P Xn
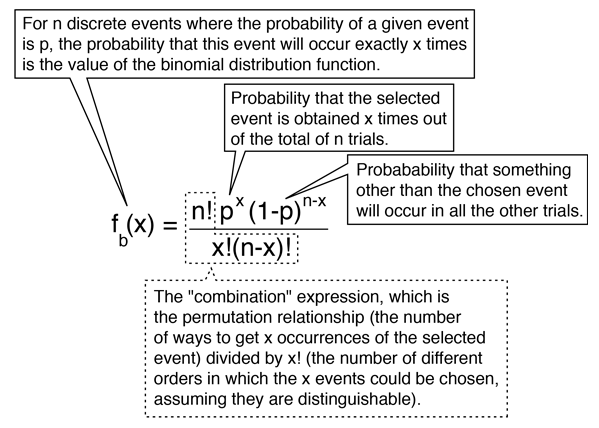
Table A Binomial Probabilities P(X = x) = nCx(px)(1 p)nx P A value of 0000 indicates that the probability is 0000 when rounded to three decimals places The actual probability is slightly greater than 0 Table A Binomial Probabilities P(X = x) =.

P xn. X n x n − px (1p) nx VAR(X) = np(1p) = 3* 03 * 07 = 063 SD(X) = np(1p) Calculations shown for Binomial (n=3, p=03) = 0794 Note this is equivalent to counting success = 1 and failure = 0. = P(X n = 2) = 2 Consider the random walk W = (Wn)n>o on Z where Wn=W X1 , and X1, X2, are independent, identically distributed random variables with 2 3 P( = 1) = P( = 1) = 7 7 We define the hitting times Tk = inf{n > 0 Wn = k}, where infØ = mo. Section 13 KolmogorovSmirnov test Suppose that we have an iid sample X1,, with some unknown distribution P and we would like to test the hypothesis that P is equal to a particular distribution P0, ie decide between the following hypotheses.
Var(X) = E(X2)¡E(X)2 = Np(1¡p) Then we deduce p = 1¡ E(X2)¡E(X)2 E(X);. Homework 4 Solutions Math 171, Spring 10 Please send corrections to henrya@mathstanfordedu 265 Let P 1 n=1 a n and P 1 n=1 b n be absolutely convergent series Prove that the series P 1 n=1 p ja. X N X X, Ciudad de México 2,111 likes · 247 talking about this https//wwwyoutubecom/channel/UCOrA6rojl4dypm2rJ7qvw.
P X n1 = i 1 X n = i = 3 8;. Lecture 18 Section 103 Limit of Sequence Section 104 Some Important Limits Jiwen He 1 Limit of Sequence 11 Properties of Limits Properties of Limits. ♡Life is painful♡ (@pxin) on TikTok 11K Likes 12K Fans Watch the latest video from ♡Life is painful♡ (@pxin).
2 Answers2 You can think of a random variable X as a function that maps events to real numbers, ie, X Ω → R The expression P ( X = n) denotes the probability that a random variable X has value n Formally, it is a short form for the probability of the event { ω X ( ω) = n }, ie, P ( X = n) = P. Given {eq}X \sim Binomial(n, p) {/eq} {eq}x {/eq} is a sample from the given binomial population We have to check whether the sample proportion {eq}\hat{p} = \dfrac{x}{n} {/eq} is unbiased for. The 07 is the probability of each choice we want, call it p The 2 is the number of choices we want, call it k And we have (so far) = p k × 03 1 The 03 is the probability of the opposite choice, so it is 1−p The 1 is the number of opposite choices, so it is n−k Which gives us = pk(1p)(nk) Where.
P(X=x) = ( n over x) p x (1p) nx The teacher has given them the formula but not taught them how to apply it or understand it When asked the teacher responds that he 'only teaches at the highest level'!!. 2 If X ∼ binomial(n,p), then X/n→P p Different sequences of convergent in probability sequences may be combined in much the same way as their realnumber counterparts Theorem 74 If X n →P X and Y n →P Y and f is continuous, then f(X n,Y n) →P f(X,Y) If X = a. P x(1−p)n−x = x=1 n!.
Then p = P(X = 1) = P(A) is the probability that the event A occurs For example, if you flip a coin once and let A = {coin lands heads}, then for X = I{A}, X = 1 if the coin lands heads, and X = 0 if it lands tails Because of this elementary and intuitive coinflipping example, a Bernoulli rv is sometimes referred to as a coin flip, where p is. We can similarly define order in probability X n = o p(n−r) if and only if nrX n = o p(1);. Here is a formal definition of convergence in distribution Convergence in Distribution A sequence of random variables X 1, X 2, X 3, ⋯ converges in distribution to a random variable X, shown by X n → d X, if lim n → ∞ F X n ( x) = F X ( x), for all x at which F X ( x) is continuous Example.
The variance of X/n is equal to the variance of X divided by n², or (np(1p))/n² = (p(1p))/n This formula indicates that as the size of the sample increases, the variance decreases In the example of rolling a sixsided die times, the probability p of rolling a six on any roll is 1/6, and the count X of sixes has a B(, 1/6) distribution. · p(1)=0027 For a Binomial Random Variable X with parameters n and p, then, P(X=x)=p(x)=""_nC_xp^nq^(nx), x=0,1,2,,n Here, n=3, p=09, x=1 Also, q=1p=109=01. Hence, P(X¯ n −µ < †) = 1 −P(X¯n −µ ≥ †) = 1 − σ 2 n†2 → 1, as n → ∞ ⁄ The weak law of large numbers (WLLN) quite elegantly states that under general conditions, the sample mean approaches the population mean as n → ∞ Example (Consistency of S2) Suppose we have a sequence X1,X2, of iid random variables with EXi = µ and VarXi = σ2 < ∞.
Looking for online definition of P/N or what P/N stands for?. P/N is listed in the World's largest and most authoritative dictionary database of abbreviations and acronyms The Free Dictionary. • If p = 1/2, the random walk is symmetric • The symmetric random in d.
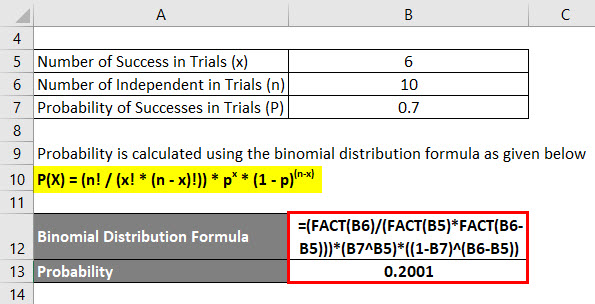
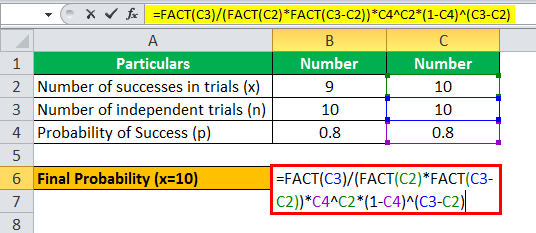
X0 = 0 and P 1= 1 = p, P 1= −1 = 1−p Example If counts the number of successes minus the number of failures for a new medical procedure, could be modeled as a random walk, with p the success rate of the procedure When should the trial be stopped?. Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history. Let X be Binomial(n, p) The probability of having x successes in n trials is (where x!.
= x(x1)(x2)1, and 0!. P X n1 = i X n = i = 1 4 Denote T k= inffn 0 X n = kg Let a;b 1 be xed integer numbers Compute P T a. Pages Public Figure Artist P L X W X N English (US) · Español · Português (Brasil) · Français (France) · Deutsch Privacy · Terms · Advertising · Ad Choices · Cookies ·.
1 P(x=3) 2 P(x=1 or x=3) 3 P(x=0 or x=1 or x=2) 4 P(x 3) 5 P(x > 2) The answers follow 1 P(x=3) = 4/16 = 1/4 = 25 2 P(x=1 or x=3) = 4/16 4/16 = 8/16 = 1/2 = 5 3 P(x=0 or x=1 or x=2) = 1/16 4/16 6/16 = 11/16 = 6875 4 P(x 3)= 11/16 = 6875, the same as question 3 5 P. 0913 · (because px xp = p,x) and results in the additional term to the right of the first term This is a very common gambit in dealing with commutators It is the only "legal" way to switch the order of noncommuting operators. N = E(X)2 E(X)¡E(X2)E(X)2 Thus, replacing E(X) by Pn i=1 Xi=n and replacing.
4 Here's a hint based upon the dependence upon n in your answer, a proof by induction is probably the way to go Your induction hypothesis should be x, p n = i n p n − 1 and you want to use this property to prove that x, p n 1 = i ( n 1) p n To see how these are related, note that. In this lecture, we look at deviation inequalities, ie, bounds on this kind of probability of deviation We need to exploit information about the random variables 1 Using moment bounds Markov (first), Chebyshev (second) 10 2 Using moment generating function bounds, for sums of independent. 1 Suppose X1;X2;¢¢¢ ; are iid random variables following B(N;p) distribution, where both N and p are unknown parameters Estimate them using the method of moments Solution By assumption we have for any X = X1;¢¢¢ ; E(X) = Np;.
P(x) = X n p(n)xn = Y1 i=1 1 1 xi = 1 (1 x)(1 x2)(1 x3) This in nite product need not disturb us If we want a particular coe cient p(n) we need only multiply out those factors involving xto a power nor less, and there nitely many of these Thus. B(x;n,p)= n x px(1−p)n−x This is the probability of having x successes in a series of n independent trials when the probability of success in any one of the trials is p If X is a random variable with this probabilitydistribution, E(X)= x=0 x n x px(1−p)n−x = x=0 x n!. = 1) E(X) = np = 3* 03 = 09 P(X=x)=!( )!!.
4 The pn junction 41 Electrostatic solution of the pn homojunction 411 Approximate solution using the full depletion approximation a) Abrupt pn junction An easy way to derive the depletion layer widths in a pn diode is to treat it as a combination of two Schottky diodes, one with an ntype semiconductor and an other with a ptype. Please help Well, the teacher is not 'teaching' if that is his response. And X n = O p(n−r) if and only if nrX n = O p(1) Proposition 1 if X n and Y n are random variables defined in the same probability space and a n > 0, b n > 0, then (i) If X n = o p(a n) and Y n = o p(b n), we have X nY n = o p(a nb n) X n Y n = o p(max(a n,b n)) X nr = o p(ar n) for r > 0 (ii.
In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomialAccording to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial (x y) n into a sum involving terms of the form ax b y c, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with b c = n, and the coefficient a of each term is a specific positive. 1422 · I guess I'm not really seeing what to do with the general case In a specific case like X^2,P^2 you can use your commutation relation to exchange X's and P's and you can get something like i*hbar*(2XP2PX) (or as an expression in terms of PX or XP alone, but I'm not really seeing how to generalize that or what combination of operators the answer should be expressed in. So when n gets large, we can approximate binomial probabilities with Poisson probabilities Proof lim n!1 µ n x ¶ px(1¡p)n¡x = lim n!1 µ n x ¶µ ‚ n ¶x µ 1¡ n ¶n¡x n!.
NCx= n!/x!(nx)!Each of 4 people is presented with gourmet coffee and ordinary coffee and asked to identify the gourmet coffee None of the 4 can really tell the difference and are merely guessing (Hint Any guess with 2 choices has what % chance of working out?) What is the probability that exactly 2 of the 4 correctly identify the gourmet coffee?. TEL FAX ・ス・ス・スA・スN・スZ・スX copyright©15 Frontier of life all rights reserved ・スT・スu・スi・スr・スQ・ス・スV・ス・ス・ス・ス ・スv・ス・ス・スC・スo・スV・ス・ス・ス・ス・スV・ス staffhtml・スヨの・ソス・ス・ス・スN staff1html・スヨの・ソス・ス・ス・スN wearehtml・スヨの・ソス・ス・ス・スN. Binomial Formula nCx p x (1p) nx ;.
Theorem If Xi ∼ exponential(λi), for i = 1,2,,n, and X1,X2,, are mutually independent random variables, then min{X1,X2,,} ∼ exponential i=1 λi ProofThe random variable Xi has cumulative distribution function FX i (x) = P(Xi ≤ x) = 1−e−λ ix i x > 0 for i = 1,2,,n Let the random variable Y = min{X1,X2,,}Then the cumulative. Home Trending History Get YouTube Premium Get YouTube TV Best of YouTube Music Sports Gaming. P X n p, which is the stated inequality because p−p/q=1 6 Submartingale upcrossing inequality Let{X n} beasubmartingale,andforrealnumbers a.
P xn = jxj;. \ i* { M A j. P(X¯ n ≥ µ ǫ)?.
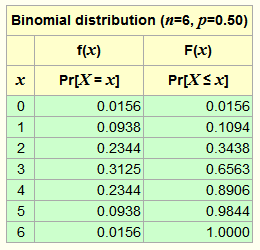
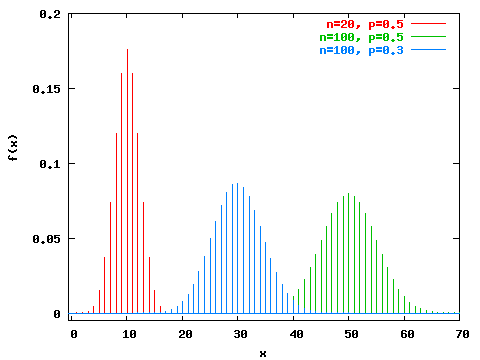
If nis even Properties of Inequalities If a. N * P C G X ~ N N 19 316;. Convergence in Distribution Theorem Let X » Bin(n;p) and let ‚ = np, Then lim n!1 PX = x = lim n!1 µ n x ¶ px(1¡p)n¡x = e¡‚‚x x!.
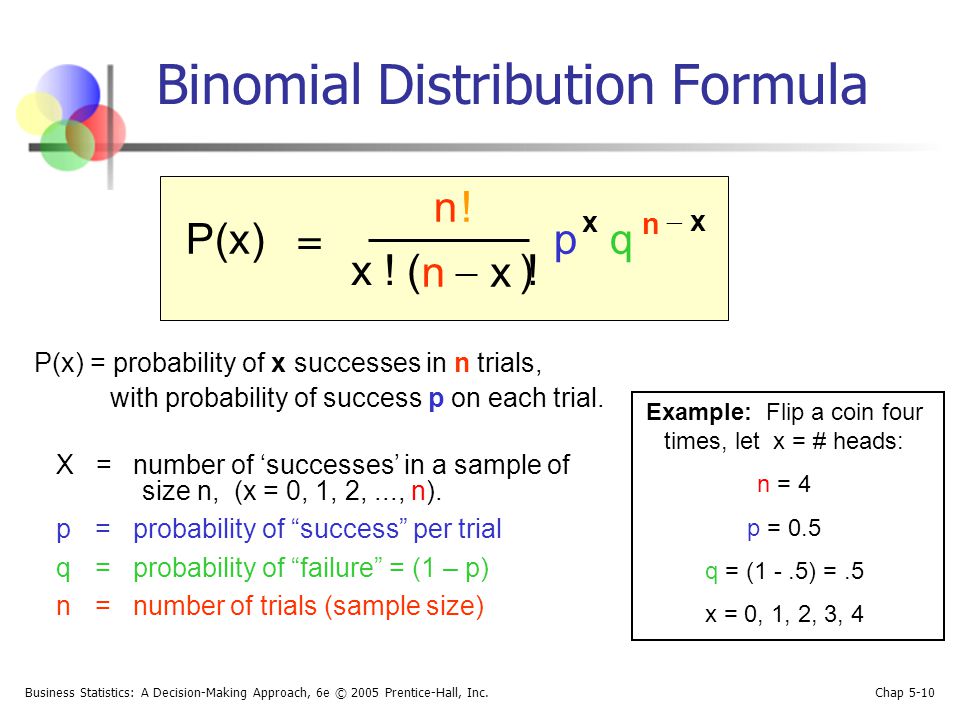
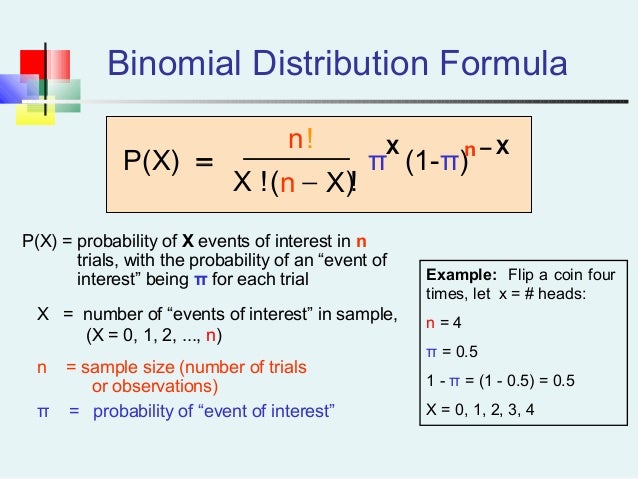
P(x) = nCx px (1p)nx p = probability of "success" n = number of trials, or the sample size x = the number of "successes" in the probability we are trying to calculate In general, it is easiest to define the "success" as what we are counting in the desired probability Note the mean and variance of this distribution are μ = np and σ2 = np(1p). P(X = n) = (1−p)n−1p where n ∈ {1,2,} Note that X∞ n=1 P(X = n) = X∞ n=1 (1−p)n−1p = X∞ k=0 (1−p)kp = p X∞ (1−p)k As this last sum is a geometric series, and 1−p < 1, X∞ j=n P(X = n) = p 1 1−(1−p) = p 1 p = 1 The cumulative distribution function is given by P(X ≤ n) = 1−P(X > n) = 1− X∞ k=n1 (1−p.

Normal Approximation To The Binomial Statistics How To

New Page 1
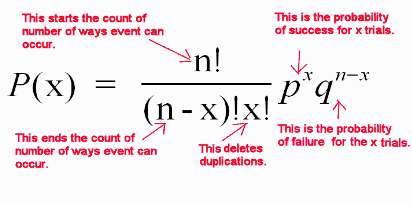
Binomial Formula Explained
P Xn のギャラリー

Pxn Pxn V9 Gaming Racing Steering Wheel Pedal Vibration Racing Game Controller For Pc Ps Xbox One For Ns Steering Wheels Video Games Wheels Aliexpress

Understanding And Choosing The Right Probability Distributions With Examples By Kessie Zhang Towards Data Science

Understanding And Choosing The Right Probability Distributions With Examples By Kessie Zhang Towards Data Science
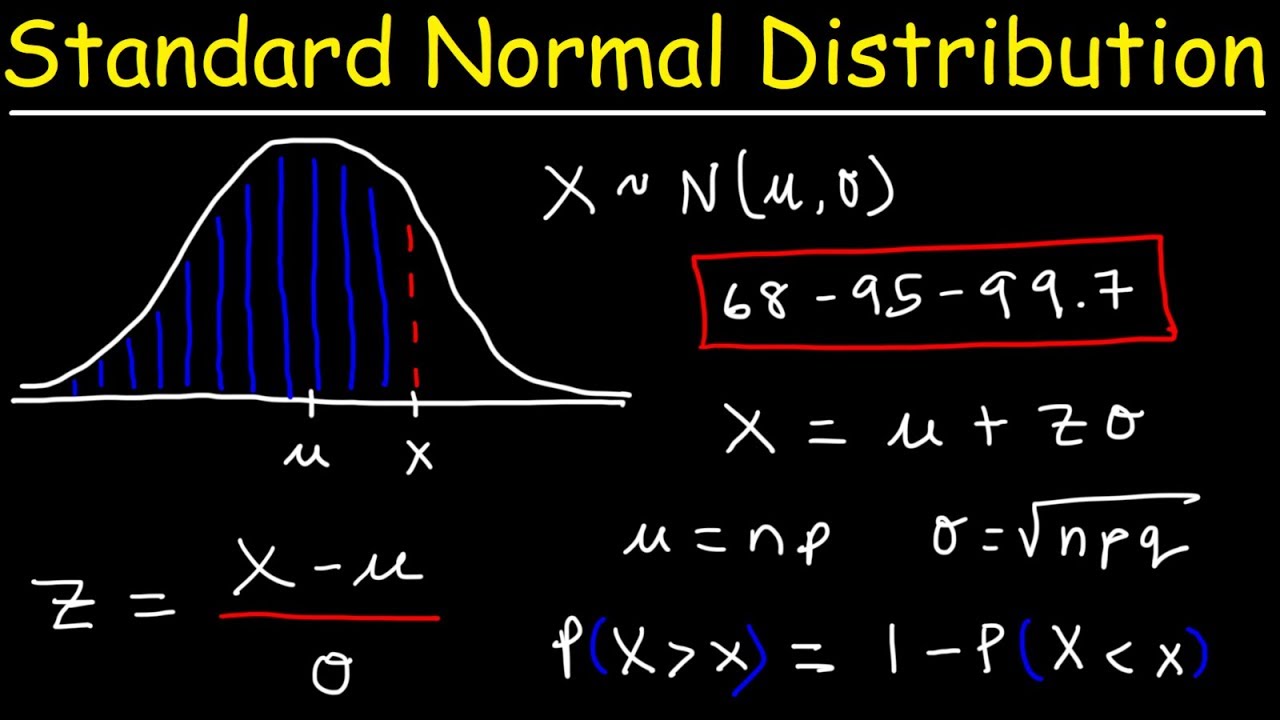
Probability Exponential Distribution Problems Youtube

If X Has A Binomial Distribution B N P With Parameters N And P Such That P X 2 P X 3 Then E X The Mean Of Variable X Is
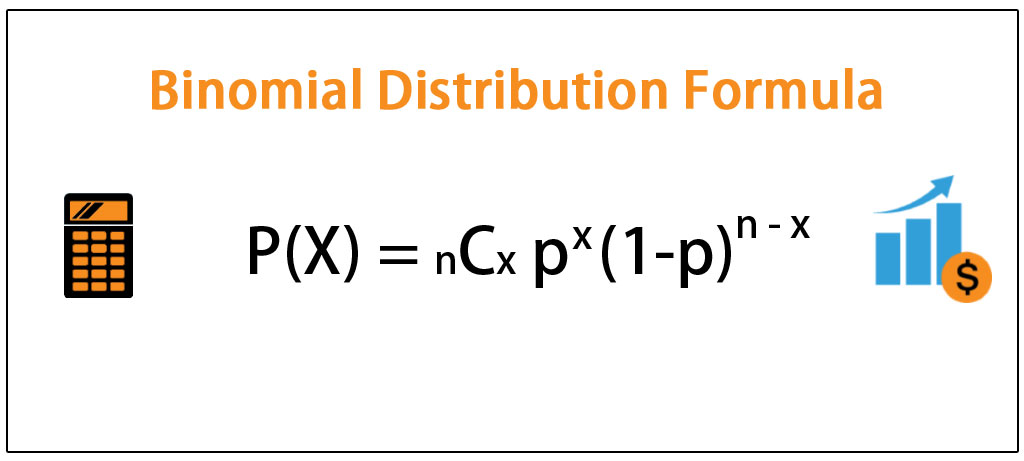
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example
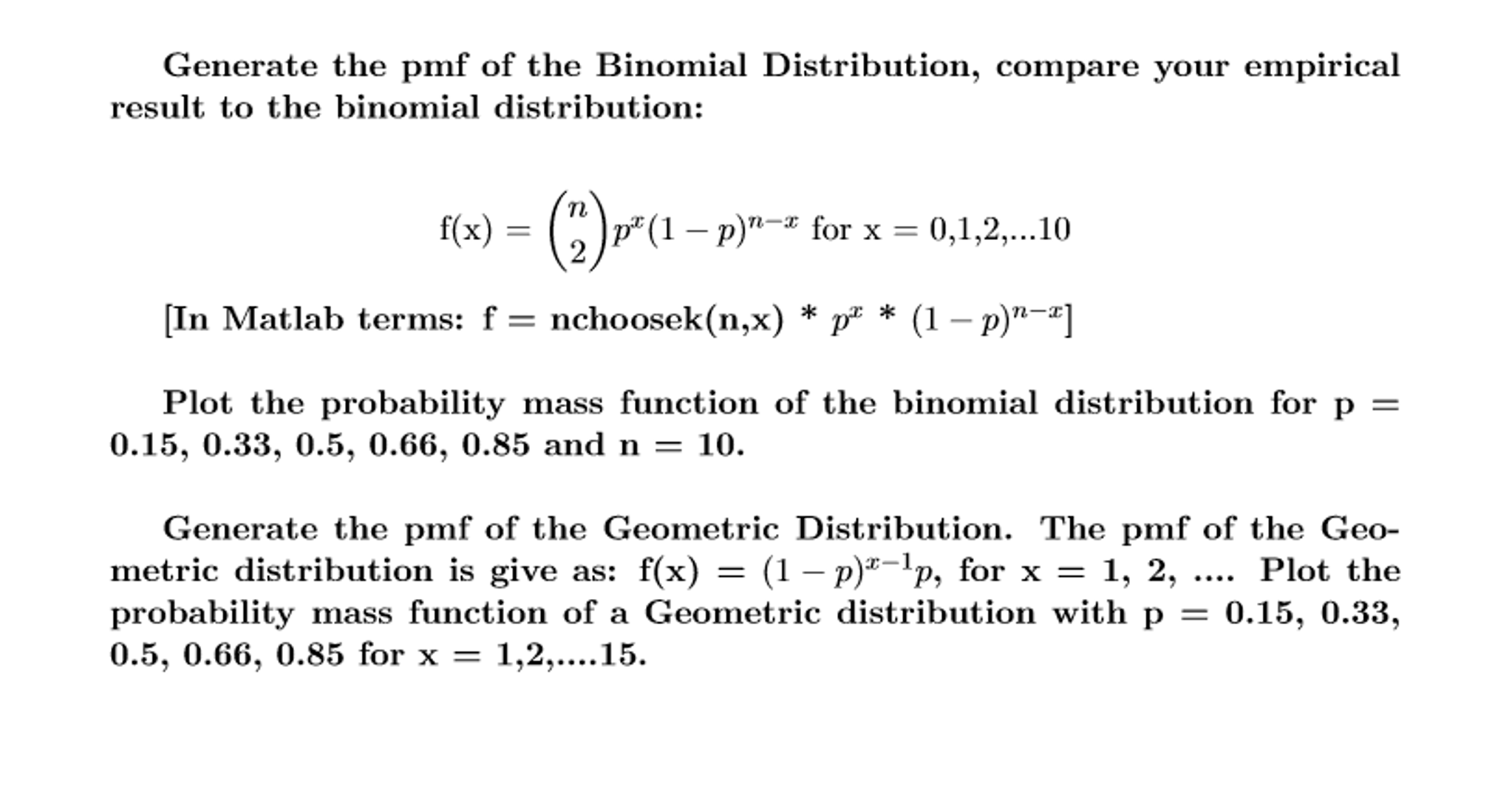
Solved Generate The Pmf Of The Binomial Distribution Com Chegg Com
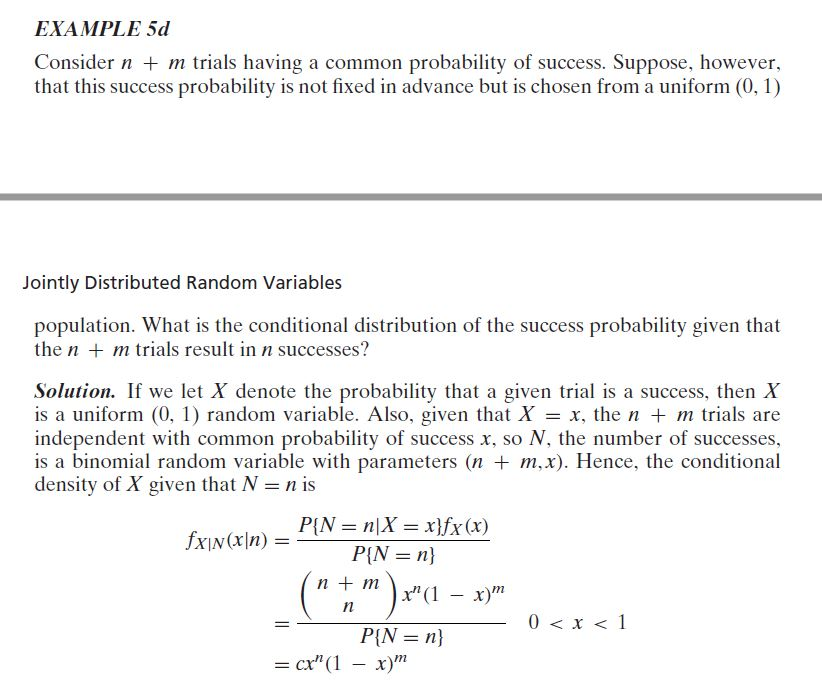
Solved Here With This Problem Below Example 4b We Exp Chegg Com

Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5 1 Overview 5 2 Random Variables 5 3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5 4 Mean Variance And Standard Deviation Ppt Download

5 3 Binomial Probability Distributions This Section Presents

Ex 13 5 8 Suppose X Has Binomial Distribution B 6 1 2
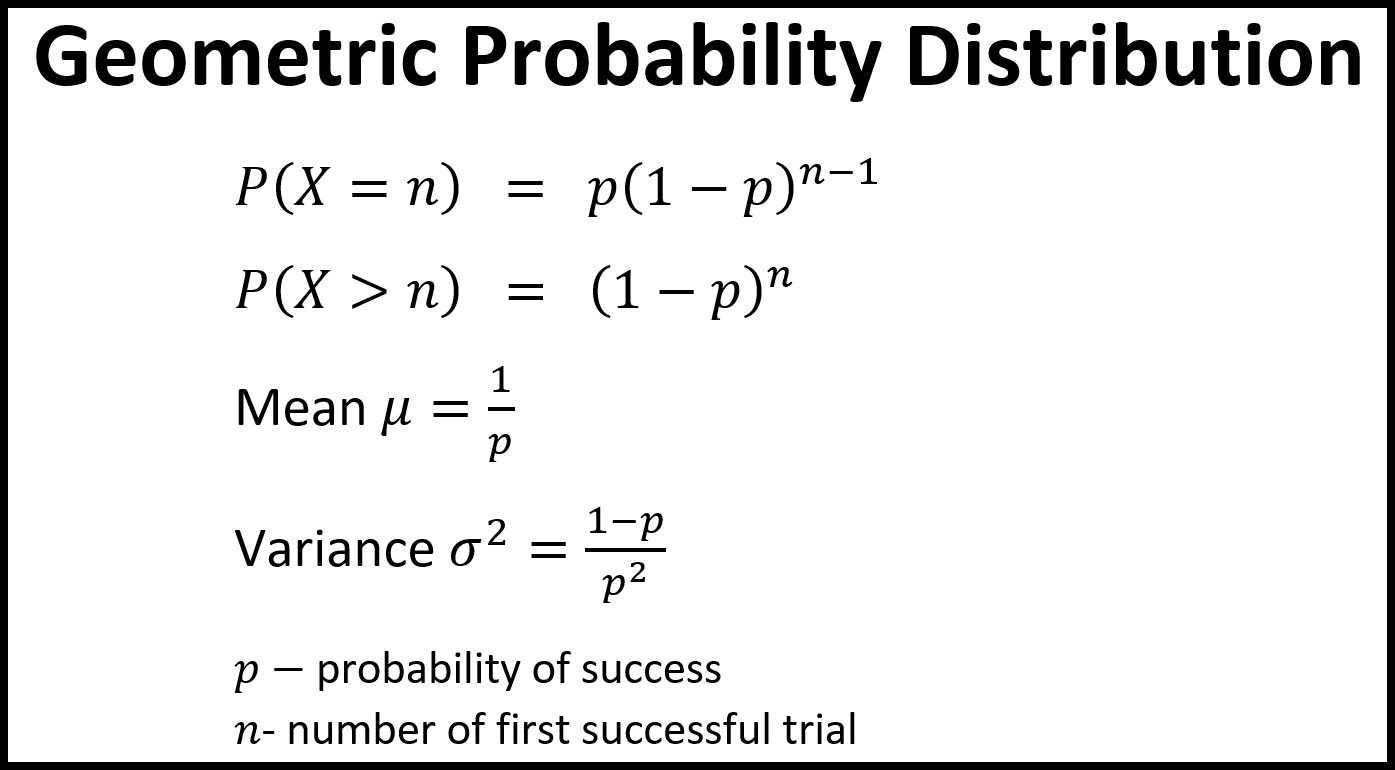
Geometric Distribution Andymath Com

Laplace S Rule Of Succession

Amazon Com Pxn V9 Pc Driving Wheel 900 Degree Vibration Racing Steering Wheel Set With Clutch And Shifter For Pc Ps3 Ps4 Xbox One Xbox Series S X Switch Video Games

If X Follows Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 5 P A N D

Order Statistics 10 30
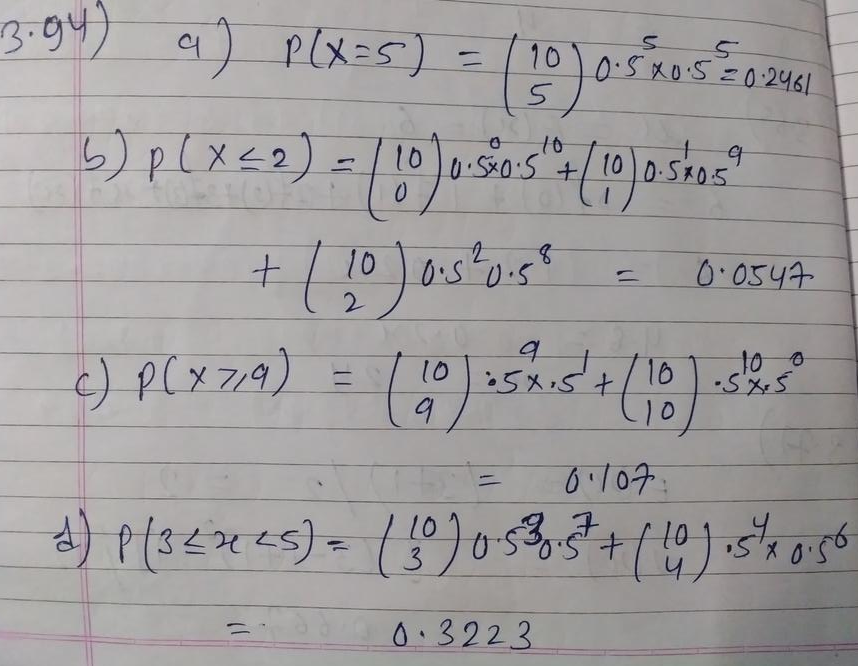
The Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With N 10 And P 0 5 Determine The Following Probabilities A P X 5 B P X 2 C P X 9
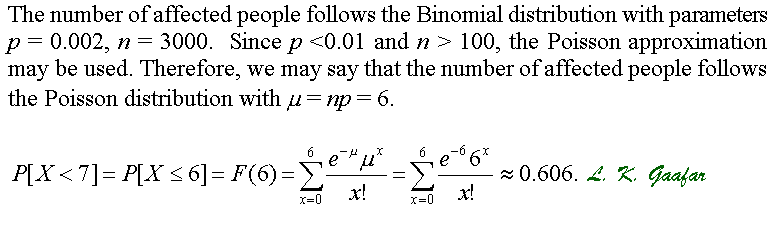
New Page 1

When Is A Sample Proportion P Hat Instead Of X Bar Cross Validated
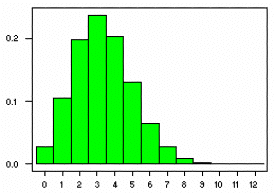
The Binomial Distribution
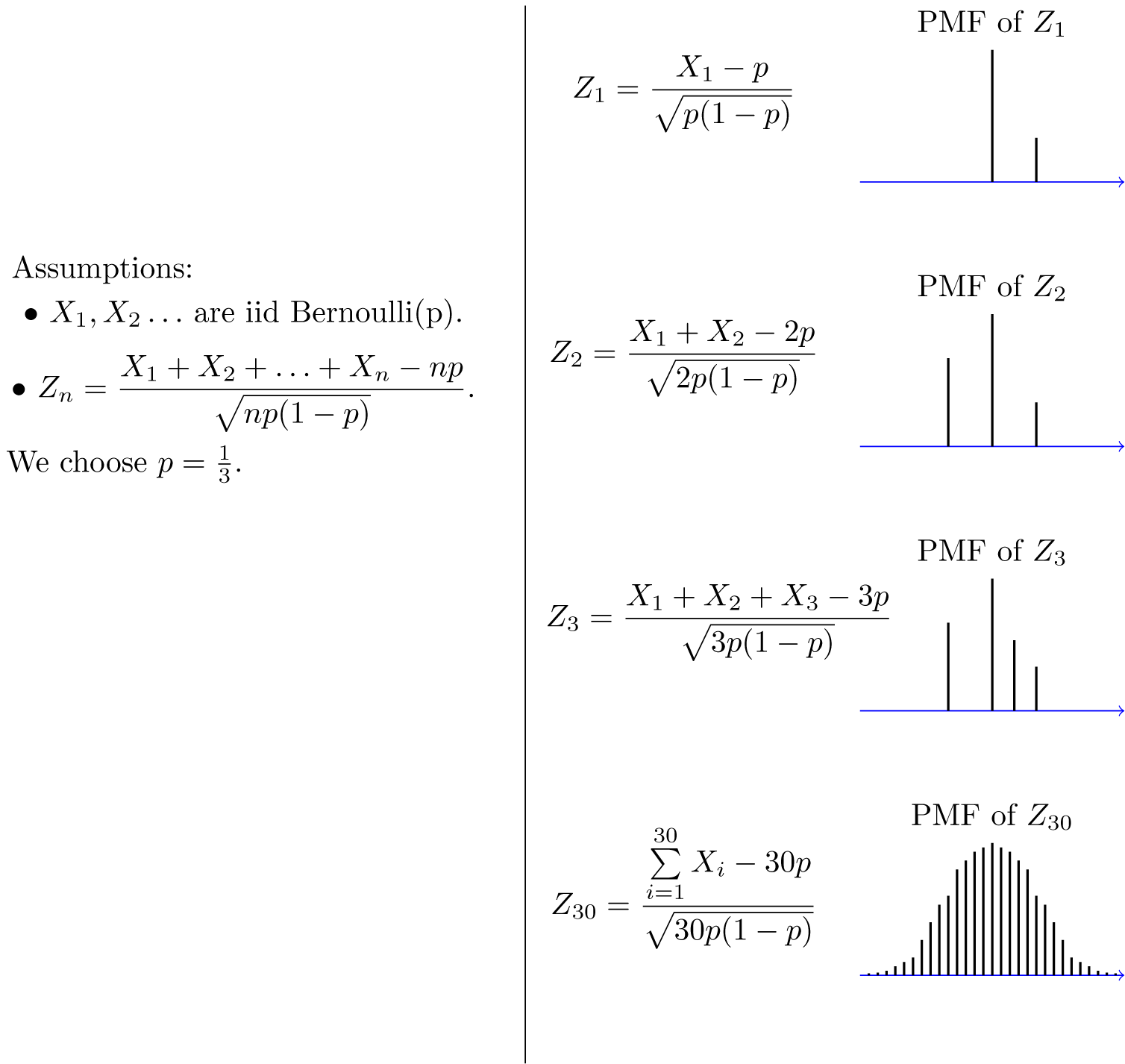
Central Limit Theorem
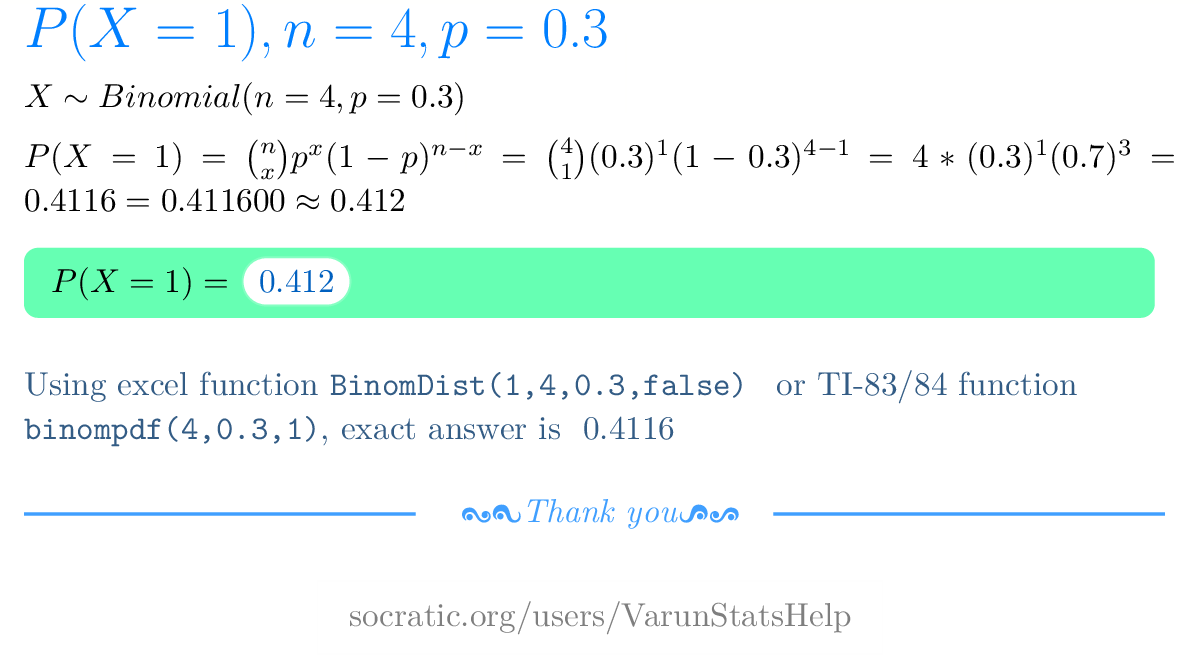
If X Is A Binomial Random Variable What Is The Probability Of X For N 4 X 1 P 0 3 Socratic

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
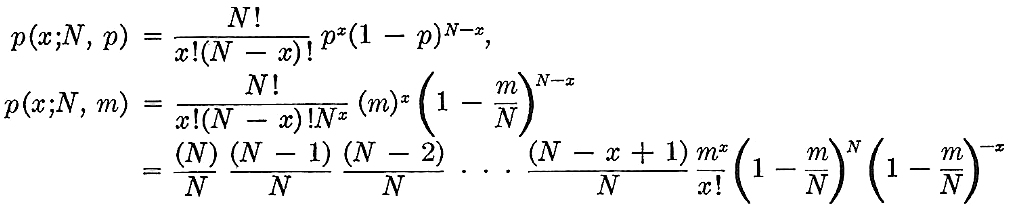
Poisson Probability Calculator

Commutator Of And
Distribution Functions

Sampling Distribution Of Sample Proportion Part 1 Video Khan Academy

Order Statistics 10 30

Binomial Distribution
Binomial Distribution Calculator

If K X X 2 And P X K X N What Is The Value Of N Pleaseee Help Asap I Will Give Brainly Com

Lecture Slides Elementary Statistics Eleventh Edition And The

Normal Distribution Probability Example Examples Solutions Worksheets Videos Activities

Probability And Discrete Random Variable Probability What Is

Important Short Objective Question And Answers Random Variables
Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template

Proof For Convergence In Distribution Implying Convergence In Probability For Constants Mathematics Stack Exchange
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example

Binomial Distribution Formula Example Calculator
Chapter 5 Discrete And Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Download

Showing That E X Sum Mathbb P X Ge N Mathematics Stack Exchange
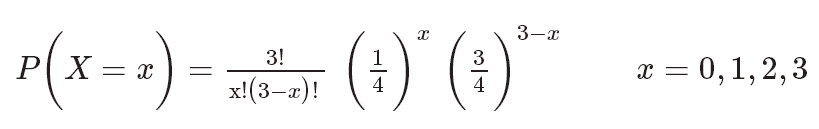
Binomial Random Variables Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida

If X Follows A Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 6 And P

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
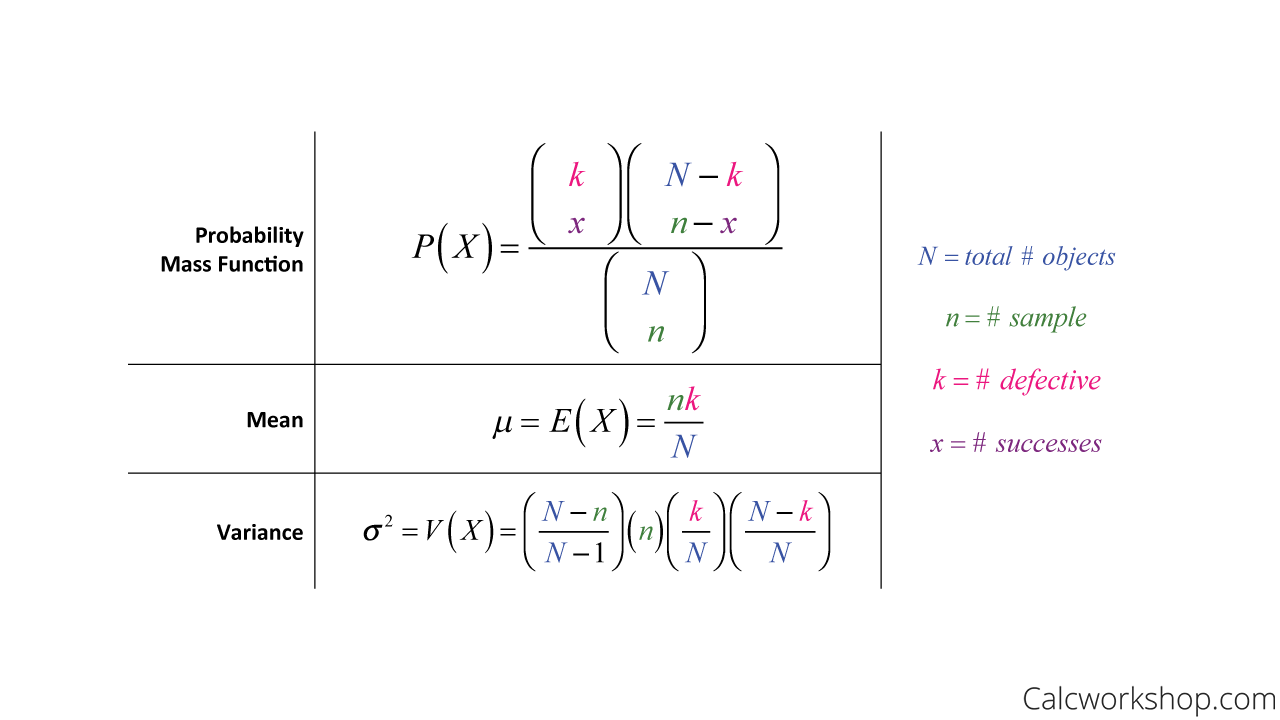
Hypergeometric Distribution Defined W 5 Examples

4 1 Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions
Probability Distribution 2

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia

Solved Why Probability Of Min X Y N Is Same As Probabi Chegg Com
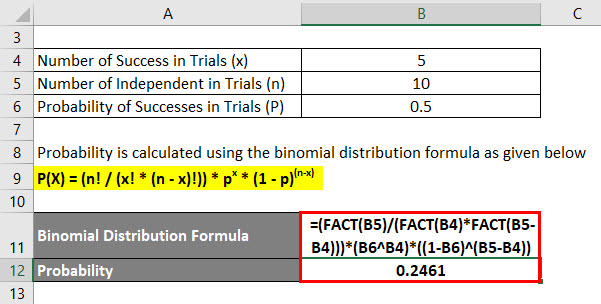
Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template
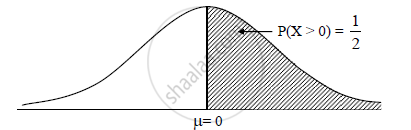
A Random Variable X N 0 1 Find P X 0 And P X 0 Mathematics And Statistics Shaalaa Com
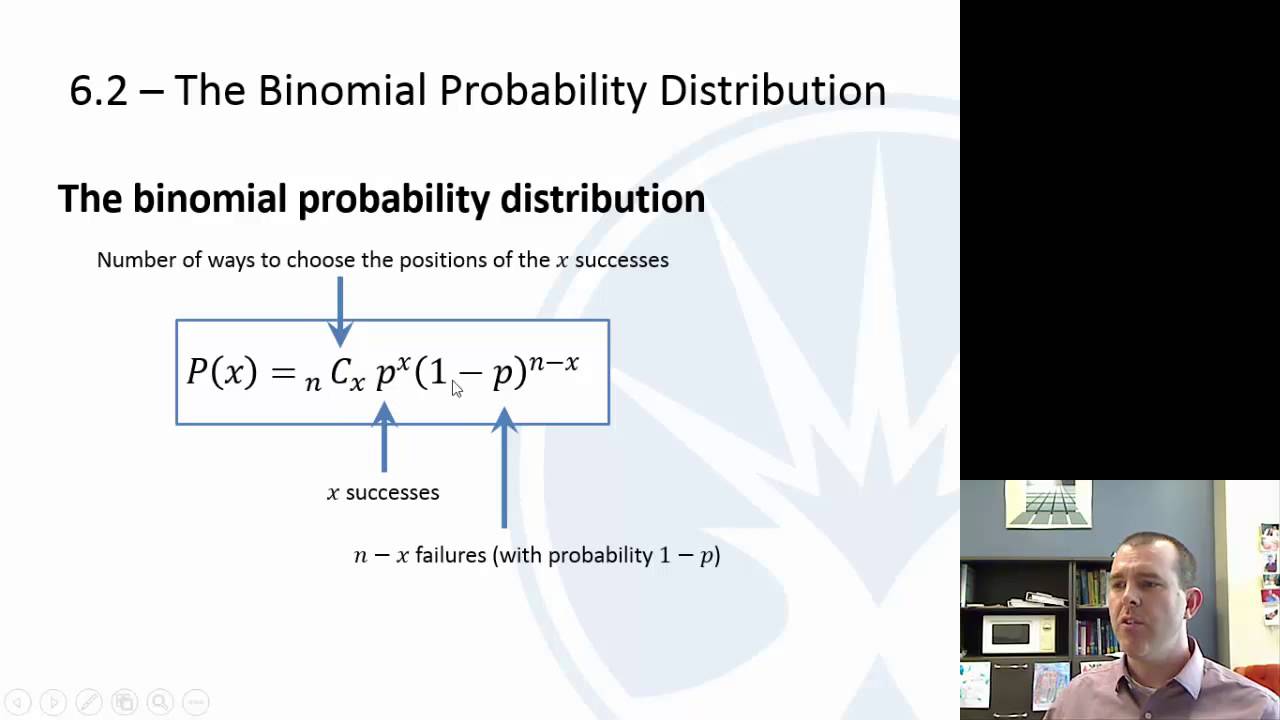
Chapter 6

Binomial Distribution From Wolfram Mathworld

Binomial Distribution Examples Problems And Formula
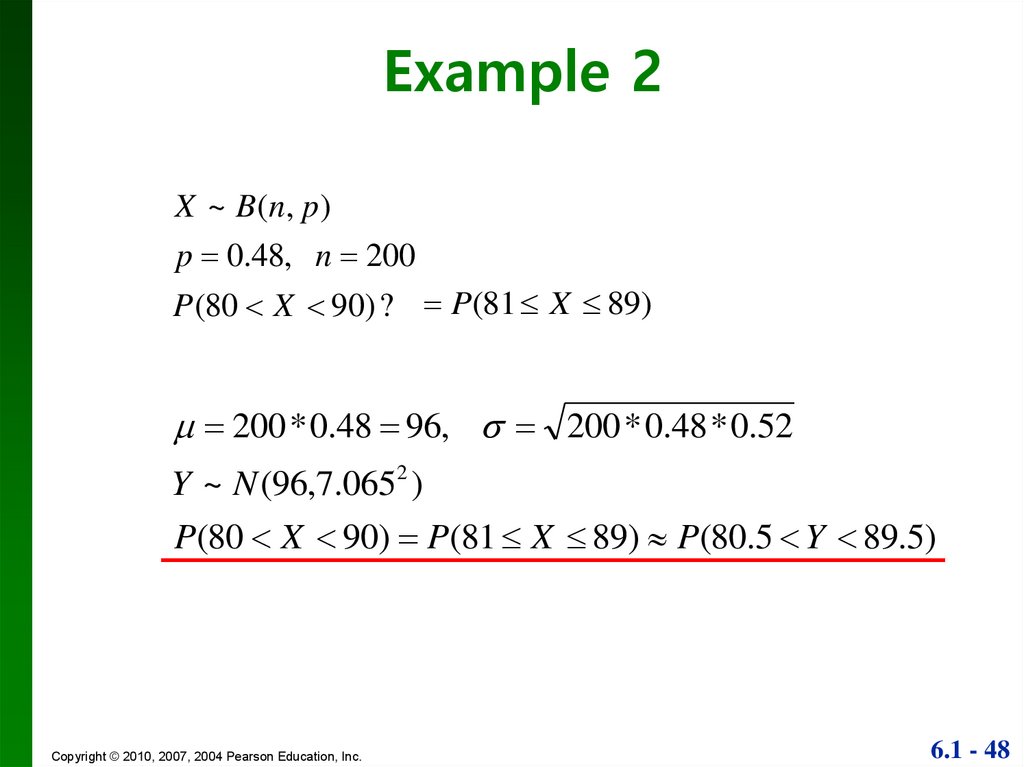
Normal Probability Distributions Online Presentation
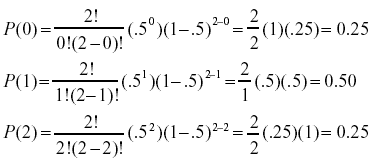
Binomial Distribution

Amazon Com Pc Racing Wheel Pxn V3ii 180 Degree Universal Usb Car Sim Race Steering Wheel With Pedals For Ps3 Ps4 Xbox One Xbox Series X S Nintendo Switch Video Games
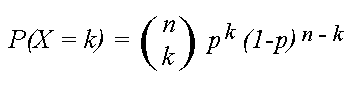
The Binomial Distribution
Finding The Probability Of A Binomial Distribution Plus Mean Standard Deviation Youtube
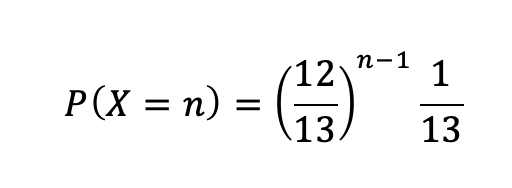
Algorithms For Fundamentals Of Probability By Nadim Kawwa The Startup Medium

Normal Distribution X N Fx X X 5 N 5 2 Ppt Video Online Download

Ppt Maximum Likelihood Estimation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
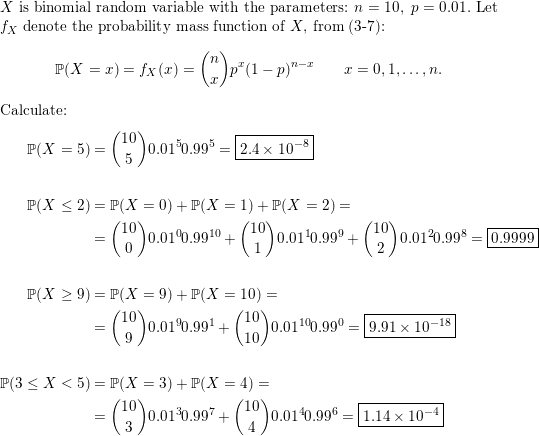
The Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With N 10 And P 0 01 Determine The Following Probabilities A P X 5 B P X 2 C P X 9
P Values

If X Is A Binomial Variate With Parameters N And P Where 0gt Pgt

Stats Year 2 Ch3 Flashcards Quizlet

Expected Value Wikipedia
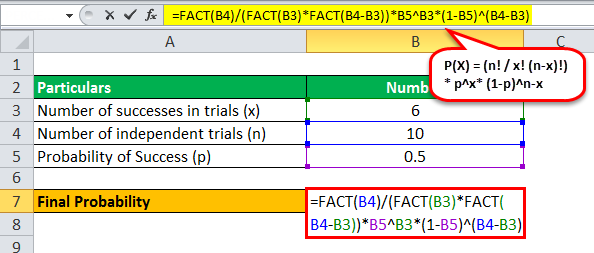
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example

Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
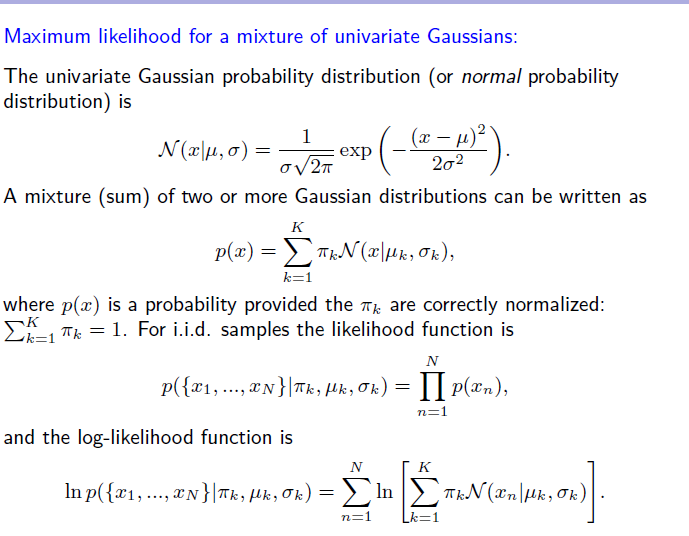
Solved Maximum Likelihood For A Mixture Of Univariate Gau Chegg Com

The Ultimate Guide To A B Testing Part 2 Data Distributions By Maria Paskevich Towards Data Science
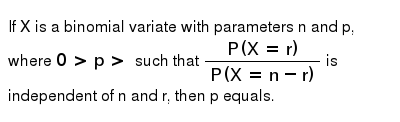
If X Is A Binomial Variate With Parameters N And P Where 0gt Pgt
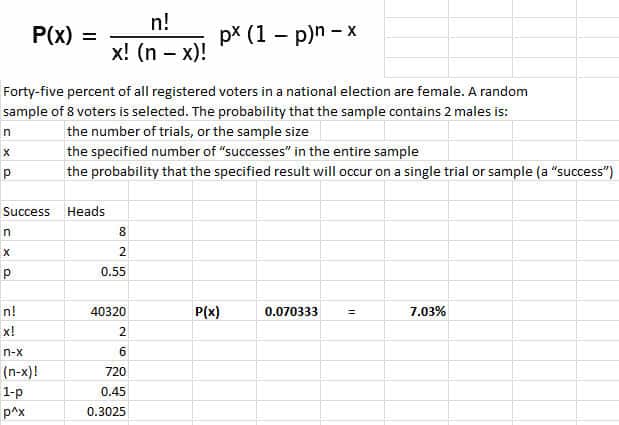
Binomial Distribution Six Sigma Study Guide

Stats Year 2 Ch3 Flashcards Quizlet

Binomial Probabilities On The Ti Or 84 Calculator Mathbootcamps
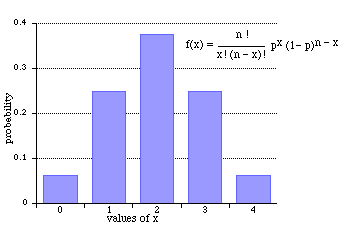
Binomial Distribution

Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions Ppt Download
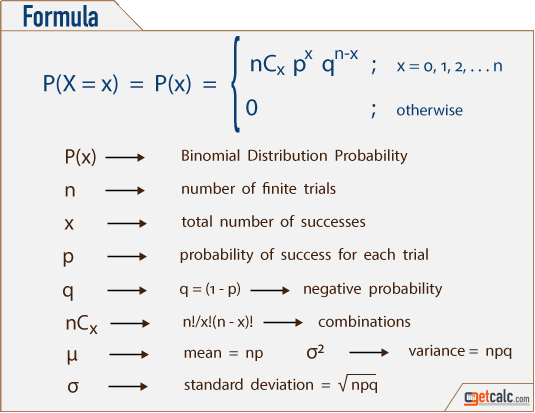
Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator

3 5 Hypergeometric And Negative Binomial Distributions Copyright
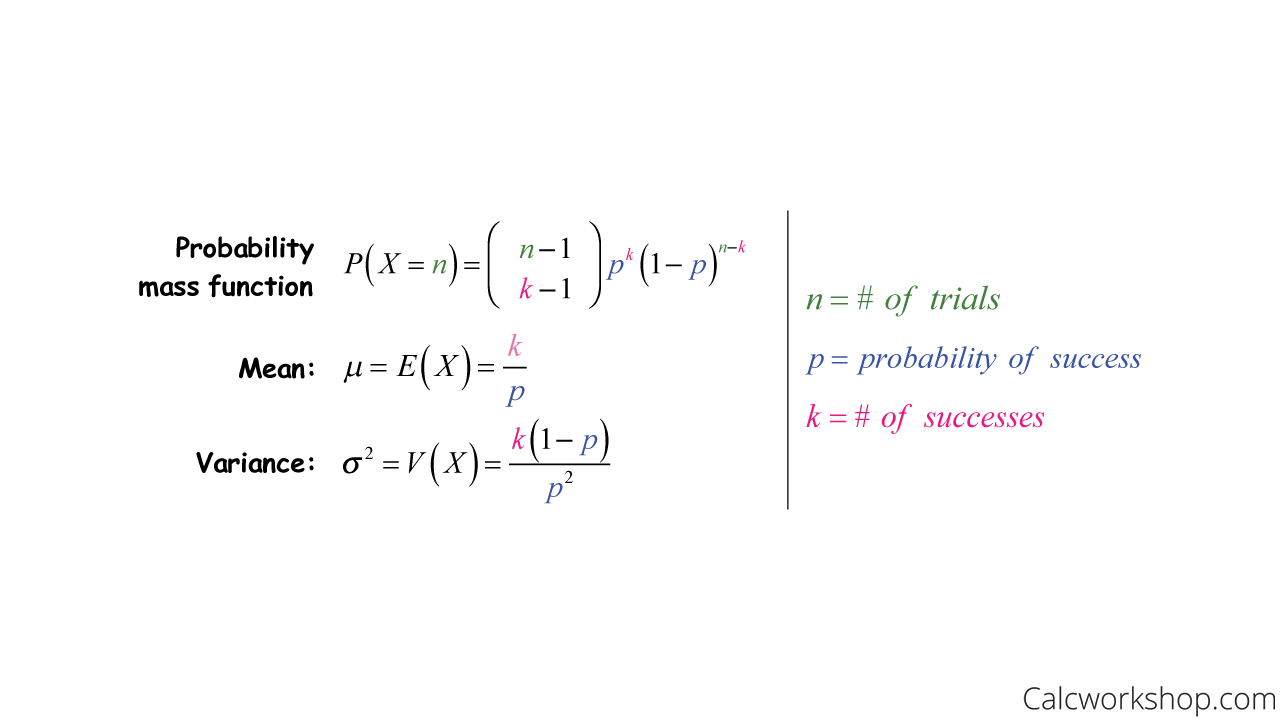
Negative Binomial Distribution W 7 Worked Examples

1 3 6 6 19 Poisson Distribution

Algorithms For Fundamentals Of Probability By Nadim Kawwa The Startup Medium

Solved Possibly Useful Formulas Binomial P X Nx Px 1 Chegg Com

Random Variables




