 0,1,2,3,,n Note Cx= 𝑛!.
Jan 27, · we have to prove P (A ∩ B) ⊂ P (A) ∩ P (B) & P(A) ∩ P(B) ⊂ P ( A ∩ B) Let a set X belong to Power set P(A ∩ B) ie X ∈ P ( A ∩ B ) As set X is in the power set of A ∩ B, X is a subset of A ∩ B because power set is the set of all subsets ⊂ Subset A ⊂ B (all elements of set A in set B) Thus, X is a subset of A ∩ B i. 1 Sum of Independent Binomial RVs • Let X and Y be independent random variables X ~ Bin(n 1, p) and Y ~ Bin(n 2, p) X Y ~ Bin(n 1 n 2, p) • Intuition X has n 1 trials and Y has n 2 trials o Each trial has same “success” probability p Define Z to be n 1 n 2 trials, each with success prob p Z ~ Bin(n 1 n 2, p), and also Z = X Y. O b N p b J Y z X e A6/2 I v B \ J n B 11 N3 17 Ђ ꂽ ɏ ł ɗ Ă Ǝv ܂ B ʃc A W ͒ ~ B h グ ɑS ͂ B X ^ b t ɎR ̂ ̍D ȕ } B k Ƃقړ R ̂ ܂ B.
FREE Gunna x Pop Smoke x Young Thug Type Beat "24 Karats" (prod stardustszn x hoops)💰 Purchase Here https//bstars/44ef7d624📑 IMPORTANTThis beat is f.
Uncertainties And Error Analysis

Example For Binomial Distribution Binomial Distribution Statistics Math Pinterest Statistics
Normal Probability Distributions Online Presentation
P Bnpx のギャラリー

Showing That E X Sum Mathbb P X Ge N Mathematics Stack Exchange
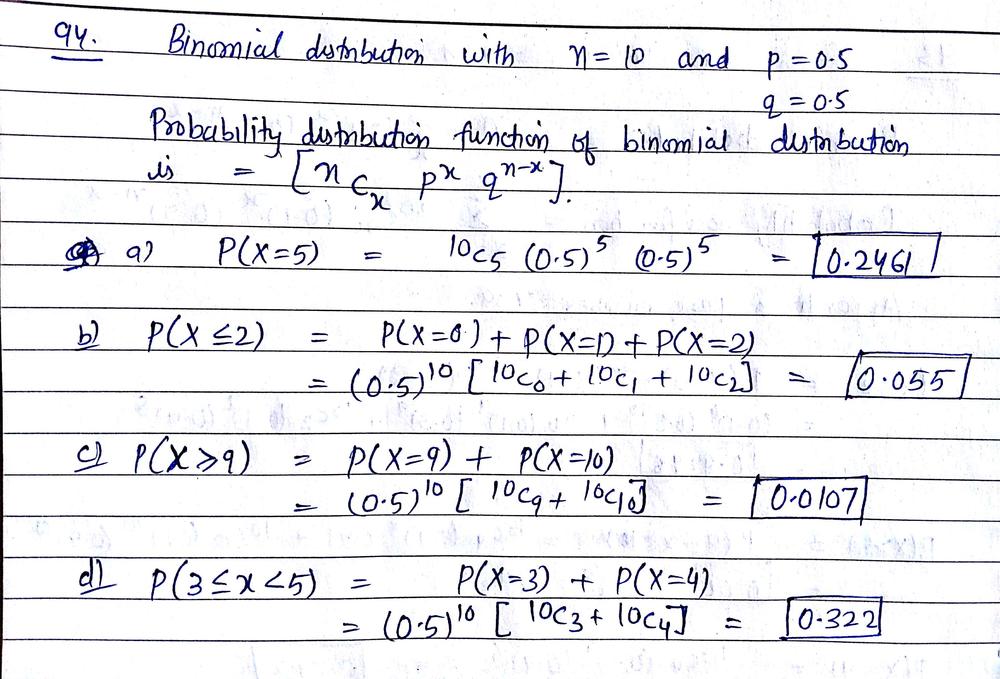
The Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With N 10 And P 0 5 Determine The Following Probabilities A P X 5 B P X 2 C P X 9
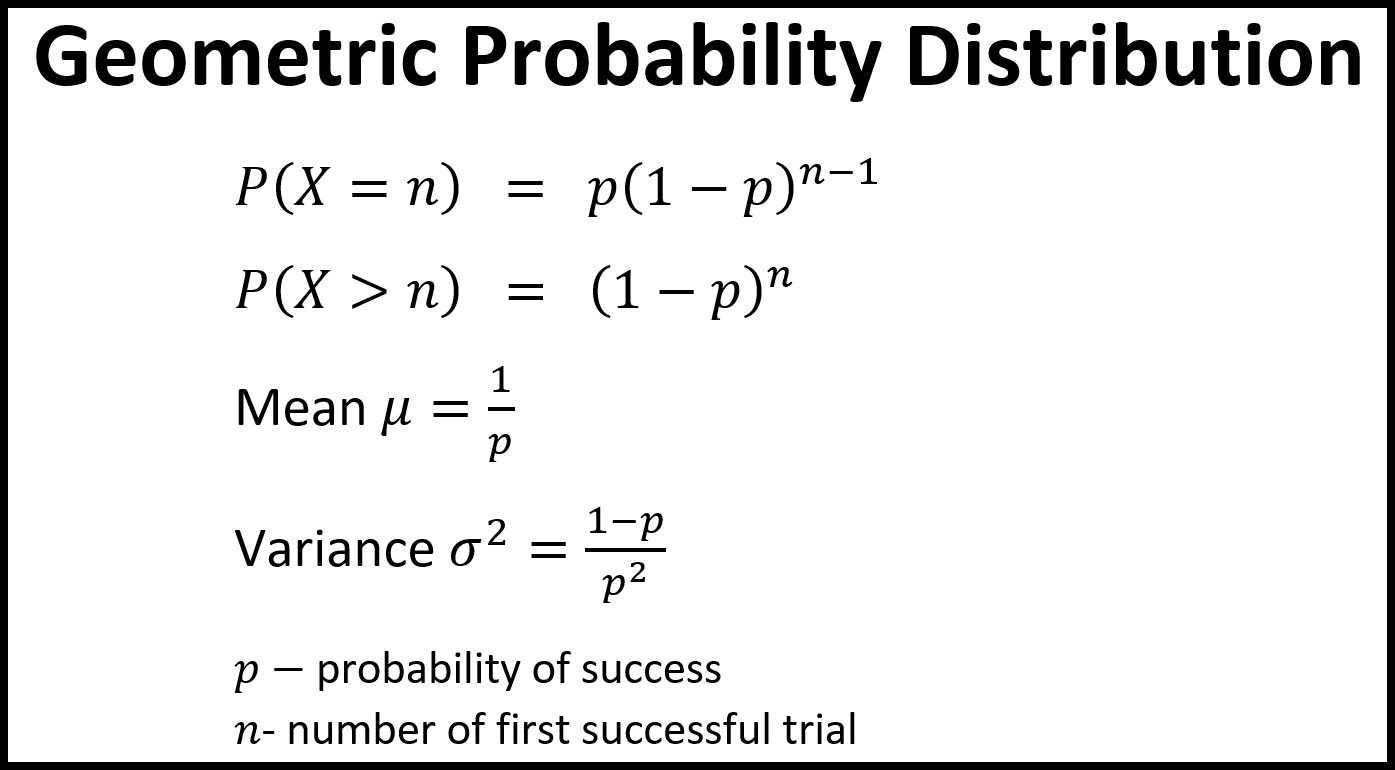
Geometric Distribution Andymath Com
Binomial Distribution Six Sigma Study Guide

If The Mean And The Variance Of A Binomial Variate X Are 2 And 1 Respectively Then Probability That X Takes A Value Greater Than Or Equal To One Is

Example 34 Find Mean Of Binomial Distribution B 4 1 3
Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch2annotated Pdf
Q Tbn And9gcsigbptwg5wf5klju7ygqr3hljhihl9vw Y60i7ot8n8ljtzypr Usqp Cau
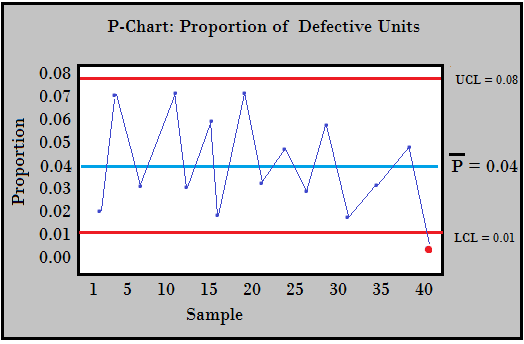
P Chart P Control Chart Statistics How To
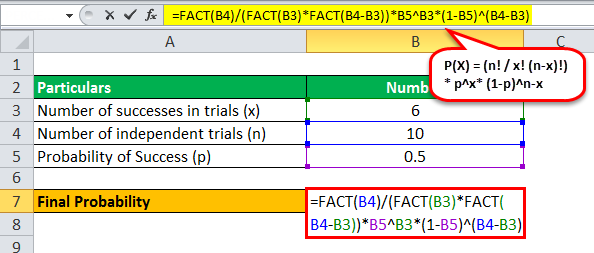
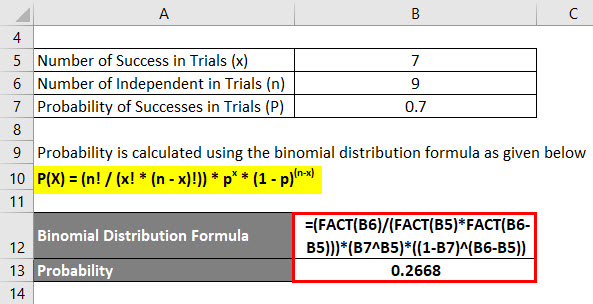
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example
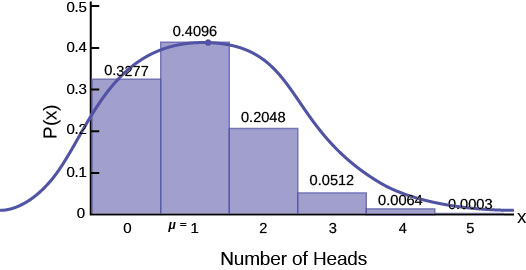
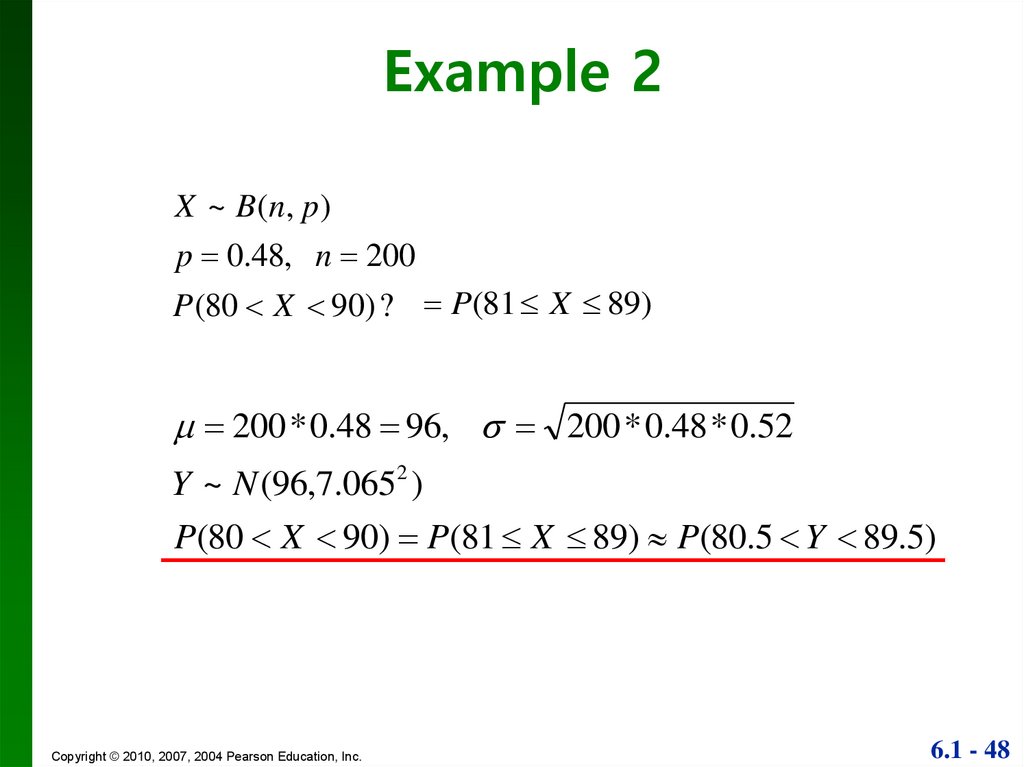
Estimating The Binomial With The Normal Distribution Introductory Business Statistics
1

The Mean And Standard Deviation Of Binomial Probability Distributions
Www Le Ac Uk Users Dsgp1 Courses Mathstat 2binome Pdf
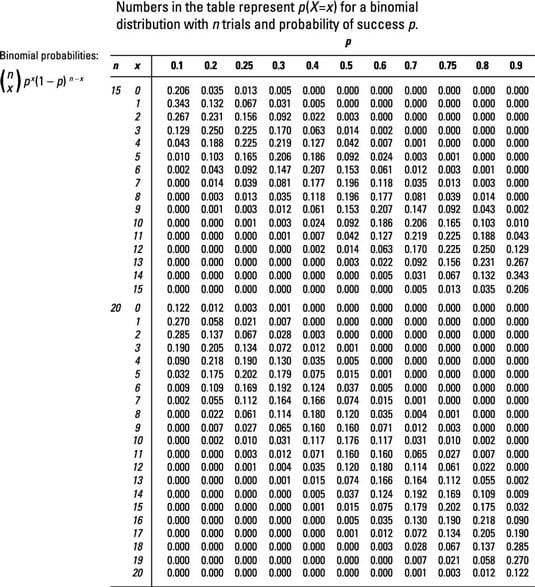
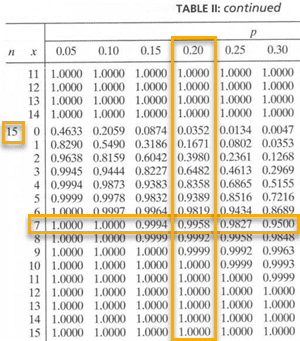
Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies

Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Ma Economics Karachi University

Applying Statistics In Python Part I By Black Raven James Ng Towards Data Science

Binomial Distribution

Given X B N P If P 0 6 E X 6 Then The Value Of Var X I
Solved 1 The Probability Mass Function Pmf Or Probabil Chegg Com
Elements Of Probability Lecture 3 Online Presentation
Www Jstor Org Stable
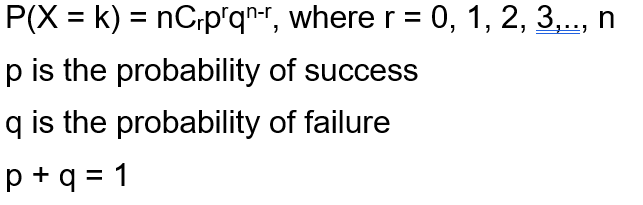
Binomial Distribution In R Programming Geeksforgeeks
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example

Sampling Distribution Of Sample Proportion Part 1 Video Khan Academy
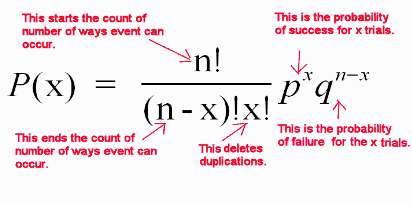
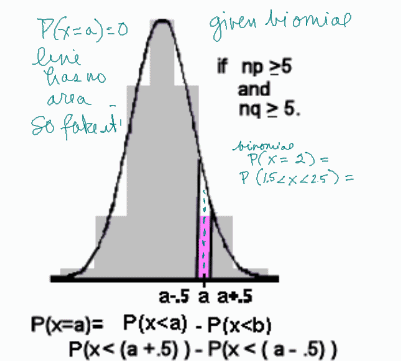
Binomial Formula Explained
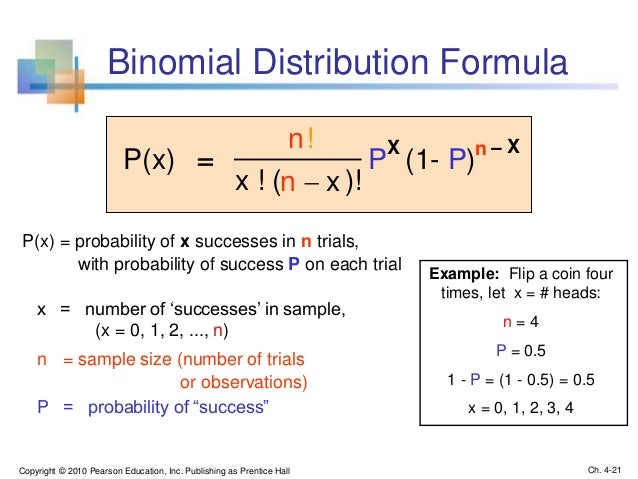
Chap04 Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distribution

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia

The Binomial Distribution Maple Programming Help

Suppose That X Is A Binomial Random Variable With 0 And P 0 4 Approximate The Following Probabilities A P X 70 B P 70 X 90 C P X 80 Homework Help And Answers Slader
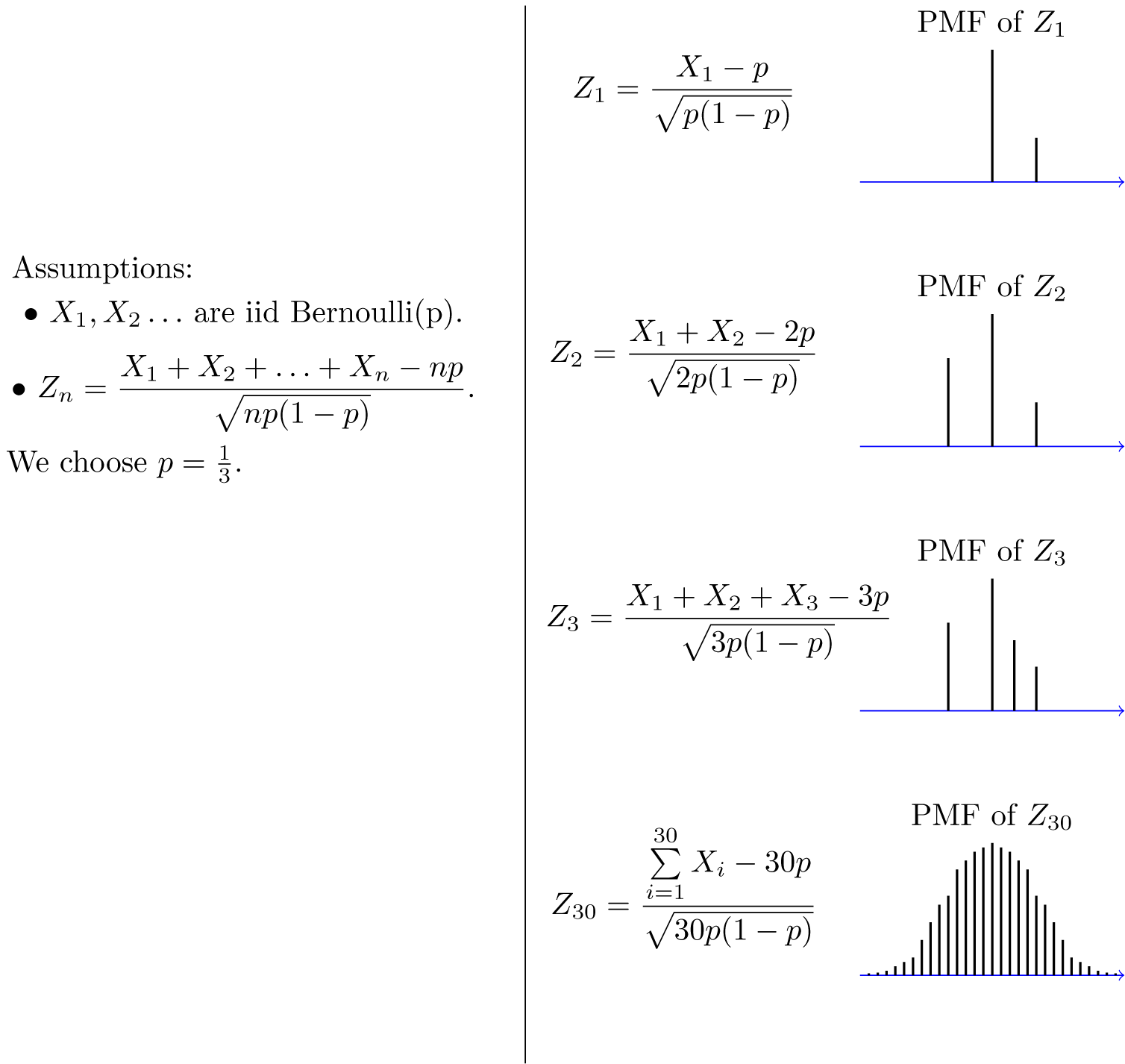
Central Limit Theorem

File P Np Np Complete Np Hard Svg Wikimedia Commons

Discrete Probability Distribution

Binomial Distribution Definition Properties Derivation Formulas Solved Example Problems
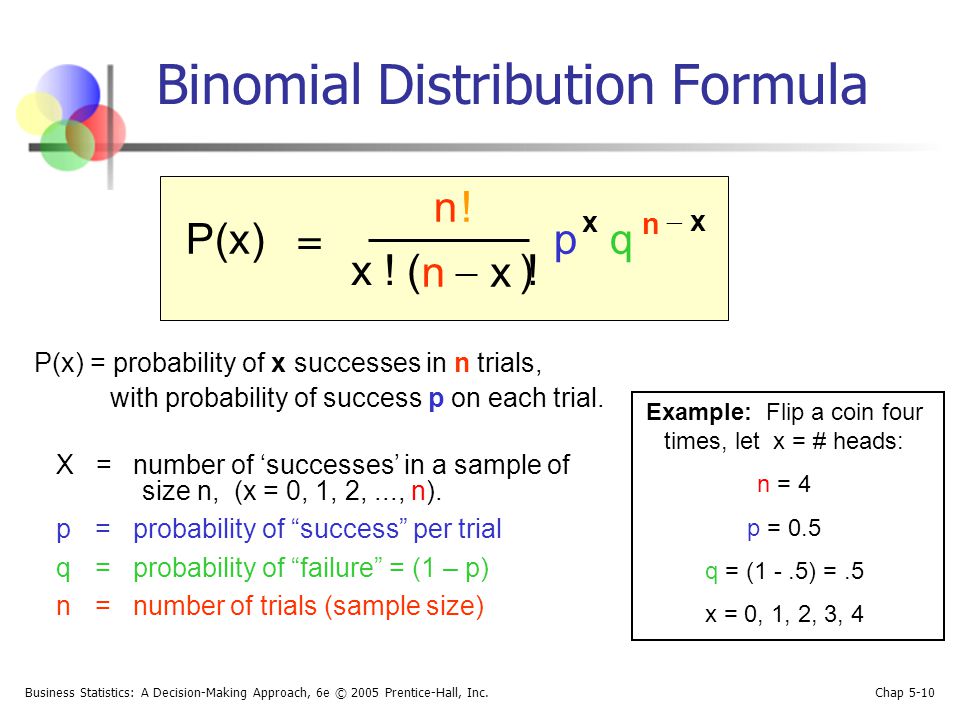
Chapter 5 Discrete And Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Download
Www Stat Auckland Ac Nz Fewster 325 Notes Ch2annotated Pdf

The Binomial Distribution Ppt Video Online Download

The Binomial Distribution Maple Programming Help
Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies

Example 31 If A Fair Coin Is Tossed 10 Times Find Probability

If X Follows A Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 6 And P
Chapter 6
P Values

Gnuplot Demo Script Prob Dem

Binomial Distribution Definition Formula Conditions Characteristics Solved Example Problems
The Binomial Distribution
Ocw Mit Edu Courses Economics 14 30 Introduction To Statistical Methods In Economics Spring 09 Assignments Mit14 30s09 Sol Pset04 Pdf
Chapter 5 4 Bernoulli And Binomial Distribution Ppt Video Online Download
Http Www Stat Rutgers Edu Hcrane Teaching 5 Lectures Chapter12 Pgf Pdf
1

Continuity Correction Filling The Cracks In The Normal Approximation To The Binomial Dawn Wright Ph D
Probability And Distributions Bernouilli Trial Binomial Distribution
Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Statistics Binomial Distribution Pdf

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
Madasmaths Com Archive Maths Booklets Statistics Binomial Distribution Pdf

Conditional Distribution

Binomial Distribution Examples Problems And Formula
Binomial Distribution Six Sigma Study Guide
Http Homepages Gac Edu Holte Courses Mcs256 Documents Probab Summation Pdf

Understanding Bernoulli And Binomial Distributions By Valentina Alto Towards Data Science
Sampling Distribution Of The Sample Mean X Bar Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida
Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard Deviation Youtube

Normal Approximation To The Binomial Statistics How To
Normal Distribution Binomial Distribution Poisson Distribution
Solved Binomial Distribution B X N P Is Defined As Fo Chegg Com
P7 Binomial Computations Data Analysis And Probability For Teachers
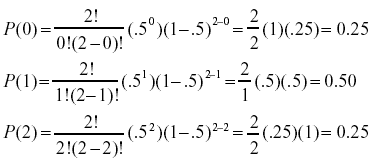
Binomial Distribution

Lesson 8 1 Discrete Distribution Binomial Knowledge Objectives

If X Follows Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 5 P A N D

Solved Possibly Useful Formulas Binomial P X Nx Px 1 Chegg Com

Binomial Distribution In Quantitative Techniques For Management Tutorial 31 May 21 Learn Binomial Distribution In Quantitative Techniques For Management Tutorial 9947 Wisdom Jobs India
Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template
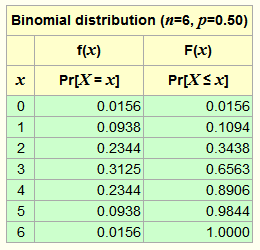
Binomial Distribution Calculator
Binomial Distribution Workout For N 18 P 0 36 X 12
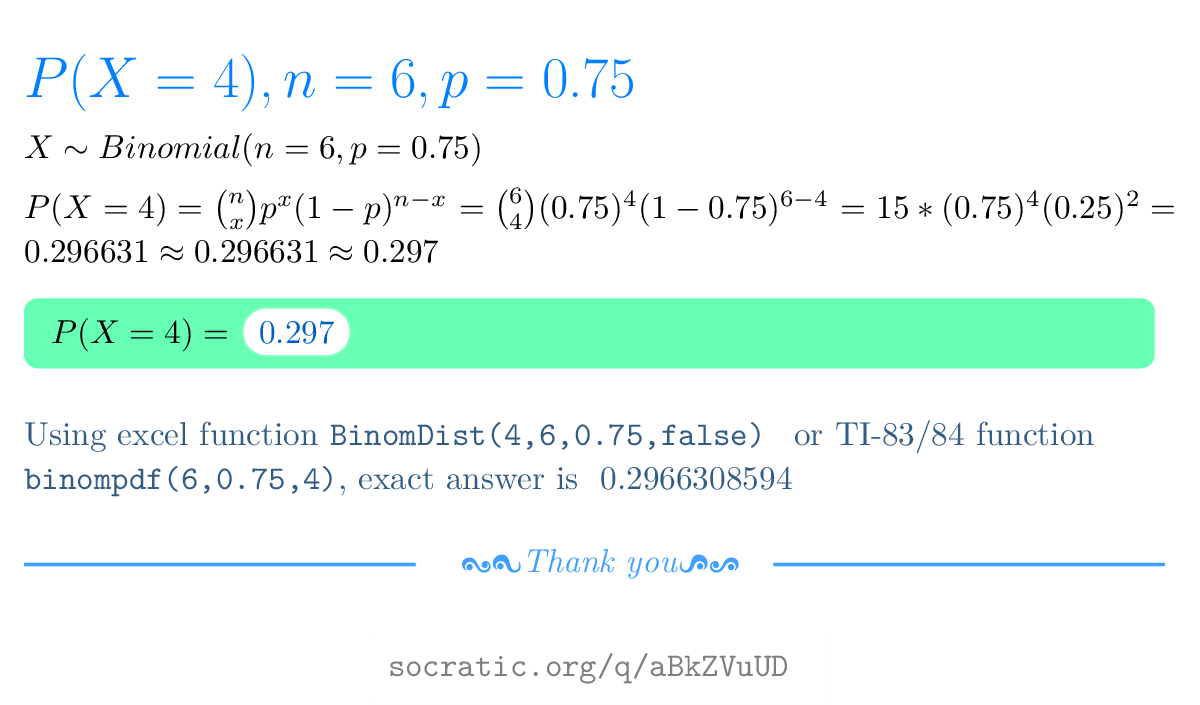
How Do You Use The Binomial Probability Formula To Find The Probability Of X Successes Given The Probability P Of Success On A Single Trial For N 6 X 4 P 0 75 Socratic
X Is A Binomial Variable Such As That 2p X 2 P X 3 And Mean Np Of X Is Known To Be 10 3 What Would Be The Probability That X Assumes At Most The
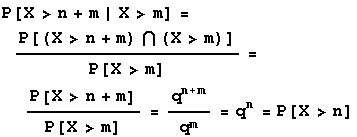
4 Discrete Rand Vars
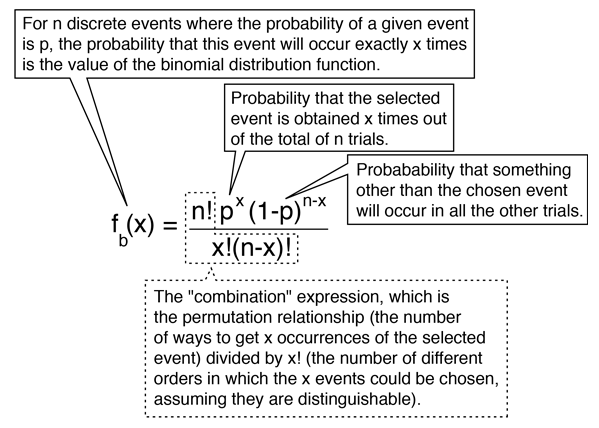
Distribution Functions
Http Faculty Wwu Edu Benyia Papers Benyi Manago Pdf
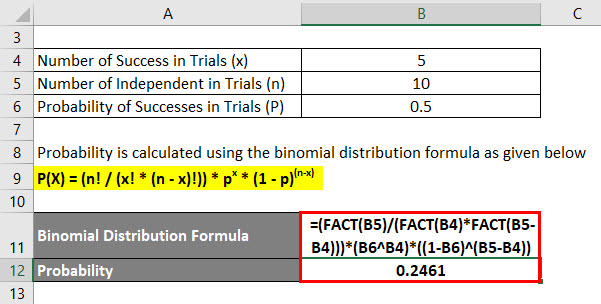
Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template

Binomial Distribution Calculator
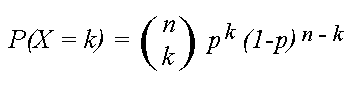
The Binomial Distribution
Www Napavalley Edu People Dvandeusen Documents Math 232 online 232 binomial poisson in statcrunch Pdf
1

Binomial Probabilities On The Ti Or 84 Calculator Mathbootcamps

Is The Maximum Of A Probability Distribution Function Of A Binomial Distribution Always The Expected Value Mathematics Stack Exchange

Calculating Binomial Probabilities With The Ti 84 Youtube

P Hat Calculator Calculator Academy

6 Binomial Distribution

If K X X 2 And P X K X N What Is The Value Of N Pleaseee Help Asap I Will Give Brainly Com

Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy

Commutator Of And

Binomial Distribution From Wolfram Mathworld
Www3 Nd Edu Rwilliam Stats1 X13 Pdf

Chapter 8 Binomial And Geometric Distributions N 8
Www Everettcc Edu Files Programs Academic Resources Transitional Studies Support Tutoring Center Math H401 Binomial And Normal Ti 84 Pdf
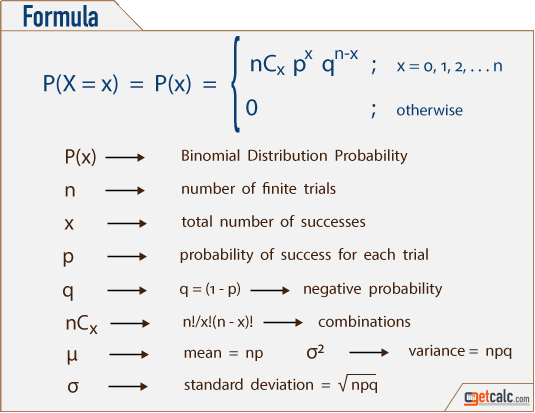
Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator
General Statistics Ch 5 Hw Flashcards Easy Notecards
Binomial Formula Explained

Probability Distributions




