Pxy Txx F
View lecture_4pdf from CS 546 at University of Washington Warm up Fix any a, b, c > 0 1 What is the x 2 R that minimizes ax2 bx c 2 What is the x 2 R that.
Pxy txx f. F 1 ⇢ F 2 ⇢ F 3 ⇢ Complexity grows as k grows fb(k) D = arg min f 2F k 1 D X (xi,yi)2D (y i f (x i))2 > Choice of hypothesis class introduces learning bias – More complex class → less bias – More complex class → more variance > But in practice??. Zhang et al Hum Cent ComputInf Sci Page 3 of 18 Comparedwithvisionsensors,laserscannercancollectthespatialandmotioninforma tionofthedetectedobjects1615. Define A= fx7!‘(f(x);y) f2Hgto be the loss class, the composition of the loss function with each of the hypotheses With probability at least 1 L(f^) L(f) 4R n(A) s 2log 2 n;.
Introduction to MOSEK and Conic Optimization DataDriven Analytics and Optimization for Energy Systems, 21 June 19 Micha l Adamaszek wwwmosekcom. ZongetalJournalofInequalitiesandApplications DOI/s RESEARCH OpenAccess OnJensen’sinequality,Hölder’sinequality, andMinkowski. Remark 8 Let f X !R be a vector then we define its inner product of matrix P X X !R as a vector hP, fi X!R, where (Pf) x = å y2X P xy f y, x 2X It follows that, we can write (Pf) x = Ef(X 1)jfX 0 = xg = E x f(X 1) 14 Strong Markov property (SMP) Let t W !Z be an almost surely finite integer valued stopping time adapted to the.
International Journal of Advanced Research in Physical Science (IJARPS) Volume 6, Issue 3, 19, PP 3943 ISSN No (Online) wwwarcjournalsorg. Apr 03, 18 · where d=x m −x f, with x m and x f the ages for male and female, respectively In our model for α, in addition to this specification, the gender of the elder partner, represented by the sign of d, is also taken into account This latter is captured through the second term of the denominator β 1 d in equations (10) and (11) Thus, for our. 5 12 21 tt ut tt εε σ εε − u Multiplying ut by the above stochastic matrix produces 2D Gaussian noise with circular covariance, whose standard deviation is equal to the length of the vector utIn Sim 16 the scale factor was set to σu =04, while in Sim 710 its value was σu =05As explained in the main text, the two parameters σs and σu were adjusted so.
This preview shows page 1 4 out of 5 pages 5 Determine all the points of R 2 where f R 2 → R is continuous, if for all (x, y) ∈ R 2, (a) f (x, y) = xy xy if x 6 = y, 0 if x = y (b) f (x, y) = xy x 2y 2 if x 2 6 = y 2, 0 if x 2 = y 2 (c) f (x, y) = xy if xy ∈ Q,xy if xy ∈ R \ Q. Txt hdrsgml accession number conformed submission type 8k public document count 36 conformed period of report item information regulation fd disclosure item information financial statements and exhibits filed as of date date as. P xy kt for y∈VG Finally, let k→ to get u y = x u x v y =v y 22 The Mean First Return Time Corresponding to a vertex x∈VG , denote by T xx the first return time to x, given that the Markov process X t starts at x That is, T xx =inftt> x X t =x X 0 =x where x is the exit time from the vertex x We denote by hxx the mean first return.
8 f yy˛ ’˘ ˆ ’!˜yyˆ 4* ’yy 42ˆ ˆ = yyg ˆ!4 ˚yy˜ yyˆ ˆ!u˚ yy h ˆ yy4x lyyi ajyy ˆ yy˛ %& \8 yyi ˆ!. Ability space, which is endowed with two filtrations, the reference filtration F= (Ft)t∈0,T and another filtration 1 G = (G t ) t∈0,T , that are assumed to satisfy the usual conditions Typically, processes considered in this paper are defined on (Ω,A,P), and are restricted. Here's a straightforward way, which is not very elegant, but is on the other hand very general, and does not require problemspecific tricks We want to calculate bounds for the function f=x y.
Loss functions and Risk usually h() is parametric h(x,α) and cannot approximate f(()) arbitrarily well there is a loss goal to find the set of parameters that minimizes the. Jan 09, · If E is the event the number appearing is a multiple of 3 are F be the event the number appearing is even, then prove that E and F are independent events Answer A die is thrown the sample space are {1,2,3,4,5,6}. T x x N p x μ C x μ C x π where µ x is the mean vector and C x is the covariance matrix { } {( )( )T} μ x =E x C x =E x −μ x x −μ x For the case of two jointly Gaussian RVs X 1 and X 2 with.
F(x)= X y (f(x)−f(y))p xy = g(x)(1) where p xy denote the transition probability from x to y For a typical random walk in a graph,p xy is often taken to be 1=d x for y adjacent to x and 0 otherwise (where d x is the degree of x, de ned to be d x = P y d xy) For some combinatorial games or di usion processes, there are additional constraints. E • ^ X c ttx lir^ a (U l^f j/C^y'X^'Xy'X^ ' X f l/f/^'/u^'X^ z^^c^ ^%^tr c^^ix^xxA^/x c^ ic/Z^ V t trt^ C^ /^^xZ y /^\M^~ XC"^ /^i 4 CX } PtA^i/t^ "LJL (i Ll 4 iir ^Jxi'X'^ /^1a Za/^ \^yji^\4^'^ (X \ X u4 X4^xx lf. X x x3P(x) To nd the k th.
Continuous time Markov Chains construction and basic tools Conrado da Costa Department of Mathematical Sciences (Durham University) emailconradodacosta@durhamacuk. Yy/ %& 5 yyk c ’yy˘ 7gyy 5 \ yyg 56 5 yyg˝f ’yy2 5 \ yyg2˛ 3yyu ˚ ^yyx * \;. Rwith marginal densities p X and p Y, the jointly typical set A(n) " (XY ) nis the set of sequences f(x i;y)gn i=1 2(XY ) nsuch that 1 P n 1 n i=1 logp X(x i) H(p X).
Recall that for any two events E and F, the conditional probability of E given F is defined, as long as P(F) > 0, by P ( E F ) = P ( E F ) P ( F ) Hence, if X and Y are discrete random variables, then it is natural to define the conditional probability mass function of X given that Y = y , by. EXERCISES IN STATISTICS 4 Demonstrate how the moments of a random variable xmay be obtained from the derivatives in respect of tof the function M(x;t)=E(expfxtg) If x2f1;2;3ghas the geometric distribution f(x)=pqx¡1 where q=1¡p, show that the moment generating function is M(x;t)= pet 1 ¡qet and thence flnd E(x) 5 Demonstrate how the moments of a random variable xif they. Warm up ©18 Kevin Jamieson 1 Fix any a,b,c > 0 2 What is the x 2 R that minimizes max{ax b,cx} 1 What is the x 2 R that minimizes ax2 bx c D caiyoIEp IExrL9CxsYD SglxDdlf ELuo fhlexisi dBll fhkxiiso3ii dRaulxHdPd OH 2 ax 16 0 x 1 a Za b.
X x x2P(x) t3 3!. F =f1 f2 where f 1 is a solution to ∆ f 1 ( x )=0 which satisfies the boundary condition σ,andf 2 , which satisfies the Dirichlet boundary condition, is defined by. Distinguishbetv;eent^^?opolarcases(i)wherethereisanoutputtariff and (ii) wherethere is an innuttarif f Xandy denote thelevelsat whichprocesses x and y are respectively.
) is the deformation oT model the deformation, we adopt the commonly used tensor product of the cubic Bspline basis function 7, where the deformation for each direction q2fx;ygis described independently by parameter coe cients f qgas follows d q(x;. Chapter 1 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods 11 Introduction MCMC(Markov Chain Monte Carlo) ’{˙Ÿ—nصe„–ºw Metropolis et al (1953)–9 Hastings (1970), –9Ùƒ‹«0 MCMC˙;˝ ˛. The random variable X is the number of heads in these 10 tosses, and Y — the number of heads in the first 3 tosses In spite of the fact that Y emerges before X it may happen that.
Where the expectation is over (x;y) ˘P XY, a distribution over XY You’re speaking my language totally comfortable Familiar, but rusty I’ll be ready to go by the start of class Never properly learned this I need to get up to speed. # P(x) or M X(t) = X x P(x) t 1!. ), where d( ;.
(a) Skizzieren Sie den Verlauf der Dichtefunktion fγ(x) für die Fälle γ = 05 und γ = 2 (b) Berechnen Sie die Verteilungsfunktion F γ (t) der Zufallsvariablen X (c) Berechnen Sie für beliebiges n ∈ IN folgende Momente. For \loss" function ‘ YY!. Tqryy_ 3yy˛ \#˚yy0 yy 56 f yy!.
’yy˘ f9 yyi 5 yy!u ˚ =˚yyg*˛ jyy2 7yy< f yyc9ˆ $ yy4x ^yy 2 5 \yy ˆx /%& ;. 2 Remember that for a continuum that is deforming or flowing smoothly, a current spatial location, ie xi, at any given time t will refer to a particle that was originally at (a1, a2, a3) when t = to (ie at initial time) xi = xi (a1,a2 ,a3,t), i =1,2,3 Since the deformation/flow is smooth, the functions )xi = xi (a1,a2 ,a3,t must be then continuous and differentiable functions. 1) z = f(x 2 y2) Differentiating z partially w rt x and y, f x y y y z f x y x q x z p '(2 2)2 , '(2 2)2 p /q = x / y or y p –x q=0 as the pde (2 ) z = f ( x ct ) g (x ct) Differentiating z partially with respect to x and t, '( ) '( ), "( ) "( ) 2 2 f x ct g x ct x z f x ct g x ct x z Thus the pde is (3 ) x y z = f.
Example 5 X and Y are jointly continuous with joint pdf f(x,y) = (e−(xy) if 0 ≤ x, 0 ≤ y 0, otherwise Let Z = X/Y Find the pdf of Z The first thing we do is draw a picture of the support set (which in this case is the first. 4 Then (X n) n≥0 is a Markov chain with transition probabilities P xy = P n Y 0 = y x o, x,y ∈ ∞k=0 {y 0 ···y k y i ∈ S} The process (X0 n) n≥0 is not Markovian since the past gives precise information on the factor Y n−1, which is contained in X n 0 but not in X n 0 1 • Simple random walk (SRW) on Z Imagine a random walker on the integers, who. Given random variables,, , that are defined on a probability space, the joint probability distribution for ,, is a probability distribution that gives the probability that each of ,, falls in any particular range or discrete set of values specified for that variable In the case of only two random variables, this is called a bivariate distribution, but the concept generalizes to any.
Let Xbe a discrete random variable M X(t) = X x etXP(x) = X x " 1 tx 1!. Q) = X i;j (i;j) x m x i y m y j (2). X otherwise (28) The Data Processing Axiom implies that for all 20;1, t20;1 and legitimate 2 > 1 0, V(P(t) 1) (1 )V(P(t) 2) V( P(t) 1 (1 )P(t) 2.
X˙ (t) = x,x ,y,y R xy,x y (λ t)p x y (t) × ln R xy,x y (λ t)p x y (t) R x y ,xy(λ t)p xy(t) (10) and using −lnx 1−x Another useful identity is ˙ (t) =−∂ t λ(t)D p xy(t) peq xy (λ t) 0, (11) where the partial derivative ∂ t λ(t) indicates that the change of Dp xy(t) Rp eq xy(λ t)isevaluatedatfixedλ tHere,weintroduced. De nition Given a joint probability density p XY!. (7) where L(f^) denotes the expected test risk of the empirical risk minimizer, L(f^) denotes the expected test risk of the expected risk minimizer, R.
R, de ne the \risk" of a function f X!Yby R(f) = E‘(f(x);y);. S dX t = ( X t ) dt W t e > 0 2 R > d X 0 = x 0 X t = ( x 0 ) e t Z t 0 e ( t s ) dW s a h 1 s E X t jX 0 = x 0 = E ( x 0 ) e t Z t 0 e ( t s ) dW s = ( x 0. Jan 07, 21 · The dynamics of the mass point was already dealt with by A Einstein in his first foundational work on the relativity principle, as well as shortly afterwards by M Planck The most important result of their investigation were the known formulas for the dependence of longitudinal and transverse mass from velocity (since then experimentally confirmed at different occasions.
Tao Min et al / Parameter Inversion Model For al, 1991), Marquardt’s procedure, and thermal wave slice tomography Most of the discussions in the literature are devoted to the qualitative analysis of the equations such as existence and. X(t) = X x etXP(x) If Xis continuous M X(t) = Z x etXf(x)dx Aside ex= 1 x 1!. Jun 05, 14 · Details The saturation pressure of component is calculated using the Antoine equation where for hexane and for octane, is saturation pressure (bar), , , and are Antoine constants, and is temperature (°C) Raoult's law is used to calculate the bubblepoint and dewpoint pressures using the factors where is the vapor mole fraction and , is the liquid mole.
> Before we saw how increasing the feature space can increase the complexity of the learned estimator BiasVariance Tradeoff. Conditioning on the discrete level Example A fair coin is tossed 10 times;. X x xP(x) t2 2!.
Similarly, etx= 1 tx 1!. Where 〈P xy (t)P xy (0)〉 is the correlation function of the xy component of the stress tensor, V is the volume of the simulation box, k B is the Boltzmann constant, T is the absolute temperature and t is the time (633) by x(t) and utilizing the relation that x v ˙ = x x ˙ = d d t (x x. C(‘;P XY) = V(P(t) 1) (1 )V(P(t) 2) V( P(t) 1 (1 )P(t) 2) (27) Note that the following transformation T(X) is a statistically su cient transformation of Xfor Y T(X) = (x 1 X2fx 1;x 2g;.
P XY 2P XY can be written as a product P XY = P X P YjX, with P X2P X, P YjX2P The space P XY is endowed with the topology of weak convergence and the associated Borel ˙algebra It is assumed that there exists a distribution on P XY, where P (1) XY;;P (N) XY are iid realizations from , and the sample S iis made of n.

Rudolf Blaschka Letters To Walter Deane Botanists Correspondence Szx P Er T Zt Iz Lt Amp X Tx Lt F2 Tx7 X X Xx T X X Xxt J Zx Z F Amp 7 Z X Y Ie T Xx7y Lt Xxt S C Xl X X I Fe Xxf Xxxx Zx

When Is The Probability Of A Variable Equivalent To A Function Of The Variable I E When Does P X F X Cross Validated

On Approximate Cubic Homomorphisms Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
Pxy Txx F のギャラリー
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)
Joint Probability Definition

First Order Linear Differential Equation Integrating Factor Idea Strategy Example Youtube

Solved The Lorentz Attractor Is Given By The Following Se Chegg Com

Content Parametric Equations Of A Parabola

Conditional Entropy Wikipedia

Nonlinear Fuzzy Approximation Of A Mixed Type Acq Functional Equation Via Fixed Point Alternative Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2

Density Of Sum Of Two Independent Uniform Random Variables On 0 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
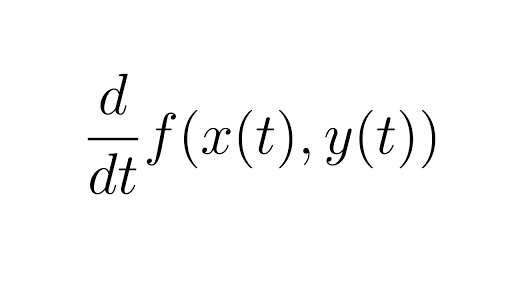
Multivariable Chain Rule Simple Version Article Khan Academy

Pdf Deriving Direct Utility Function From Indirect Utility Function Pokemon 16 Academia Edu

Cumulative Distribution Function An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Probability Density Functions Video Khan Academy

Conditional Entropy Wikipedia
Umd Banach Spaces And The Maximal Regularity For The Square Root Of Several Operators Springerlink
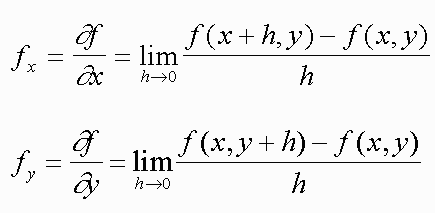
Partial Derivatives

Function Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica
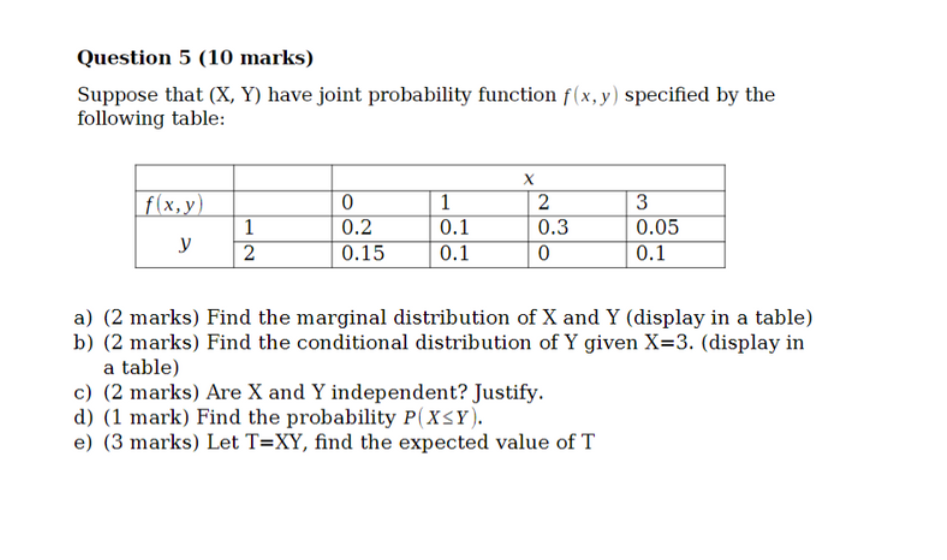
Solved Question 5 10 Marks Suppose That X Y Have Joi Chegg Com
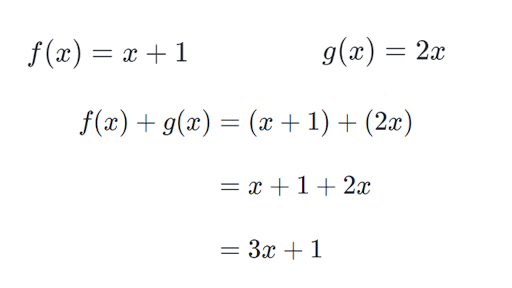
Intro To Combining Functions Article Khan Academy
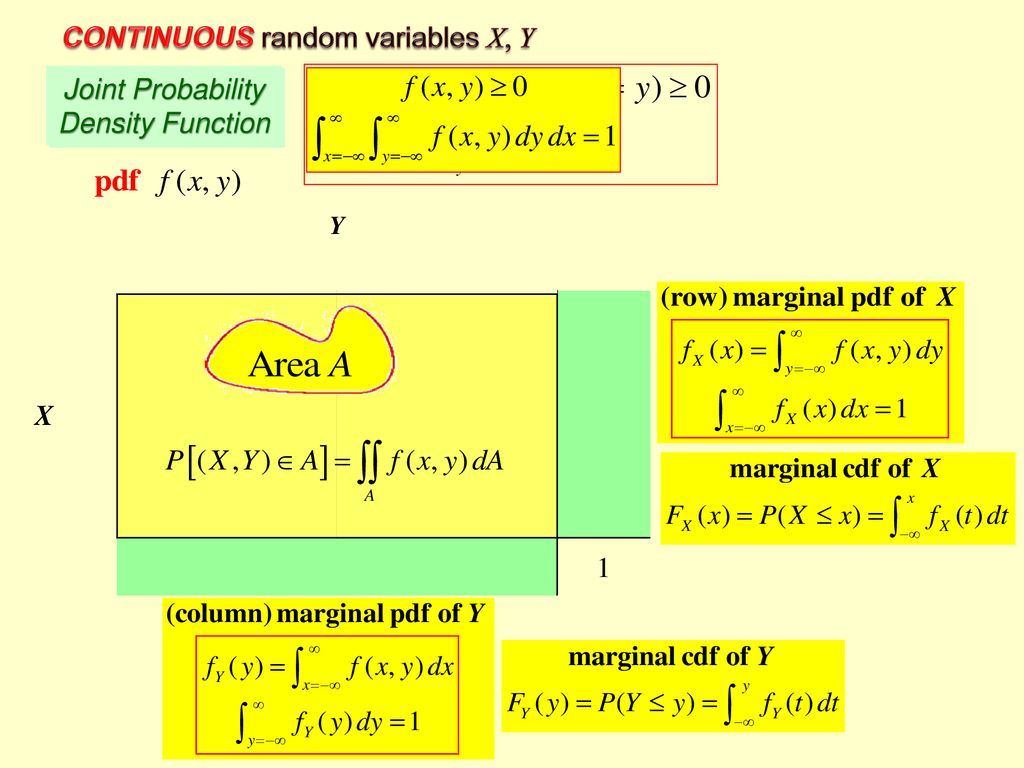
Discrete Random Variables X Y Joint Probability Mass Function Y1 Ppt Download

14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts
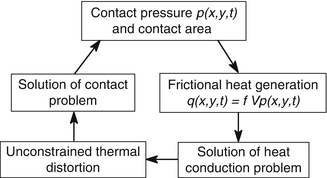
Frictionally Excited Thermoelastic Instability Tei Springerlink

Class 40 Alternate Computing Models Cs 11 Fall

Pdf An Integral For Multifunctions With Respect To A Multimeasure
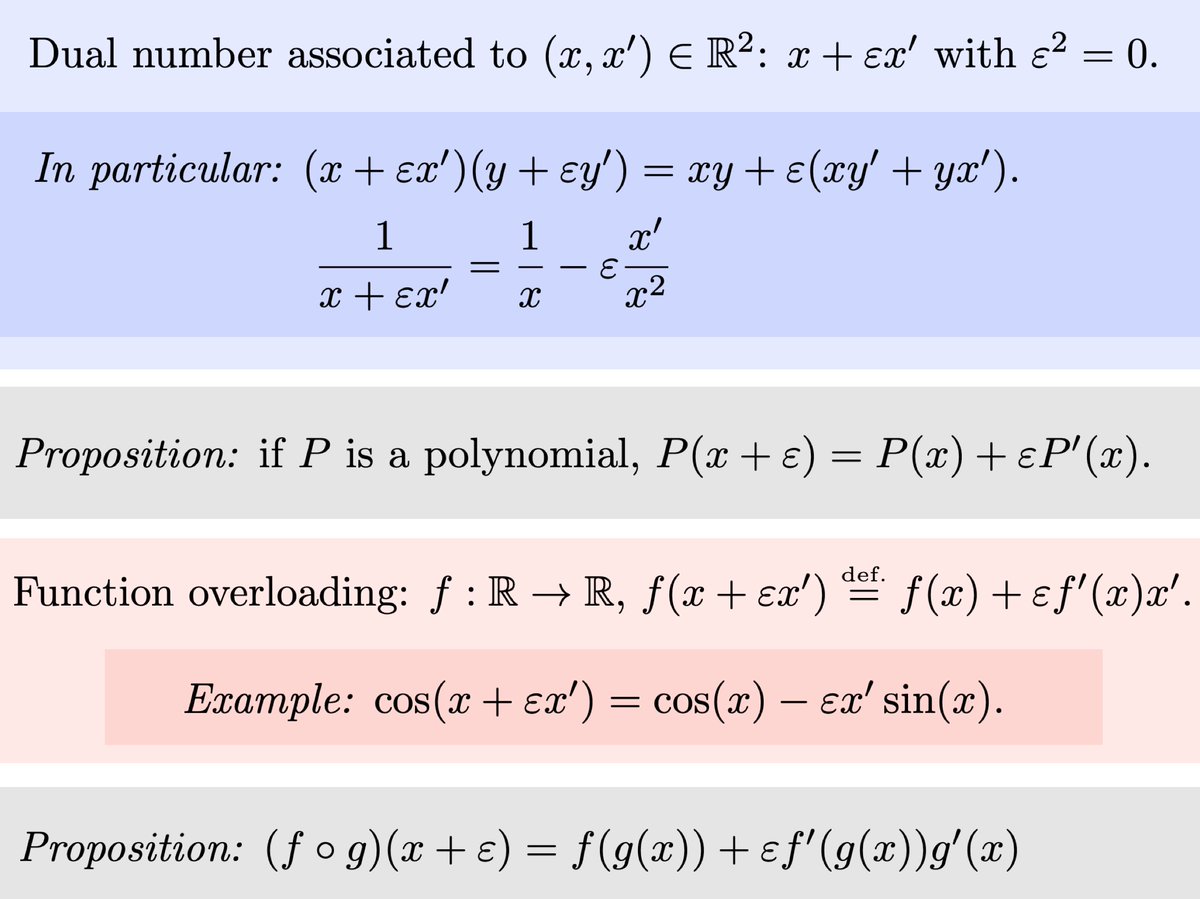
Gabriel Peyre Dual Number Is A Convenient Way To Implement Forward Mode Of Automatic Differentiation T Co Yini7bsvao

Example Choice Of The Probability Distribution P X T With F 2 And T Download Scientific Diagram

Chapter 1 Use The Following To Answer Questions 1 5 In The Questions Below Determine Whether The Proposition Is True Or False Pdf Free Download

T02 Doc First Order Logic Mathematical Logic

How To Solve A Differential Equation With Series X 1 Y Xy Y 0 With Y 0 2 Y 0 6 Youtube
5 2 Joint Distributions Of Continuous Random Variables Statistics Libretexts

Important Short Objective Questions And Answers Two Dimensional Random Variables

Answered X X P Q S Y Y P U V S S U V Bartleby
Osa Radial Grating Lateral Shear Heterodyne Interferometer

Definition Let X And Y Be Random Variables The Chegg Com

Find All F Such That F F Y F X Y F Xf Y X Mathematics Stack Exchange

14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts
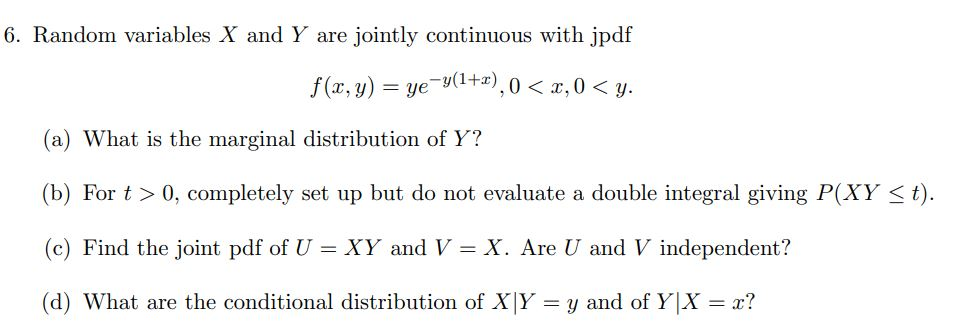
Solved 6 Random Variables X And Y Are Jointly Continuous Chegg Com

An Example Of An Easy Question

Wave Optics Chapter 1 Introduction To Modern Digital Holography

3aa If F Xy F X F Y Then F T See How To Solve It At Qanda
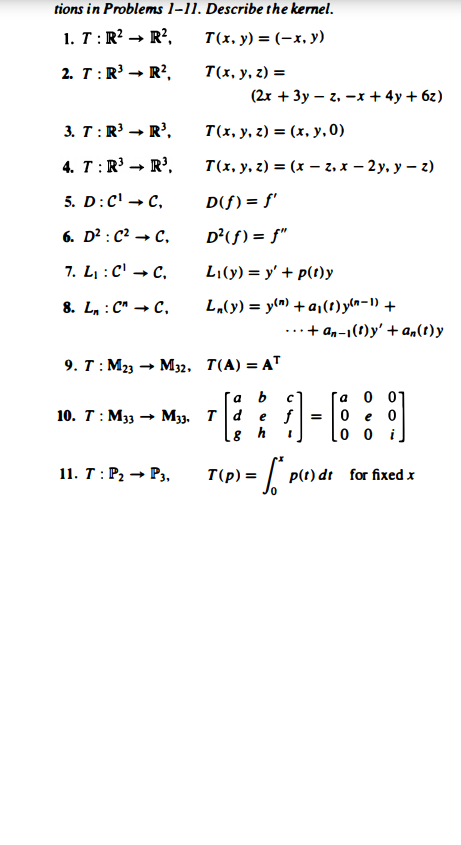
Answered Tions In Problems 1 11 Describe The Bartleby

Reasoning Under Uncertainty Marginalization Conditional Prob And Bayes

Solved The Random Vector T X F Has A Uniform Joint D Chegg Com

2 3 Tangent Plane To A Surface Mathematics Libretexts

Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy

Cs 1 Sections Slides Created By Eva Mok Modified By Jgm April 13 Ppt Download
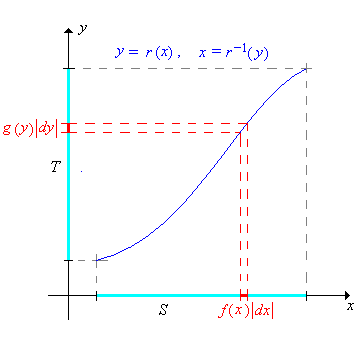
3 7 Transformations Of Random Variables Statistics Libretexts

Parent Of Origin Differences In Dna Methylation Of X Chromosome Genes In T Lymphocytes Pnas

Seebeck S M Xx De F Th Red Line And Nernst S M Xy De F Th Green Download Scientific Diagram

Intro To Combining Functions Article Khan Academy

Solved Xx And Yy Are Discrete Random Variables With Joint Chegg Com

Multiple Periodic Solutions To A Class Of Nonautonomous Second Order Delay Differential Equation Topic Of Research Paper In Mathematics Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub
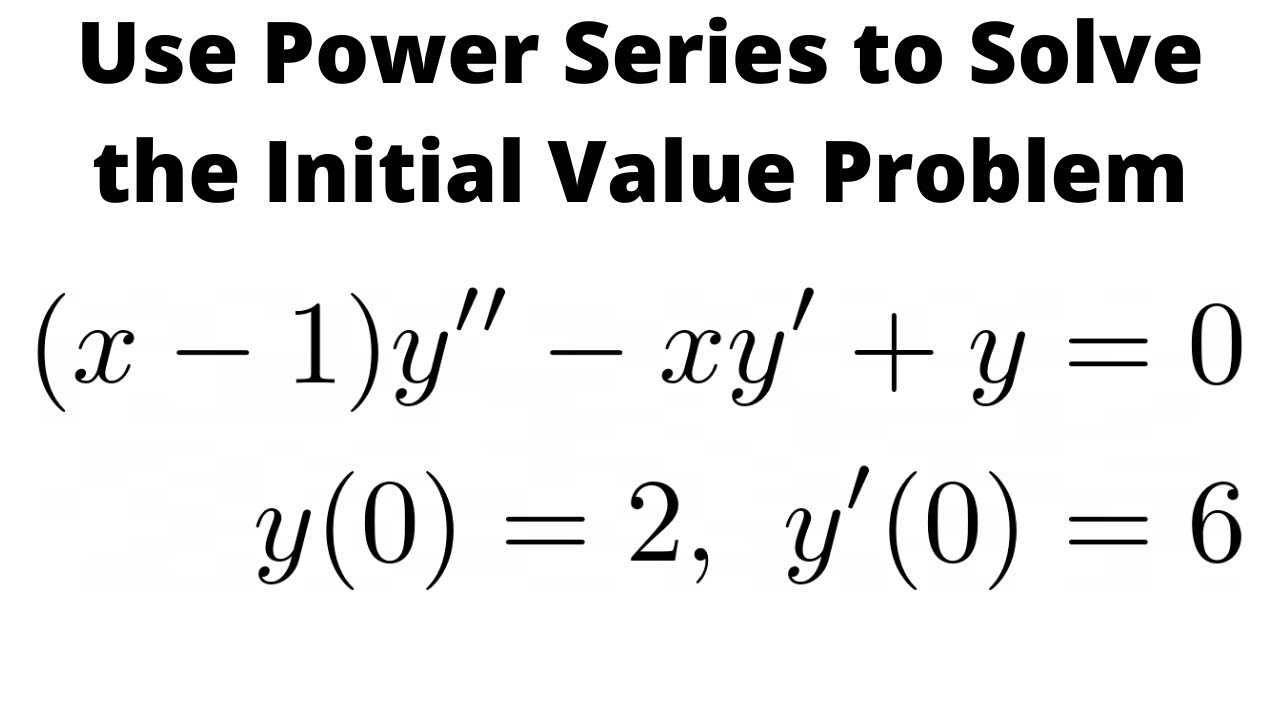
How To Solve A Differential Equation With Series X 1 Y Xy Y 0 With Y 0 2 Y 0 6 Youtube

Chi Square Distribution An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Example Configuration With Two Features X 1 And X 2 And Class Variable Download Scientific Diagram
Joint Probability Distribution Wikipedia
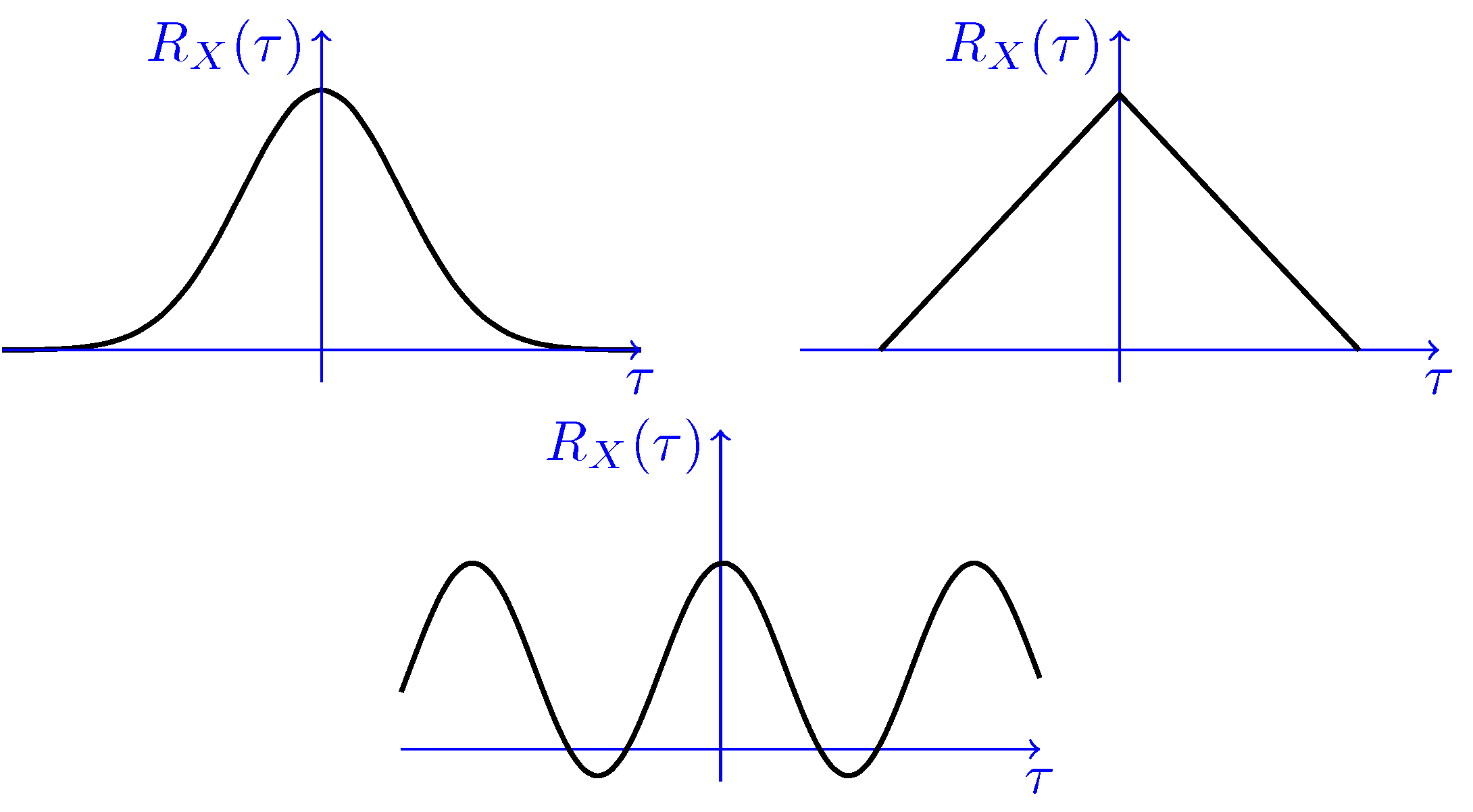
Stationary Processes

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2

Product Distribution Wikipedia
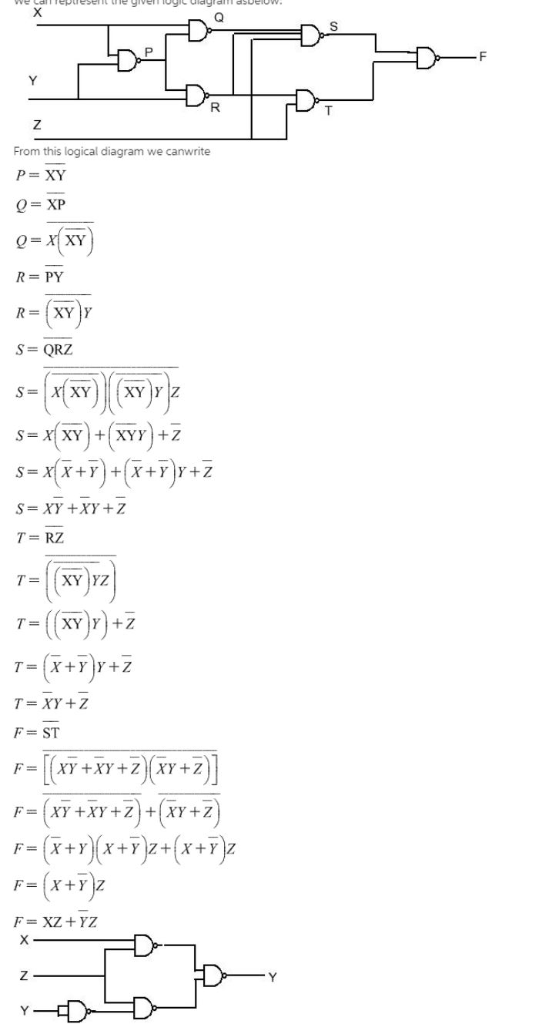
Solved L E Y Very Ay Uluw From This Logical Diagram We C Chegg Com




