T Px N
• Expectation of the sum of a random number of random variables If X = PN i=1 Xi, N is a random variable independent of Xi’sXi’s have common mean µThen EX = ENµ • Example Suppose that the expected number of acci.
T px n. 0 In probability P(jX n ¡Xj >†)!. P(X ≥ x) = 05 This is too hard to solve as it stands so instead, compute Z = (X 500)/100 (NOTE Z ~ N(0,1) ) and find z for the problem, P(Z ≥ z) = 05 Note that P(Z ≥ z) = 1 F(z) (Rule 2) If 1 F(z) = 05, then F(z) = 95 Looking at Table I in Appx E, F(z) = 95 for z = 165 (approximately). The formula pn = P(X = n) = 1 n!.
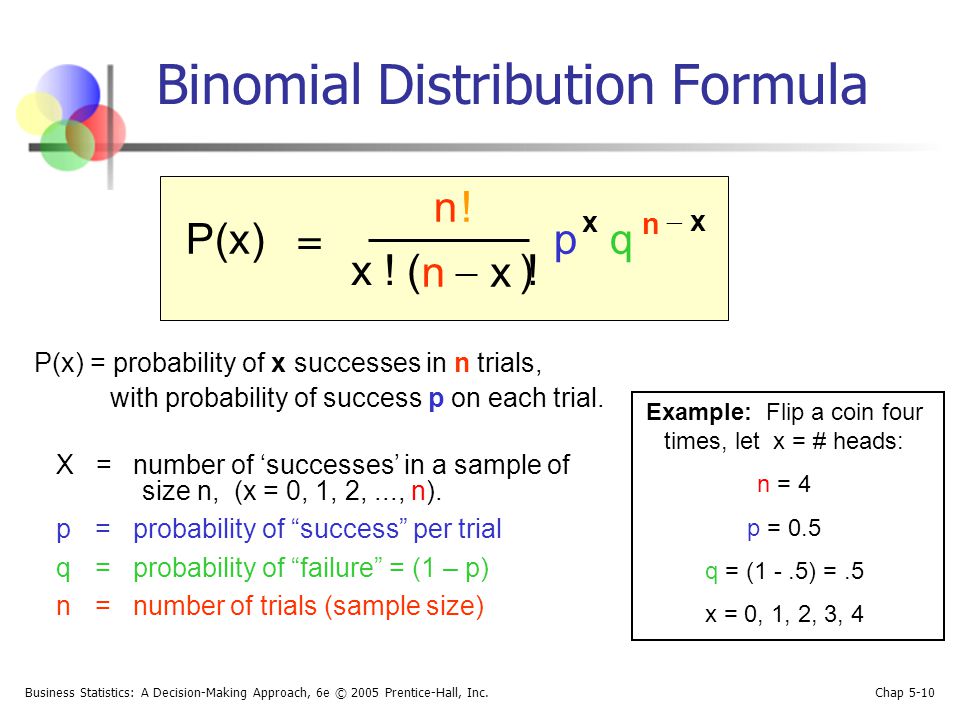
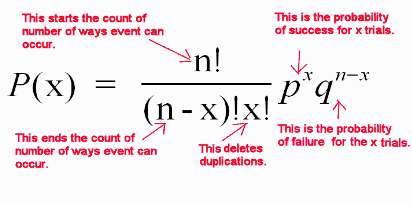
), and then (by dividing by x!), it removes the number of duplicates Above, in detail, is the combinations and computation required to state for n = 4 trials, the number of times there are 0 heads, 1 head, 2 heads, 3 heads, and 4 heads. ©21 Matt Bognar Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science University of Iowa. P(x;t) = 1 p 4ˇDt exp x vt)2 4Dt (217) with the starting condition p(x;t) = (x) Any asymmetry in the transition rates (p6= q) produces a net drift velocity of the walker 23 Rate Equation The combinatorial method used above to derive the expression for the probability distri.
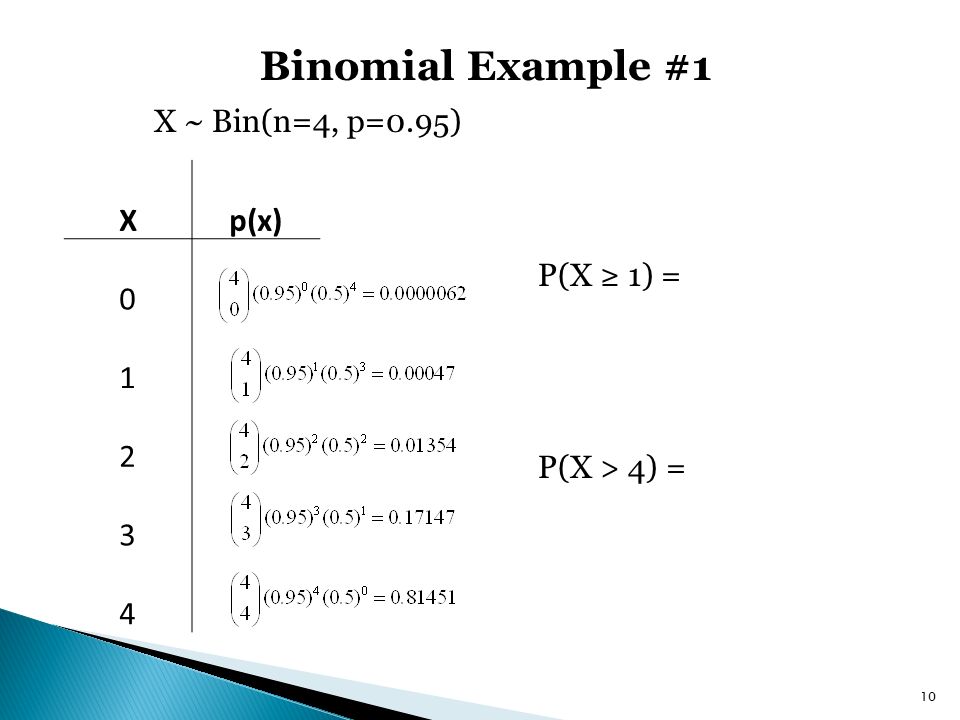
10 MOMENT GENERATING FUNCTIONS 119 10 Moment generating functions If Xis a random variable, then its moment generating function is φ(t) = φX(t) = E(etX) = (P x e txP(X= x) in discrete case, R∞ −∞ e txf X(x)dx in continuous case Example 101. 0 as n !1 Let F n denote the cdf of X n and let F denote the cdf of X X n converges to X in distribution, written X n!d X, if, lim n F n(t)=F(t) at all t for which F is continuous Here is a summary Quadratic Mean E(X n ¡X)2!. Binomial with n = and p = x P( X = x) 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 6 7 097 8 9 The corresponding graphs for the probability density function and cumulative distribution function for the B(,1/6) distribution are shown below.
Mar 30, 21 · Let $(\Omega, \mathcal{F},P, \mathbb{F}=(\mathcal{F}_{t})_{t \geq 0})$ be a filtered probability space and $(X_{t})_{t \geq 0}$ be a Markov process taking values in a. Show that for any natural numbers m and n, P(X > mn X > m) = P(X > n) This is known as the memoryless property of a geometric random variable b Show that the converse of part a is also true, ie, if X is a positive integervalued random variable. Free Online Integral Calculator allows you to solve definite and indefinite integration problems Answers, graphs, alternate forms Powered by WolframAlpha.
The cumulative distribution function (CDF or cdf) of the random variable \(X\) has the following definition \(F_X(t)=P(X\le t)\) The cdf is discussed in the text as well as in the notes but I wanted to point out a few things about this function. Quality Care For The Greater Houston Area UT Physicians provides comprehensive care for the entire family Whether you need primary or specialty care, you can expect the latest treatments, advanced technology, and minimally invasive techniques to help you. Transcribed image text Given time evolution of the probability distribution 1 P(x, n 1) {P(x – 1, n) P(x 1, n)} (1) {p(x 1 C(x,t At) = ¿ {C(x – Ax, t) C(x 4x, t)} (2) where, P(x,n) probability that a particle is located at position x at time n So, we can get diffusion equation ac 02C = D at ax2 (4x)2 ,D = At (3) Question derive the diffusion equation given by equation (3.
N n X t X X X t and n n n X t X X X X Consequently n n n n n P X t P X t X X P from STA 6327 at University of Central Florida. In elementary algebra, the binomial theorem (or binomial expansion) describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomialAccording to the theorem, it is possible to expand the polynomial (x y) n into a sum involving terms of the form ax b y c, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with b c = n, and the coefficient a of each term is a specific positive. The same probability of success, p X has n trials and Y has m trials We argued before that Z = X Y should be binomial with n m trials Now we can see this from the mgf The mgf of Z is M Z(t) = M X(t)M Y (t) = pet 1−p n pet 1−p m = pet 1− p nm.
EC02 Spring 15 HW10 Solutions May 3, 15 2 (d)The variance of M 16(X) is much less than VarX 1Hence, the PDF of M 16(X) should be much more concentrated about EX than the PDF of X. P X n t exp nt2 2(b a)2 Repeating this in the other direction we get P jX nj t 2exp nt2 2(b 2a) More generally, if X i has mean then P jX n j t 2exp nt2 2(b a)2 This is a twosided exponential tail inequality for the averages of bounded random variables. Y(x,t) = P(xvt) y(x,t) P(xvt) y(x,t) P(xvt) Submit (Survey Question) 2) Briefly explain your answer to the previous question.
After knowing T (X ) = t, the additional information in X is the sequence/order information which does not depend on θ To make decision concerning θ, we should only need the. This gives MZn(t) = µ 1 t2 2n O µ 1 n3=2 ¶¶n!. P X N D X P O S T E O 2,8 likes · 2 talking about this Una página de un wey para weyes que todavía no aceptan que pxndx terminó y pues no hay nada más que hacer que reír ajajaja.
P(X > t) = P(X > s t) P(X > t) = e−λ(st) e−λt = e−λs = P(X > s) – Example Suppose that the amount of time one spends in a bank isexponentially distributed with mean 10 minutes, λ = 1/10 What is the probability that a customer will spend more than 15. Mx t E e xt x e xt P x x P x x 1 e x 1 t P x x 2 e x 2 t P x x n e x n t by from STATS 425 at University of Michigan 31 Bernoulli Trials Def An experiment is called Bernoulli Trials if each of the following is true 1) Two possible outcomes “success” or “failure” 2) Trials are independent 3) The probability of success P (success)= p is constant. Attention A T users To access the menus on this page please perform the following steps 1 Please switch auto forms mode to off 2 Hit enter to expand a main menu option (Health, Benefits, etc) 3 To enter and activate the submenu links, hit the down arrow You will now be able to tab or arrow up or down through the submenu options to.
N 2b(ˆzb−1),y n 3b) ∈T (PX1X2Y3) and wbis assigned index zb(ˆzb−1 is assumed to be correctly decoded from previous blocks) The probability of this step is easily seen to go to zero with nif R. D y w k ɂ c t X ^ C ̎q p X N BLUEBERRY( u x ) English Preschool B o C K Ă܂ B BLUEBERRY is a school that teaches more than just English Our staff believes in respect for all people and that when children learn to respect others, it creates a perfect learning environment where almost any type of child can feel comfortable. When X 1;;X nare iid random variables, for nay t>0 P(jX n j ) 2e 2nt Yn i=1 et (b i a i)2=8 = 2e nt et2n(b a)2=8 This is minimized by setting t= 4 =(b a)2, giving P(jX n j ) 2e 22n 2=(b a) 3 Bernstein’s Inequality Hieffding’s bound depends only on the bounds of the random variable but not expli.
As n !1 X n converges to X in probability, written X n!p X, if, for every †>0, P(jX n ¡Xj >†)!. 179 From the first and second moments we can compute the variance as Var(X) = EX2−EX2 = 2 λ2 − 1 λ2 1 λ2 The Memoryless Property The following plot illustrates a key property of the exponential distri. A combination takes the number of ways to make an ordered list of n elements (n!), shortens the list to exactly x elements ( by dividing this number by (nx)!.
2 1MarkovChains 11 Introduction This section introduces Markov chains and describes a few examples A discretetime stochastic process {X n n ≥ 0} on a countable set S is a collection of Svalued random variables defined on a probability space (Ω,F,P)The Pis a probability measure on a family of events F (a σfield) in an eventspace Ω1 The set Sis the state space of the process,. Theorem Thegeometricdistributionhasthememoryless(forgetfulness)property Proof AgeometricrandomvariableX hasthememorylesspropertyifforallnonnegative. P(X nt = j X n = i) = Pt ij for any n 87 Distribution of Xt Let {X 0,X 1,X 2,} be a Markov chain with state space S = {1,2,,N} Now each X t is a random variable, so it has a probability distribution We can write the probability distribution of X t as an N ×1 vector For example, consider X 0 Let π be an N × 1 vector denoting the.
Then p = P(X = 1) = P(A) is the probability that the event A occurs For example, if you flip a coin once and let A = {coin lands heads}, then for X = I{A}, X = 1 if the coin lands heads, and X = 0 if it lands tails Because of this elementary and intuitive. Solution This is a subspace, because if p(x);q(x) have no x2 term, then neither do p(x)q(x) and rq(x) for r 2R 3 Let M m n be the vector space of m n matrices, with the usual operations of addition and scalar multiplication (a) Let A be an m m matrix Is the function T M m n!M m n. G(n) X (0) shows that the whole sequence of probabilities p0,p1,p2, is determined by the values of the PGF and its derivatives at s = 0 It follows that the PGF specifies a unique set of probabilities Fact If two power series agree on any interval containing 0, however small, then.
= P(X>n) This is exactly what we wanted to show This property is called memoryless because even knowing that we have waited mtrials and have not yet seen a success, the probability of seeing a success in the next ntrials is exactly the same as if we had not seen any trials at all 7. Example (A Reward Process) Suppose events occur as a Poisson process, rate λ Each event Sk leads to a reward Xk which is an independent draw from Fs(x) conditional on Sk=sThe total reward at t is R = PN(t) k=1Xk Show that R has the same distribution as. N p · x ≤ w } = B (p, w ) Nothing changes if scale prices and income by same factor Theorem If p » 0, then B (p, w ) is compact Proof For any p, B (p, w ) is closed If p » 0, then B (p, w ) is also bounded 8 Marshallian Demand Existence Theorem.
Jun 12, 16 · Stack Exchange network consists of 176 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack Exchange. Where Y is an (n×1)vector of response variables (random sample), X is an (n× 2) matrix called the design matrix, β is a (2 × 1) vector of unknown parameters and ε is an (n. X x x3P(x) We see that M X(0)00 = P x x 2P(x) = E(X2) Examples Find the moment generating function of X˘ b(n;p) Find the moment generating function of X˘ Poisson( ).
Similarly, Second moment M X(t)00 = X x x2P(x) 6t 3!. Et 2=2 2 Note that the requirement of a MGF is not needed for the theorem to hold In fact, all that is needed is that Var(Xi) =. 0 for all †>0 In.
Theorem Let Z˘N(0;1) Then, if X= Z2, we say that Xfollows the chisquare distribution with 1 degree of freedom We write, X˘˜2 1 Probability density function of X˘˜2 1 Find the probability density function of X= Z2, where f(z) = p1 2ˇ. Solve for t A=P(1r/n)^(nt) Rewrite the equation as Divide each term by and simplify Tap for more steps Divide each term in by Cancel the common factor of Tap for more steps Cancel the common factor Divide by Take the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation to remove the variable from the exponent. Wave Pulse y(x, t)P( ) →y x vt Case A Case B The pulse in Case A is described by the function y(x,t) P(xvt) 1) Which of the following functions describes the pulse in Case B?.
Followers, 138 Following, 2 Posts See Instagram photos and videos from Imxz Iqbxl (@p_x_n_t_x). EC02 Spring 06 HW3 Solutions February 2, 06 3 Problem 224 • The random variable X has PMF PX (x) = ˆ c/x x = 2,4,8, 0 otherwise (a) What is the value of the constant c?. T~ is now known to be (A(p~), ~'), and therefore T~0 is determined by A(/~) (and 7r) As n varies, T"0 runs through a dense subset of 0, A I), and therefore by (16).
Wenn du den Kanal unterstützen möchtesthttps//paypalme/chemistrykicksass?localex=de_DE.

Probability And Random Process Notes

If X Follows The Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 6 And P A
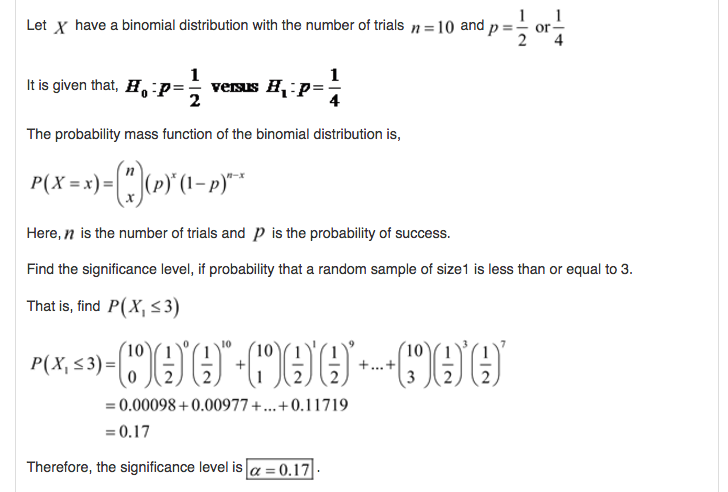
Solved Question Let X Have A Binomial Distribution With Chegg Com
T Px N のギャラリー

Suppose X Follows A Binomial Distribution With Parameters N And P Where 0 P 1 1 P X R P X N R Is Independent Of N For Every R Then P

Applying Statistics In Python Part I By Black Raven James Ng Towards Data Science
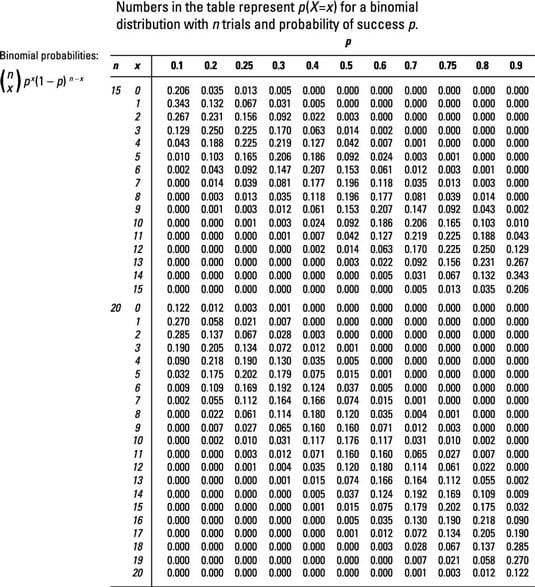
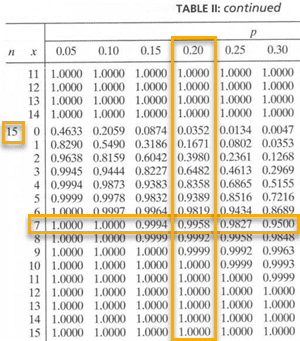
Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies

Solved Why Probability Of Min X Y N Is Same As Probabi Chegg Com
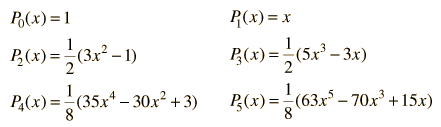
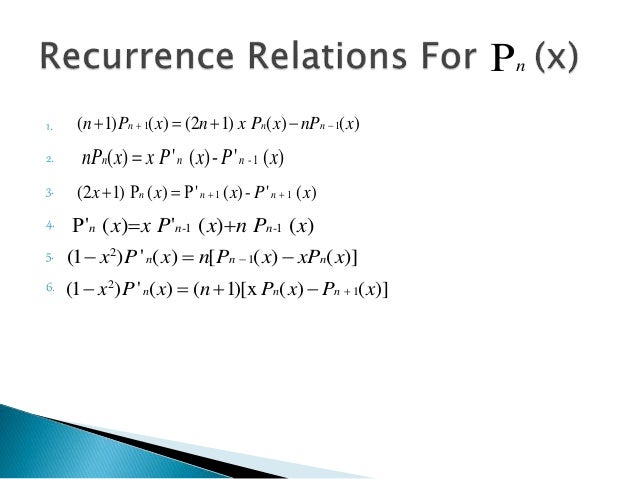
Legendre Polynomials
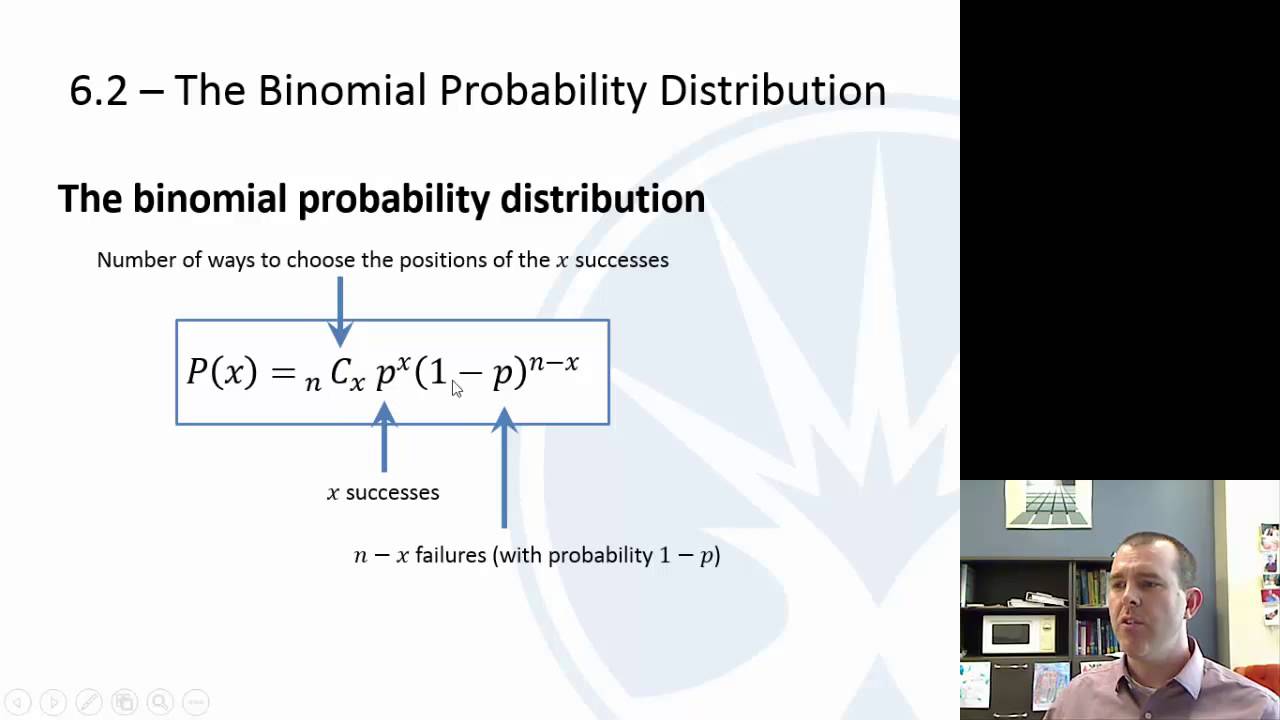
Chapter 6
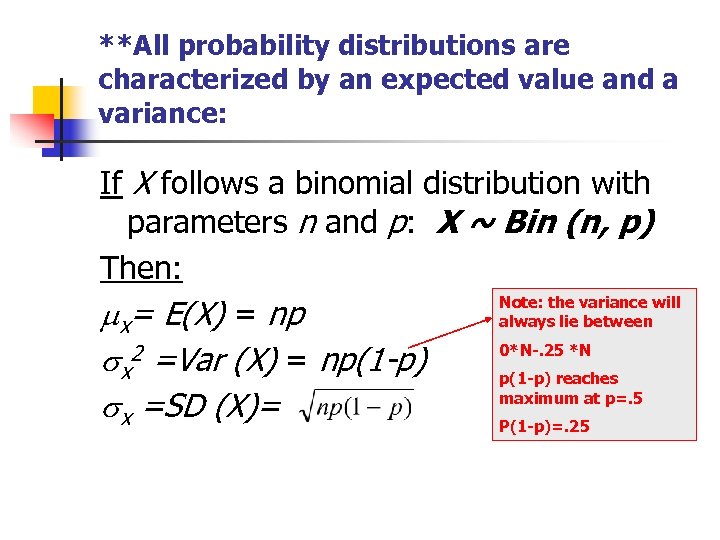
Examples Of Discrete Probability Distributions The Binomial And

Consider A Random Variable X Find Its Pmf Mathematics Stack Exchange

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2
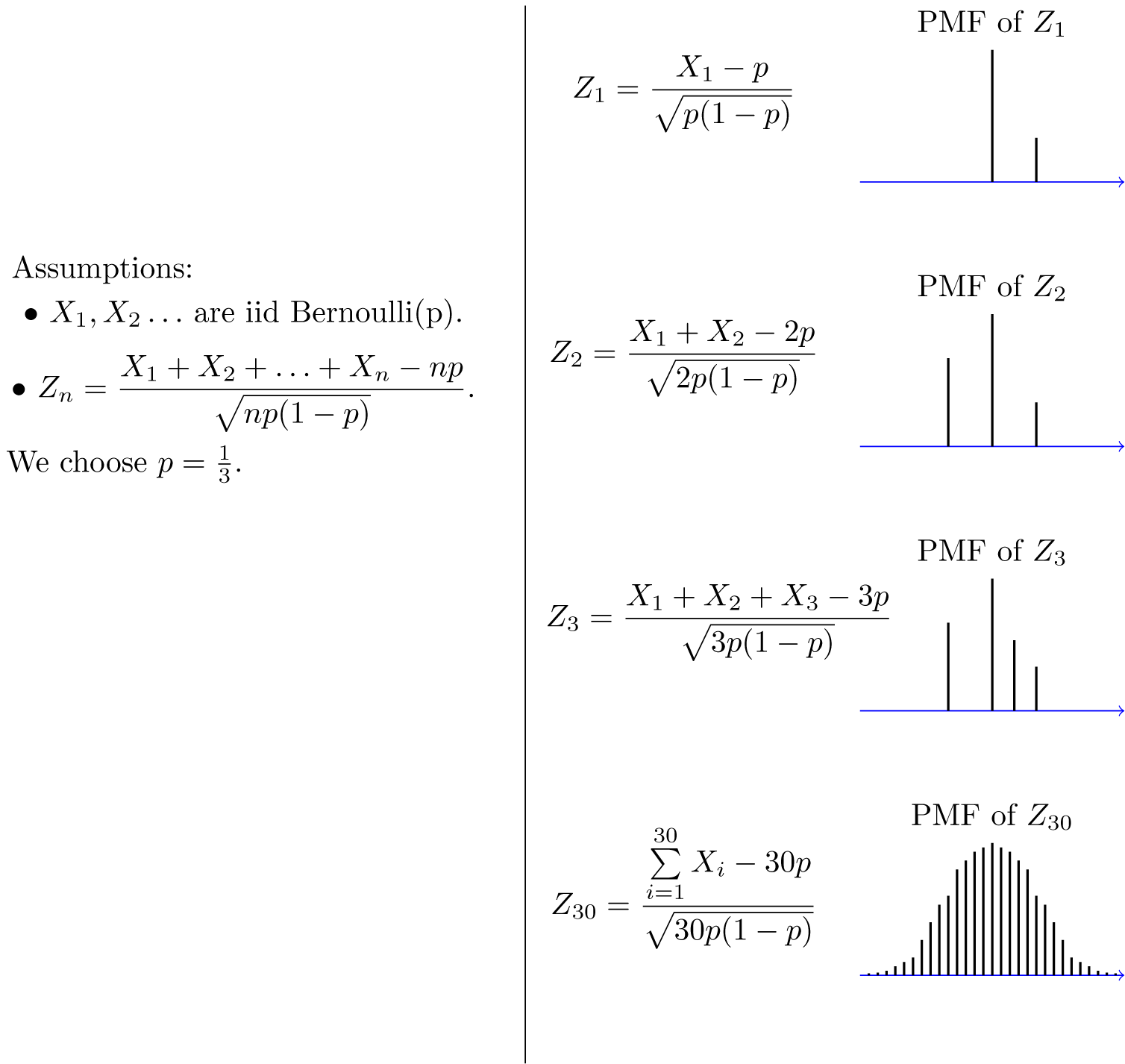
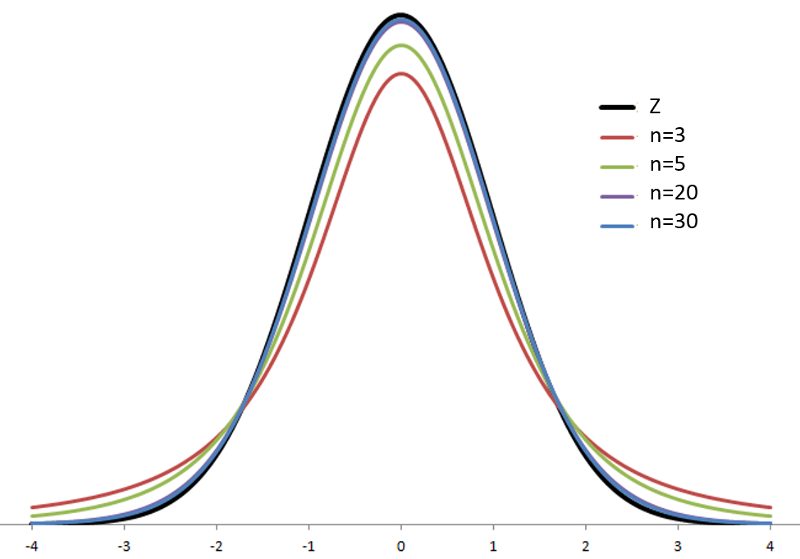
Central Limit Theorem

Binomial Distribution Definition Properties Derivation Formulas Solved Example Problems

Normal Distribution X N Fx X X 5 N 5 2 Ppt Video Online Download
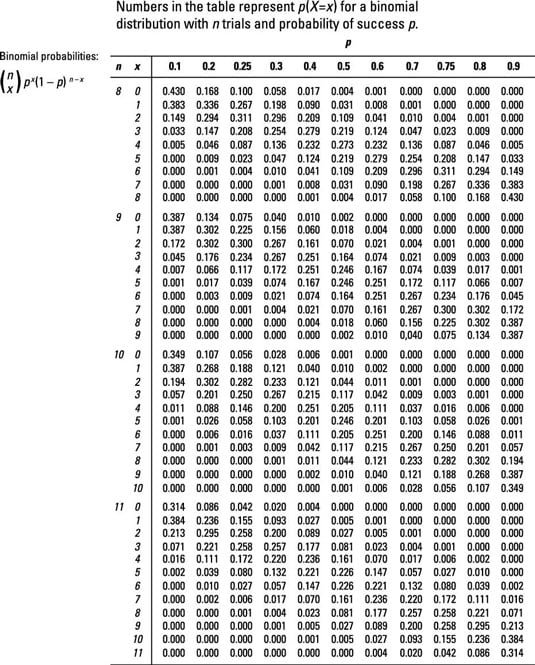
Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies
Distribution Of The Sample Mean

Chapter 5 Probability Distributions 5 1 Overview 5 2 Random Variables 5 3 Binomial Probability Distributions 5 4 Mean Variance And Standard Deviation Ppt Download

If X Follows A Binomial Distribution With Parameters N 6 And P
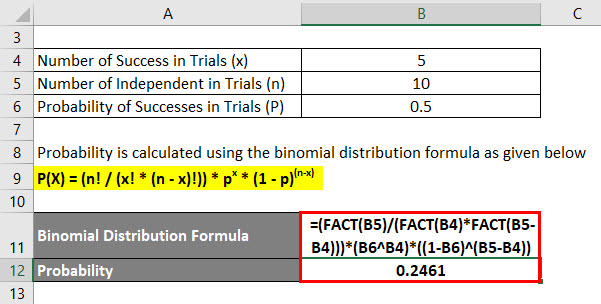
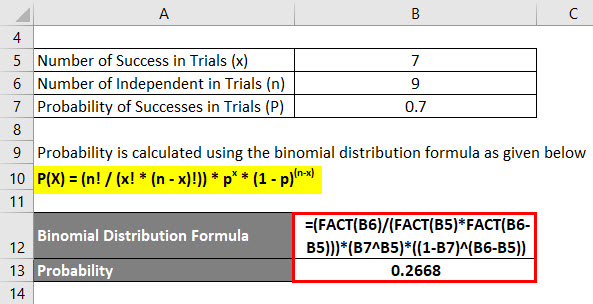
Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template
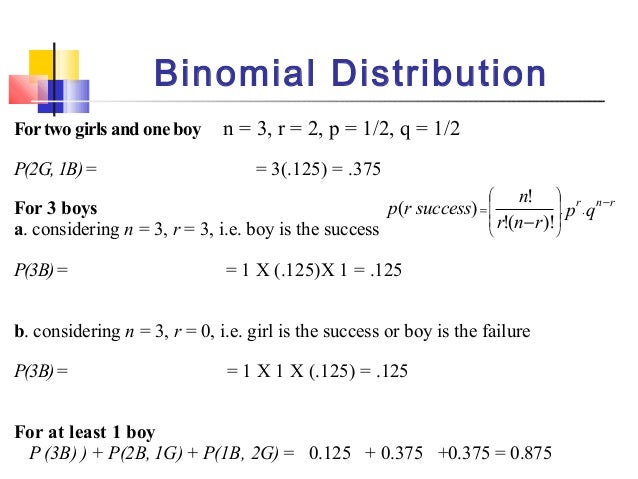
4 1 Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2
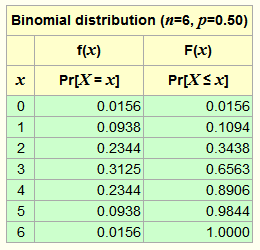
Binomial Distribution Calculator

Normal Approximation To The Binomial A Bin N P Random Variable X Counts The Number Of Successes In N Bernoulli Trials With Probability Of Success P On Ppt Download
Laplace Periodic Function

On A Probability Of An Exponential Random Variable Mathematics Stack Exchange

Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions Ppt Download
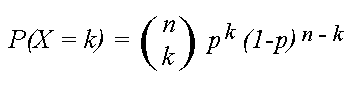
The Binomial Distribution

Gnuplot Demo Script Prob Dem
Binomial Distribution Six Sigma Study Guide

If X B N P With N 10 P 0 4 Then E X 2

Binomial Distribution Calculator
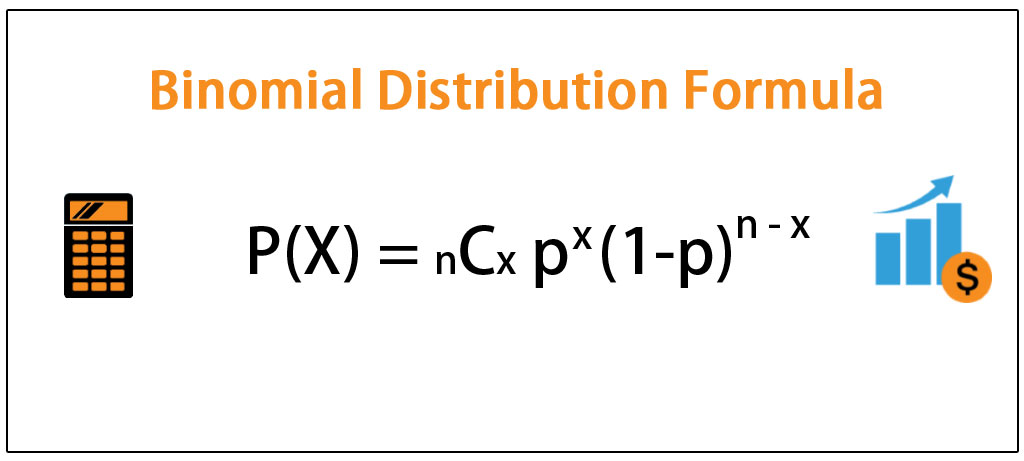
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example

Binomial Distribution Examples Problems And Formula
Solved Let X Denote A Random Variable That Has A Binomial Chegg Com

Suppose That X Is A Binomial Random Variable With 0 And P 0 4 Approximate The Following Probabilities A P X 70 B P 70 X 90 C P X 80 Homework Help And Answers Slader
Introduction To Signals

Basic Business Statistics 11 Th Edition Chapter 5
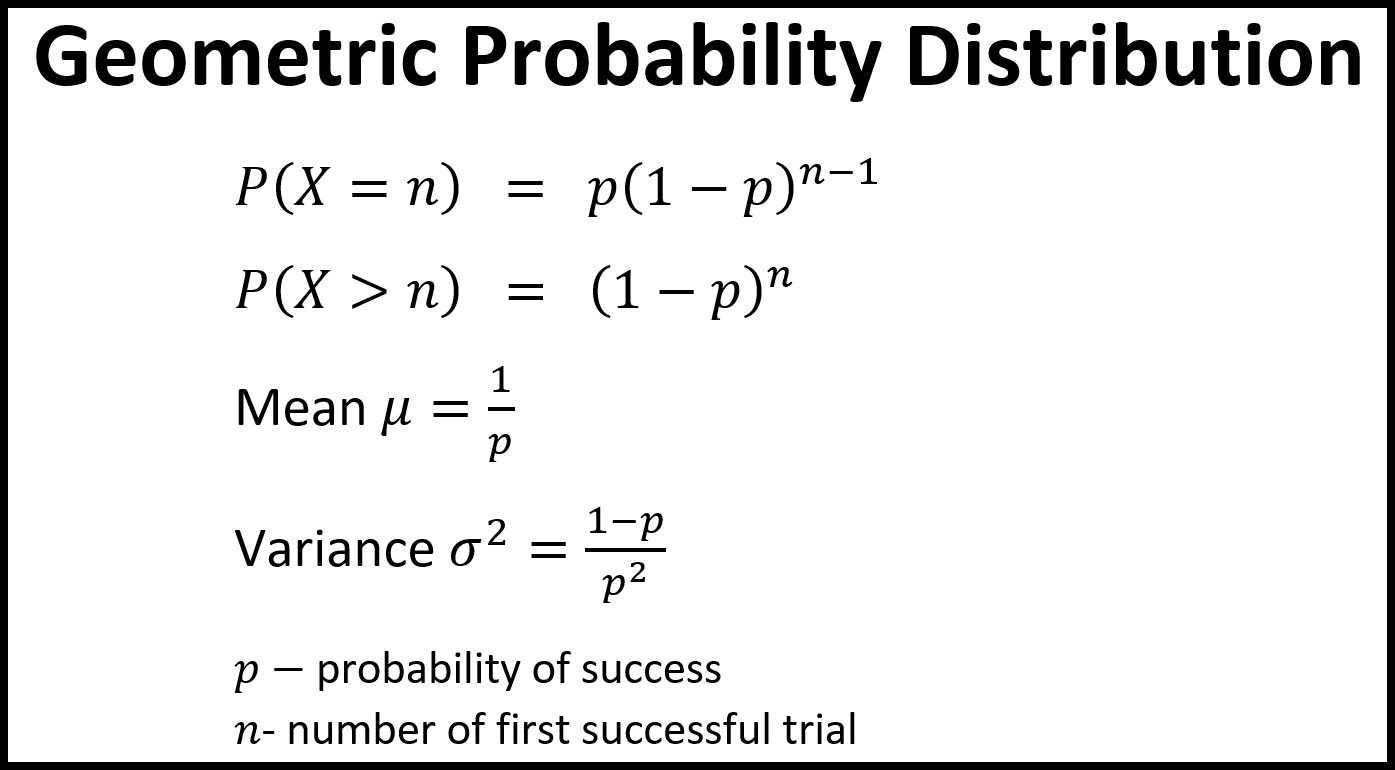
Geometric Distribution Andymath Com
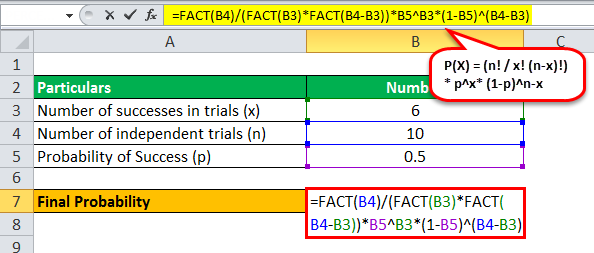
Binomial Distribution Formula Step By Step Calculation Example

Maths Hl Ib Stats Exam Binomial Distributions Franklyandjournal

If K X X 2 And P X K X N What Is The Value Of N Pleaseee Help Asap I Will Give Brainly Com

Solved Possibly Useful Formulas Binomial P X Nx Px 1 Chegg Com
Binomial Distribution Workout For N 18 P 0 36 X 12

Understanding And Choosing The Right Probability Distributions With Examples By Kessie Zhang Towards Data Science
Sampling Distribution Of Sample Proportion Part 1 Video Khan Academy

Poisson Distribution Explained Intuition Examples And Derivation Towards Data Science

Random Variable And Its Probability Distribution Ma Economics Karachi University
X Is A Binomial Variable Such As That 2p X 2 P X 3 And Mean Np Of X Is Known To Be 10 3 What Would Be The Probability That X Assumes At Most The

Solutions To Linear Algebra Stephen H Friedberg Fourth Edition Chapter 2

Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template
Normal Probability Distributions Online Presentation

Commutator Of And
Normal Probability Distributions Online Presentation
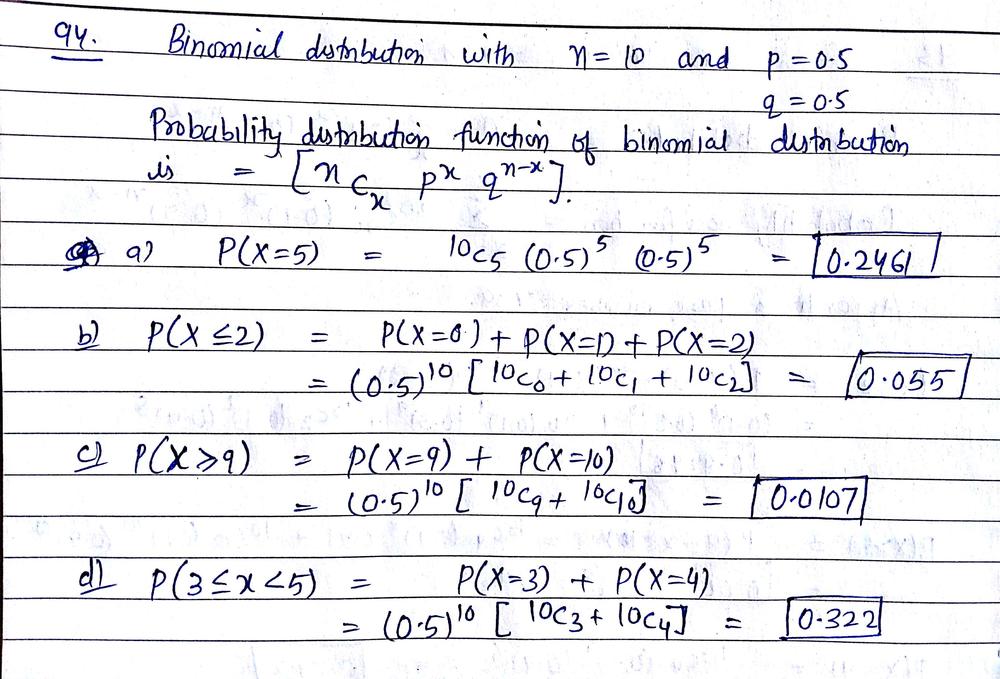
The Random Variable X Has A Binomial Distribution With N 10 And P 0 5 Determine The Following Probabilities A P X 5 B P X 2 C P X 9

Showing That E X Sum Mathbb P X Ge N Mathematics Stack Exchange

Given X B N P If P 0 6 E X 6 Then The Value Of Var X I

Discrete Random Variables And Probability Distributions Ppt Download
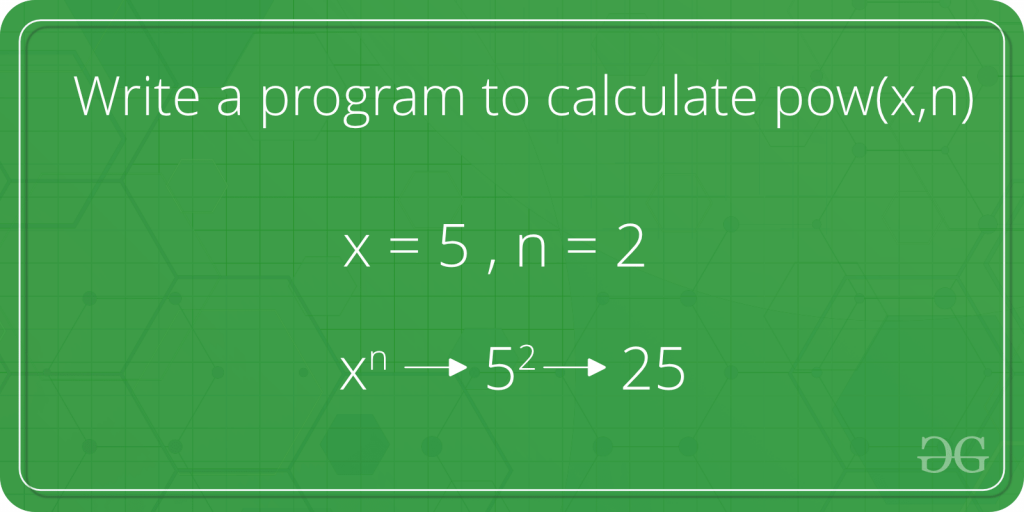
Write A Program To Calculate Pow X N Geeksforgeeks
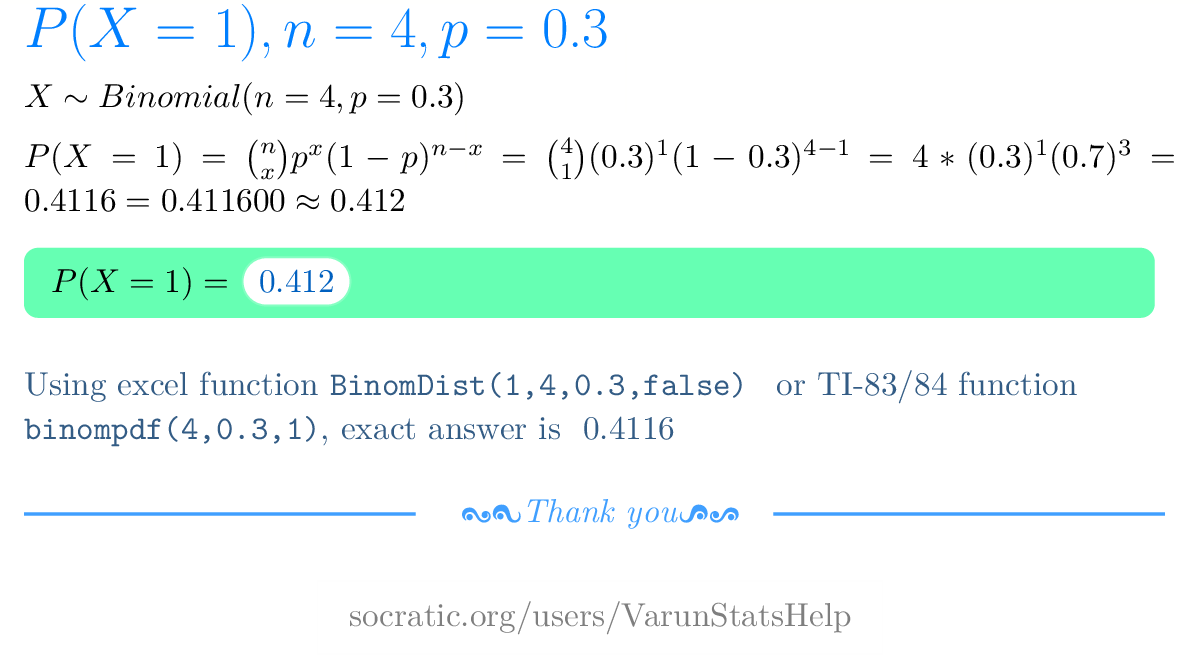
If X Is A Binomial Random Variable What Is The Probability Of X For N 4 X 1 P 0 3 Socratic

Expected Value Wikipedia

Proof For Convergence In Distribution Implying Convergence In Probability For Constants Mathematics Stack Exchange

4 1 Probability And Discrete Probability Distributions
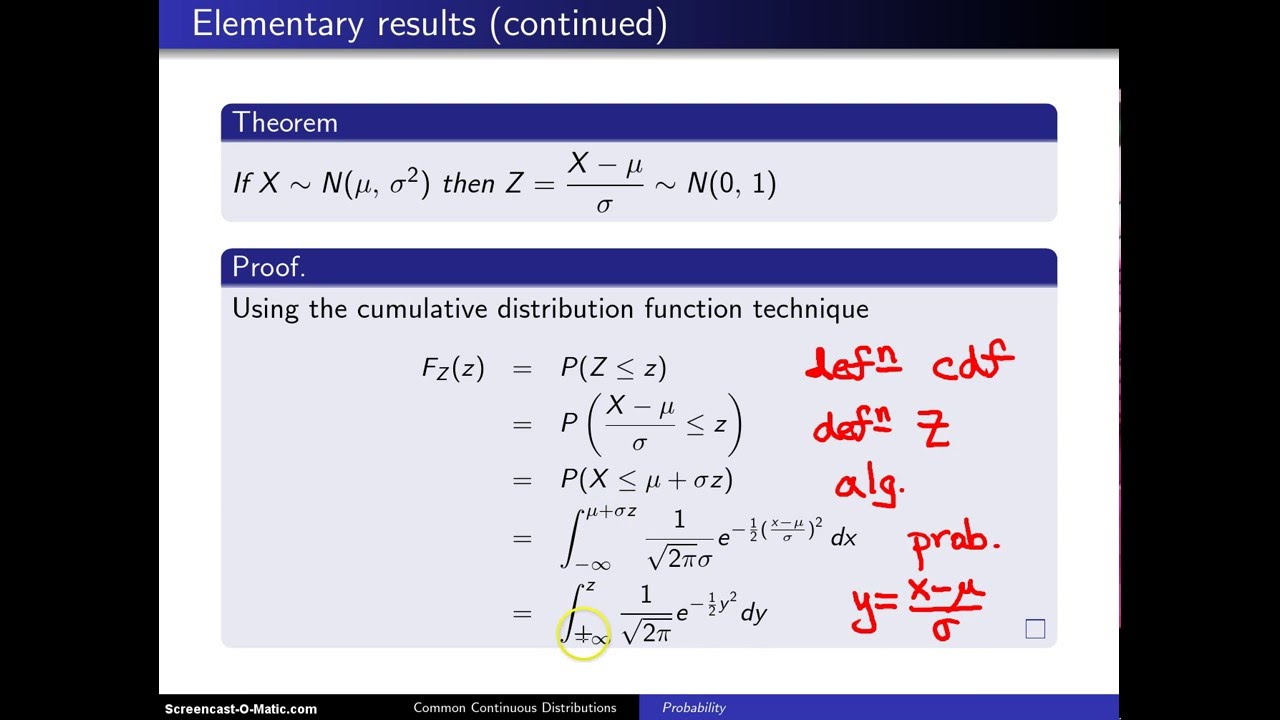
Normal Distribution Z X Mu Sigma Youtube

Expected Value Of A Binomial Variable Video Khan Academy
Chapter 5 Discrete And Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Download
Binomial Formula Explained
P Values
Sampling Distribution Of The Sample Mean X Bar Biostatistics College Of Public Health And Health Professions University Of Florida

Binomial Probabilities On The Ti Or 84 Calculator Mathbootcamps

The Binomial Distribution S Cool The Revision Website
Probability And Distributions Bernouilli Trial Binomial Distribution

Expected Value Wikipedia

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
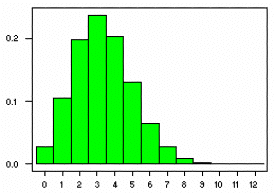
The Binomial Distribution

Normal Approximation To The Binomial Statistics How To
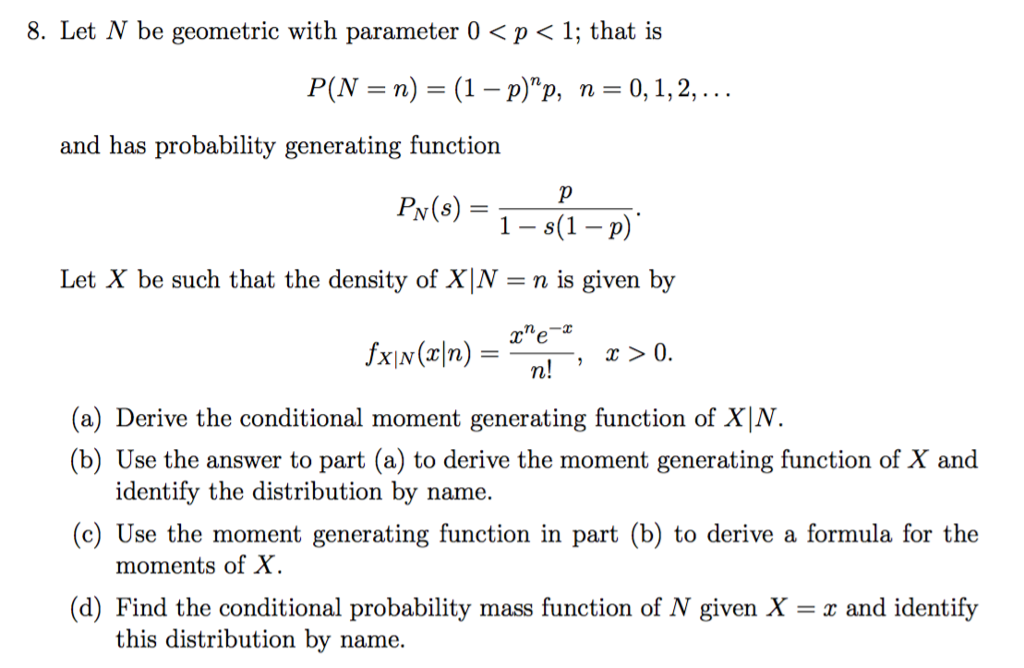
Solved Let N Be Geometric With Parameter 0 P 1 That Chegg Com
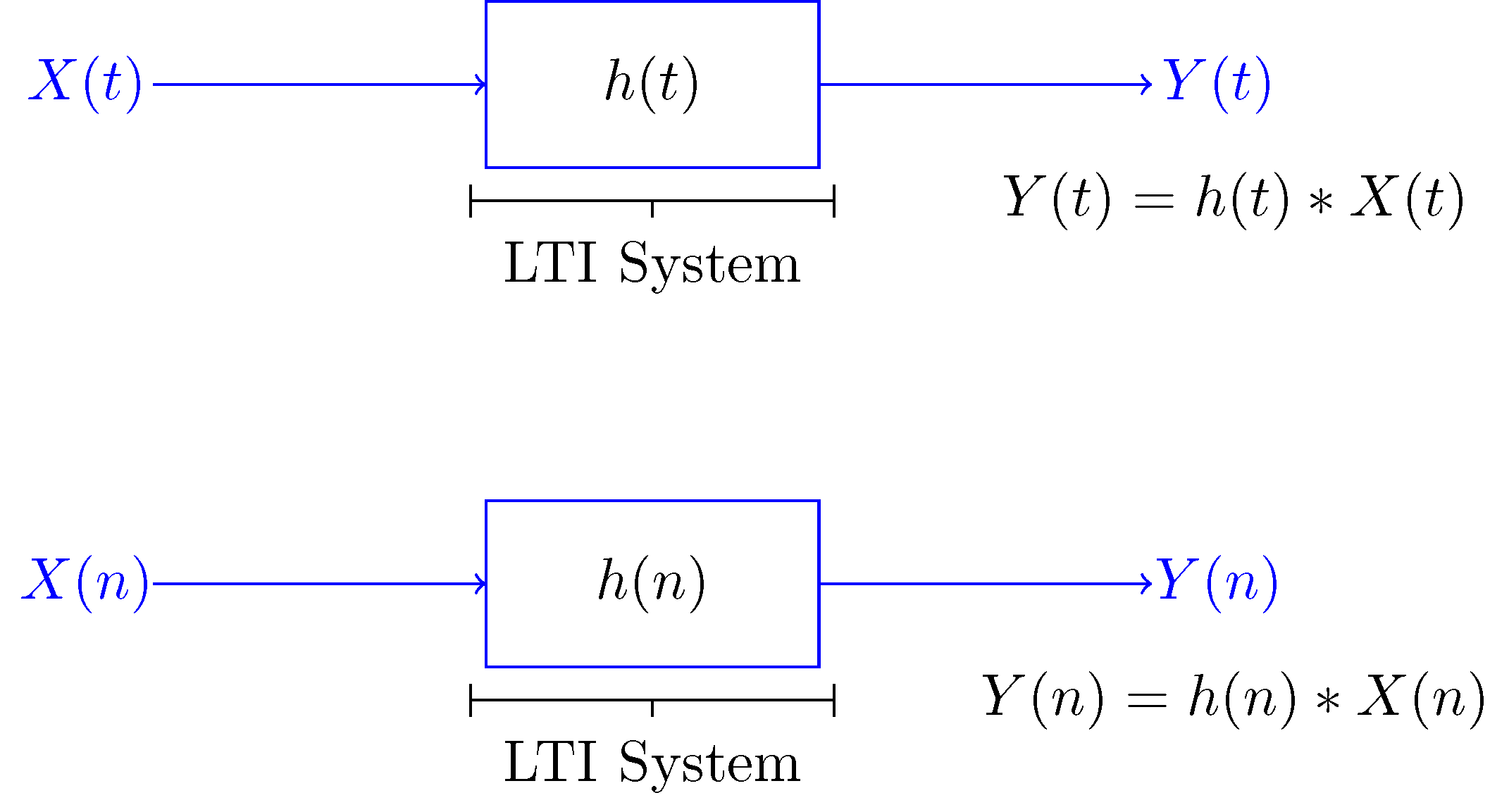
Linear Time Invariant Lti Systems With Random Inputs

7 8 Transcendency

Binomial Distribution From Wolfram Mathworld

Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
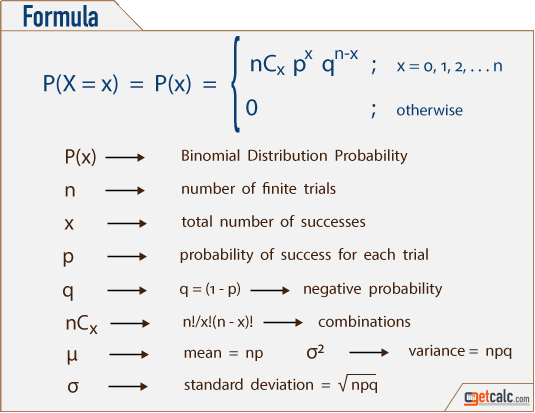
Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator
Chapter 5 4 Bernoulli And Binomial Distribution Ppt Video Online Download
Tutorial 6 The Normal Distribution Econ 41 Labs

Lesson 8 1 Discrete Distribution Binomial Knowledge Objectives




